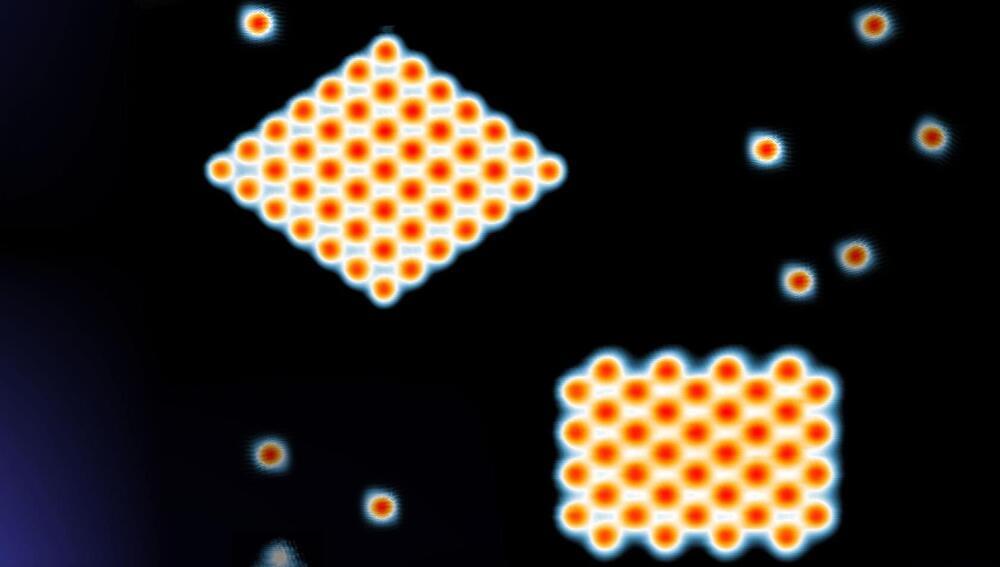
Physicists at Harvard University in the US have created a novel strongly interacting quantum liquid known as a Laughlin state in a gas of ultracold atoms for the first time. The state, which is an example of a fractional quantum Hall (FQH) state, had previously been seen in condensed-matter systems and in photons, but observations in atoms had been elusive due to stringent experimental requirements. Because atomic systems are simpler than their condensed-matter counterparts, the result could lead to fresh insights into fundamental physics.
“Some of the most intriguing phenomena in condensed-matter physics emerge when you confine electrons in two dimensions and apply a strong magnetic field,” explains Julian Léonard, a postdoctoral researcher in the Rubidium Lab at Harvard and the lead author of a paper in Nature on the new work. “For example, the particles can behave collectively as if they have a charge that is only a fraction of the elementary charge – something that does not occur anywhere else in nature and is even ruled out by the Standard Model for all fundamental particles.”
The way in which such fractional charges arise is still not fully understood because it is difficult to study solid-state systems at an atomic scale. This is why it is so desirable to study the behaviour of FQHs in synthetic quantum systems such as cold atoms, which act as quantum simulators for more complex condensed-matter phenomena.