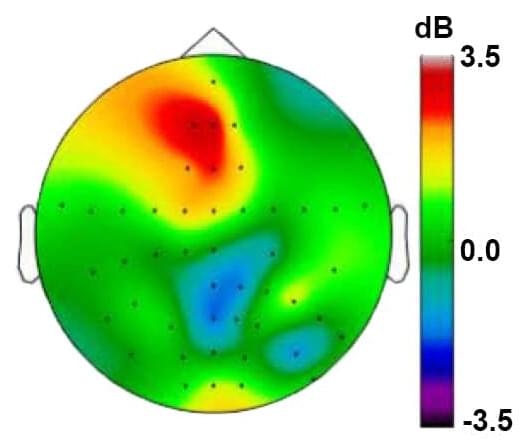
Since the infancy of functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) in 1990, people have been fascinated by the potential for brain scans to unlock the mysteries of the human mind, our behaviors and beliefs. Many breathtaking applications for brain scans have been devised, but hype often exceeds what empirical science can deliver. It’s time to ask: What’s the big picture of neuroscience and what are the limitations of brain scans?
The specific aims of any research endeavor depend on who you ask and what funding agency is involved, says Michael Spezio, associate professor of psychology, data science and neuroscience at Scripps College. Some people believe neuroscience has the potential to explain human cognition and behavior as a fully mechanistic process, ultimately debunking an “illusion of free will.” Not all neuroscientists agree that free will is a myth, but it’s a strong current these days. Neuroscience also has applications in finance, artificial intelligence, weapons research and national security.
For other researchers and funders, the specific aim of neuroscience involves focusing on medical imaging, genetics, the study of proteins (proteomics) and the study of neural connections (connectomics). As caring persons who are biological, neurological, physical, social and spiritual, we can use neuroscience to think carefully and understand our humanity and possible ways to escape some of the traps we’ve built for ourselves, says Spezio. Also, brain scans can enhance research into spirituality, mindfulness and theory of mind – the awareness of emotions, values, empathy, beliefs, intentions and mental states to explain or predict others’ behavior.