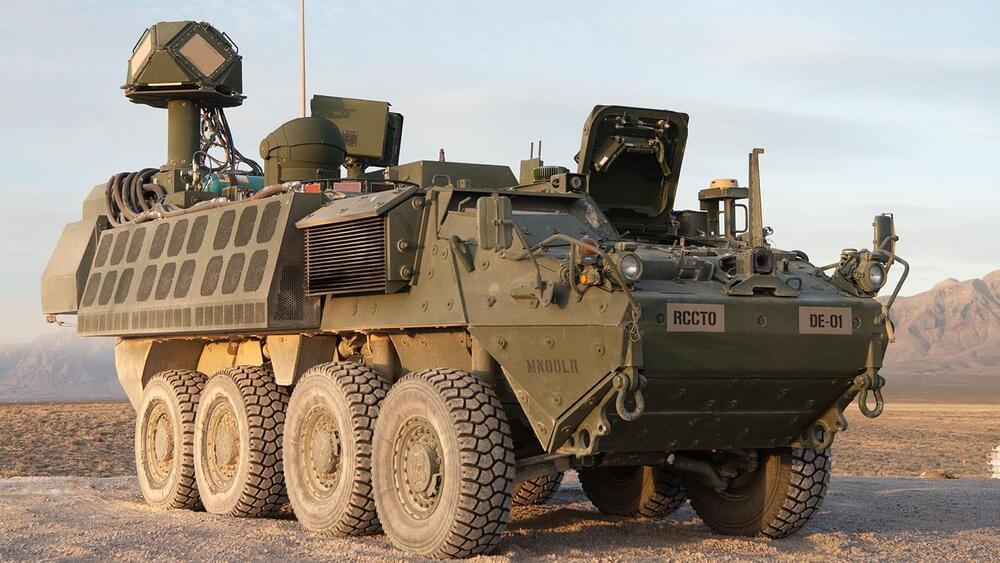
LAS CRUCES, N.M., May 16, 2022 /PRNewswire/ — In four weeks of continuous live-fire exercises, an industry team led by Raytheon Intelligence & Space, a Raytheon Technologies (NYSE: RTX) business, and Kord, a wholly owned subsidiary of KBR, defeated multiple 60mm mortar rounds with a 50kW-class high energy laser integrated on a Stryker combat vehicle.
The directed energy weapon system — part of the U.S. Army’s Directed Energy Maneuver-Short Range Air Defense, or DE M-SHORAD — acquired, tracked, targeted and defeated multiple mortars and successfully accomplished multiple tests simulating real-world scenarios.
Continuing to put the DE M-SHORAD system to the test, the recent operational assessment at White Sands Missile Range also included defeating several small, medium and large drones.