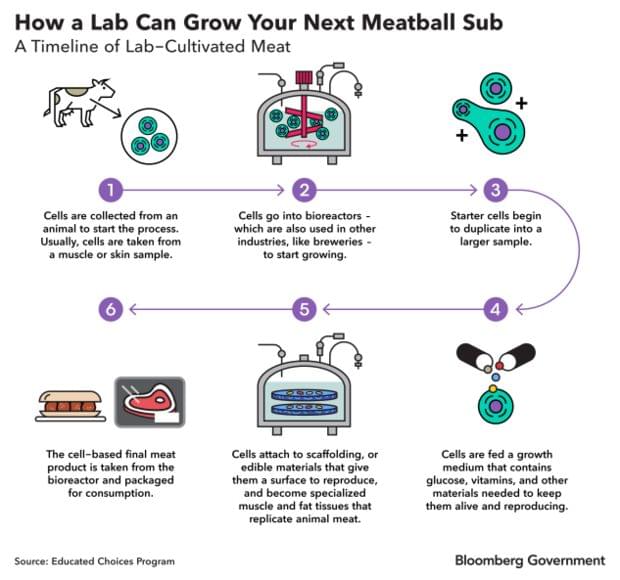
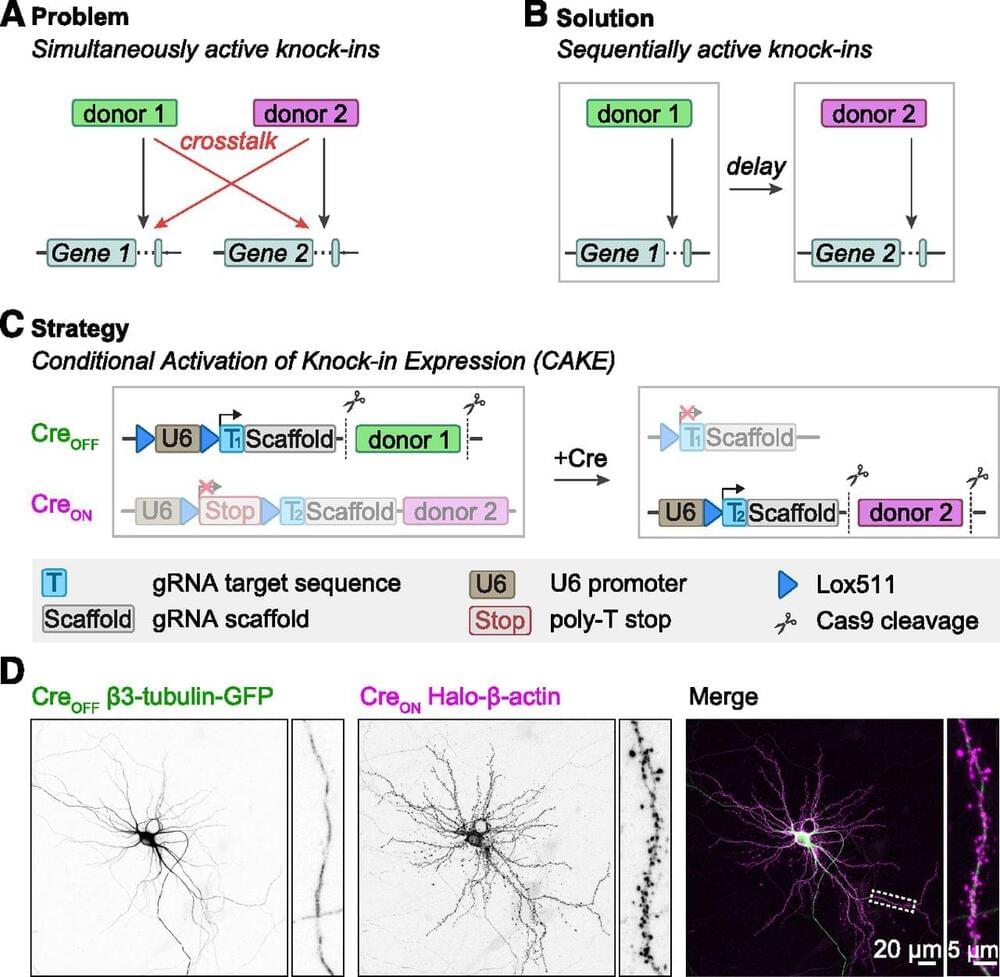
Accurate detection and manipulation of endogenous proteins is essential to understand cell biological processes, which motivated laboratories across cell biology to develop highly efficient CRISPR genome editing methods for endogenous epitope tagging (Auer et al., 2014; Nakade et al., 2014; Lackner et al., 2015; Schmid-Burgk et al., 2016; Suzuki et al., 2016; Nishiyama et al., 2017; Artegiani et al., 2020; Danner et al., 2021). Multiplex editing using NHEJ-based CRISPR/Cas9 methods remains limited because of the high degree of cross talk that occurs between two knock-in loci (Gao et al., 2019; Willems et al., 2020). In the current study we present CAKE, a mechanism to diminish cross talk between NHEJ-based CRISPR/Cas9 knock-ins using sequential activation of gRNA expression. We demonstrate that this mechanism strongly reduces cross talk between knock-in loci, and results in dual knock-ins for a wide variety of genes. Finally, we showed that CAKE can be directly applied to reveal new biological insights. CAKE allowed us to perform two-color super-resolution microscopy and acute manipulation of the dynamics of endogenous proteins in neurons, together revealing new insights in the nanoscale organization of synaptic proteins.
The CAKE mechanism presented here creates a mosaic of CreON and CreOFF knock-ins, and the number of double knock-in cells depends on the efficacy of each knock-in vector. Therefore, to obtain a high number of double knock-in cells, the efficacy of both the CreON and CreOFF knock-in vector must be optimized. We identified three parameters that regulate the efficacy for single and double knock-ins in neurons. First, the efficacy of gRNAs varies widely, and even gRNAs that target sequences a few base pairs apart in the same locus can have dramatically different knock-in rates (Willems et al., 2020; Danner et al., 2021; Fang et al., 2021; Zhong et al., 2021). Thus, the efficacy of each individual gRNA must be optimized to increase the chance of successful multiplex labeling in neurons. gRNA performance is dependent on many factors, including the rate of DNA cleavage and repair (Rose et al., 2017; Liu et al., 2020; Park et al.