Elon Musk’s brain interface company is planning an event to show its latest efforts to connect brains and computers.


@Meet Kevin is a 30-year-old dad and financial analyst. He’s amassed a following of nearly 2 million subscribers on YouTube with his large library of financial content. He recently ran for California governor and owns a lot of Tesla stock.
Meet Kevin’s YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/@MeetKevin.
Neura Pod is a series covering topics related to Neuralink, Inc. Topics such as brain-machine interfaces, brain injuries, and artificial intelligence will be explored. Host Ryan Tanaka synthesizes informationopinions, and conducts interviews to easily learn about Neuralink and its future.
Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/ryantanaka3/
Support: https://www.patreon.com/neurapod/
Please consider supporting by joining the channel above, or sharing my other company website with retirees: https://www.reterns.com/. Opinions are my own. Neura Pod receives no compensation from Neuralink and has no affiliation to the company.
More people are opting to go vegetarian or vegan as factory farming’s impact on the planet becomes more apparent. But one carnivorous delight they may not have to give up is bacon, especially if they’re willing to be a bit flexible. A Dutch startup has been working on cultured bacon for a few years now, and New York-based MyForest Foods is producing a bacon substitute made from mushroom roots. They’ll soon have a competitor that will tempt consumers’ palates with yet another variety, this one made from a most unexpected source: seaweed (though to be fair, mushroom root is a pretty unexpected source for imitation bacon too).
Seaweed is good for you; it contains iodine as well as critical nutrients and antioxidants. But it doesn’t have the greatest taste (though this is admittedly a matter of personal preference; plenty of people love to snack on roasted sheets of the stuff). Umaro Foods, based in Berkeley, California, think they’ve found the perfect combination of ingredients to make seaweed taste—and feel—like bacon.
They start with red seaweed protein, which they say accounts for the bulk of the final product’s meaty taste, color, and texture. They add chickpea protein, which contains fatty acids and amino acids. Coconut oil and sunflower oil provide the fat, and spices like paprika and sea salt boost the flavor. Red radish juice adds color to make it all look more like real bacon. The product has a little less protein than real bacon, and about the same amount of fat.
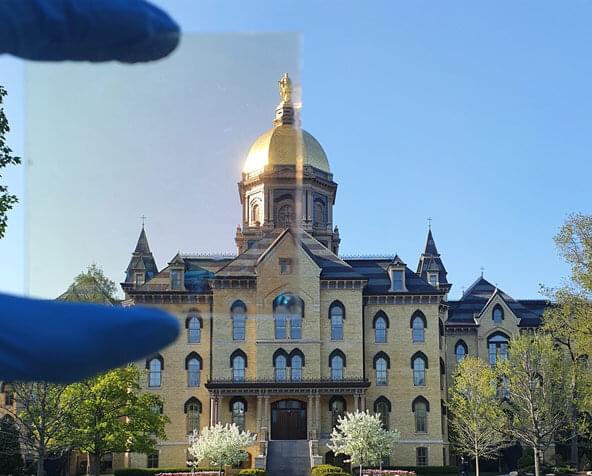


Cooling accounts for about 15 percent of global energy consumption. Conventional clear windows allow the sun to heat up interior spaces, which energy-guzzling air-conditioners must then cool down. But what if a window could help cool the room, use no energy and preserve the view?
Tengfei Luo, the Dorini Family Professor of Energy Studies at the University of Notre Dame, and postdoctoral associate Seongmin Kim have devised a transparent coating for windows that does just that.
The coating, or transparent radiative cooler (TRC), allows visible light to come in and keeps other heat-producing light out. The researchers estimate that this invention can reduce electric cooling costs by one-third in hot climates compared to conventional glass windows.


