The LCLS-II will be the world’s brightest x-ray laser when it delivers “first light” in the early 2020’s. With this superconducting accelerator online, scientists will be able to see the hidden world of atoms and molecules like never before.
» Subscribe to Seeker! http://bit.ly/subscribeseeker.
» Watch more Focal Point | https://bit.ly/2s0cf7w.
» Visit our shop at http://shop.seeker.com.
Cover image credit: Nathan Taylor.
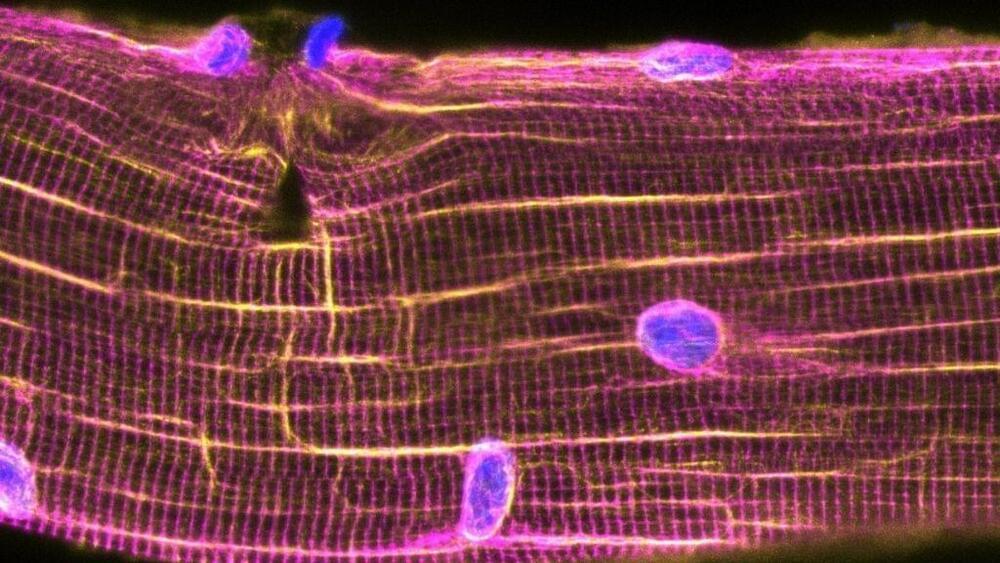
The LCLS is short for the Linac Coherent Light Source. It’s the world’s first hard x-ray free electron laser. The LCLS uses a particle accelerator to fire extremely bright electrons to create fast pulses of hard x-rays, which is why the machine is called an x-ray laser.
At the time of its first light in 2,009 the Linac Coherent Light Source generated x-ray pulses a billion times brighter than anything around. The LCLS is a tool unlike anything before it. We’re able to deliver these pulses of x-rays in one millionth of one billionth of a second.