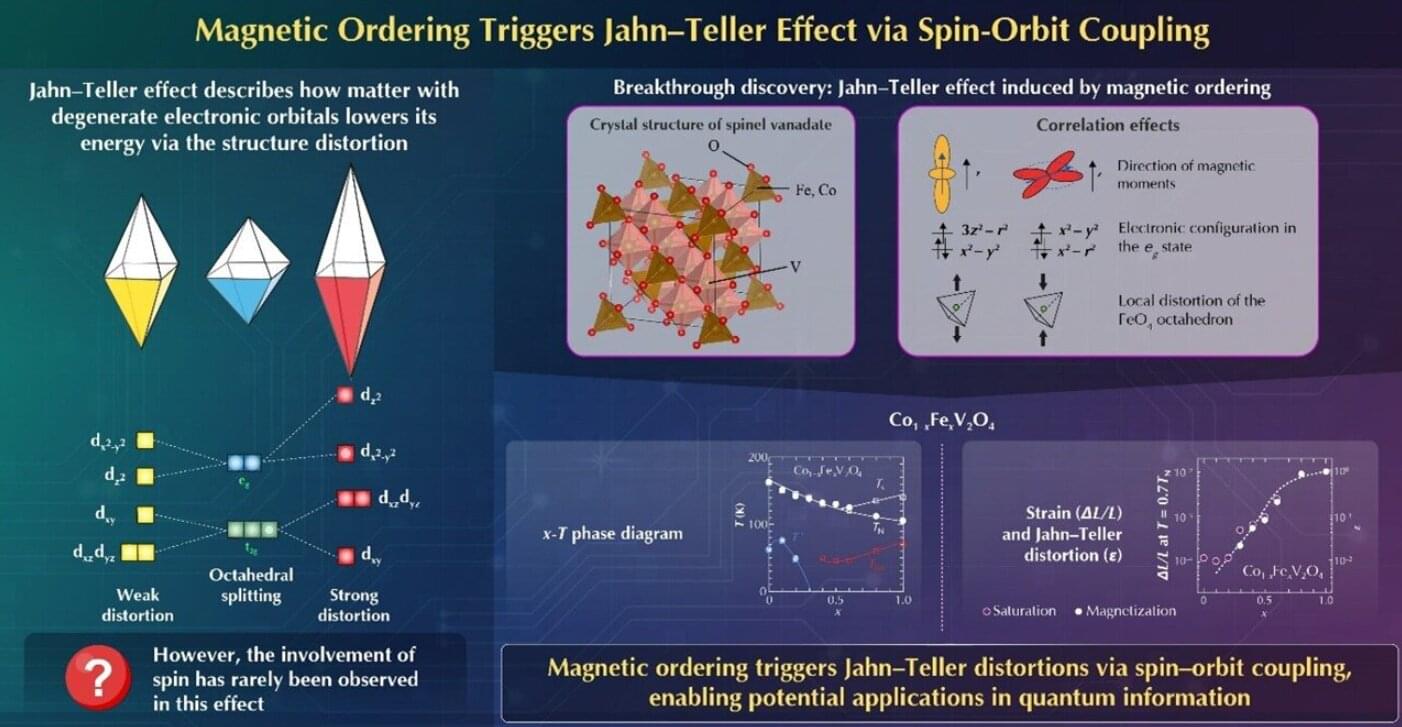
The Jahn-Teller effect, proposed by Jahn and Teller in 1937, describes how molecules or crystals with degenerate electronic orbitals can lower their total energy by distorting their structure. This distortion lifts the degeneracy, stabilizing certain orbitals that become occupied by electrons. While many materials exhibiting this effect have been found, the involvement of spin—the source of magnetism—has rarely been observed because magnetic ordering usually occurs at much lower temperatures than structural distortions caused by the Jahn-Teller effect.
In a new study, a team of researchers, led by Professor Takuro Katsufuji, including Master’s students Minato Nakano and Taichi Kobayashi, all from the Department of Physics, Waseda University, Japan, has discovered a new phenomenon in which magnetic ordering induces the Jahn-Teller effect, where spin-orbit coupling—the coupling between electron spin and orbital angular momentum—plays a crucial role. Their findings were published in the journal Physical Review Letters on October 29, 2025.
“Our group has been investigating degenerate orbitals and their coupling with the spin of electrons in materials. So far, we have found various compounds that exhibit orbital ordering, a phase transition in which electrons begin to occupy specific orbitals. During this research, we identified a new phenomenon in which a structural phase transition occurs simultaneously with magnetic ordering in Co₁₋ₓFeₓV₂O₄,” highlights Katsufuji.