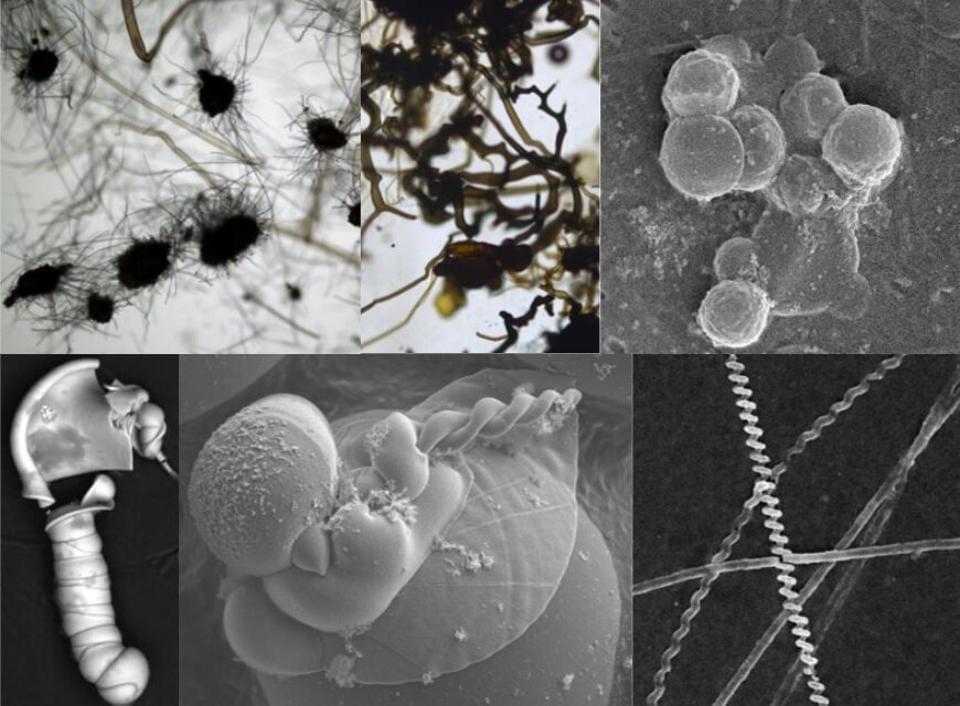
Geological evidence suggests that Mars was temporarily habitable three billion years ago when liquid water existed on the surface of the planet. Because life had little time to develop and flourish, possible microfossils found in the Martian rocks will likely resemble simple organisms. On Earth, life persisted for over three billion years in the form of single-celled bacteria and algae.
In a new open-access study published in the Journal of the Geological Society, the two authors, astrobiologists Sean McMahon and Julie Cosmidis from the Universities of Edinburgh and Oxford, note that the origins of any fossil-like specimens found on Mars are likely to be very ambiguous.
Rocks on Mars may contain numerous types of pseudofossils, structures formed by chemical processes or minerals resembling organic structures, that look similar to the kinds of fossils likely to be found if the planet ever supported life, a press release provided by University of Edinburgh explains.