Physicists have simulated a black hole in a lab. Then it started glowing.
This allowed the team to realise that their black hole analogue may help explain so-called “Hawking radiation”, theorised to be emitted by black holes in nature.
Their analysis of the black hole in a bottle is presented in a paper published in the Physical Review Research journal.
You can’t discuss fulfillment robots without mentioning Amazon. Over the past decade, the retail juggernaut has become the 800-pound gorilla in the category, courtesy of several key acquisitions and seemingly endless resources. And while warehouse robotics and automation have been accelerated amid the pandemic and resulting employment crunch, Amazon Robotics has been driving these categories for years now.
This week at its annual Re: Mars conference in Las Vegas, the company celebrated a decade of its robotics division, which was effectively born with its acquisition of Kiva Systems. Over the course of its life, Amazon Robotics has deployed more than 520,000 robotic drive units, across its fulfillment and sort centers. From the outside, it’s been a tremendous success in the company’s push toward same-and next-day package delivery, and its driven the competition to look for their own third-party robotics solutions, bolstering startups like Locus, Fetch and Berkshire Grey.
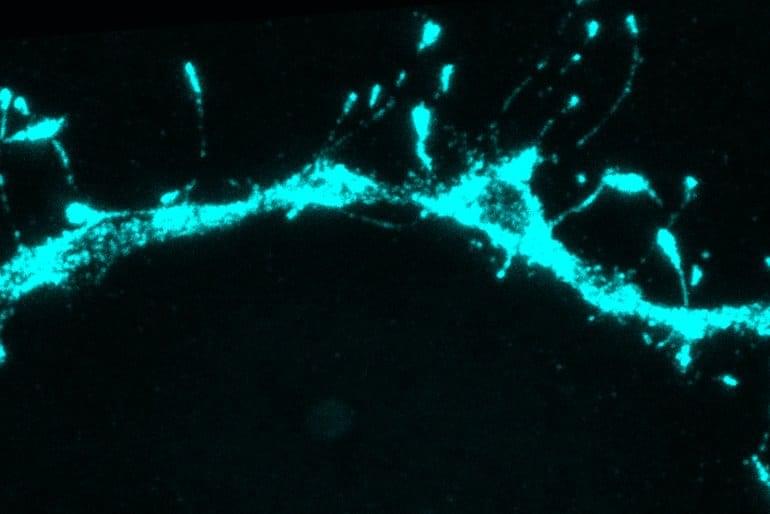
Summary: The adult brain contains millions of “silent synapses”, or immature connections between neurons that remain inactive until they are required for learning new information and storing new memories.
Source: MIT
MIT neuroscientists have discovered that the adult brain contains millions of “silent synapses” — immature connections between neurons that remain inactive until they’re recruited to help form new memories.
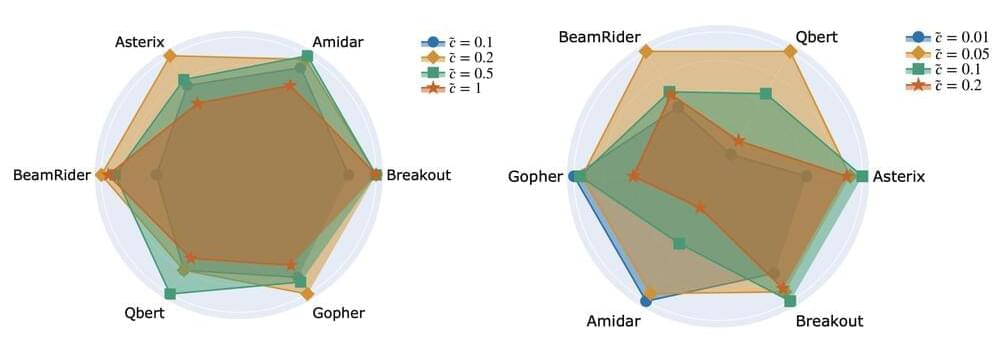
We then tested the new algorithms, called DQN with Proximal updates (or DQN Pro) and Rainbow Pro on a standard set of 55 Atari games. We can see from the graph of the results that the Pro agents overperform their counterparts; the basic DQN agent is able to obtain human-level performance after 120 million interactions with the environment (frames); and Rainbow Pro achieves a 40% relative improvement over the original Rainbow agent.
Further, to ensure that proximal updates do in fact result in smoother and slower parameter changes, we measure the norm differences between consecutive DQN solutions. We expect the magnitude of our updates to be smaller when using proximal updates. In the graphs below, we confirm this expectation on the four different Atari games tested.
Overall, our empirical and theoretical results support the claim that when optimizing for a new solution in deep RL, it is beneficial for the optimizer to gravitate toward the previous solution. More importantly, we see that simple improvements in deep-RL optimization can lead to significant positive gains in the agent’s performance. We take this as evidence that further exploration of optimization algorithms in deep RL would be fruitful.