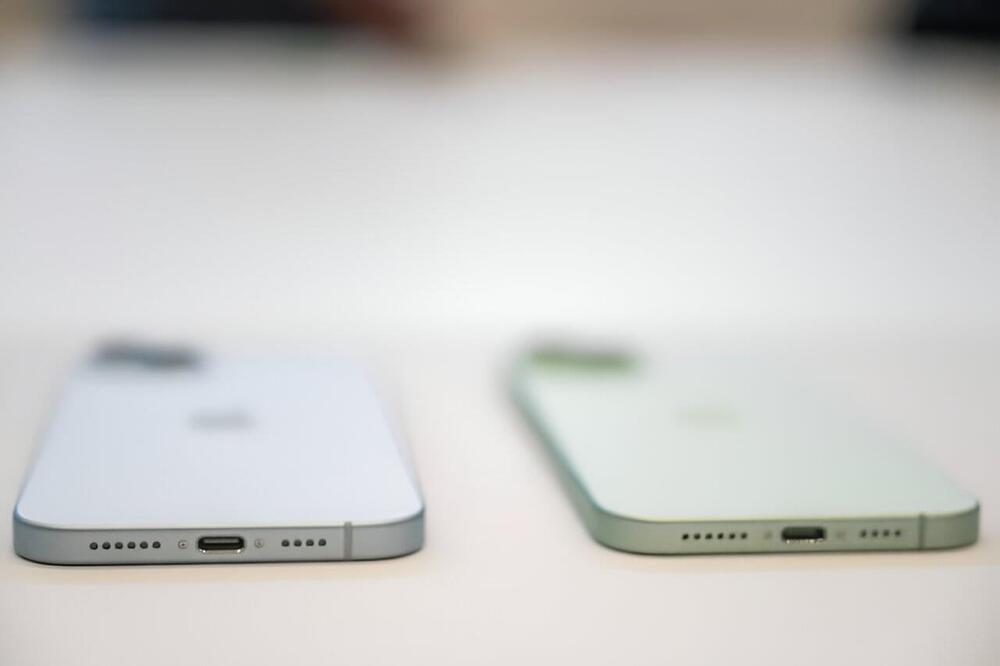
Apple unveiled its new iPhone lineup on Tuesday, with its Lightning charger ports replaced on the newest models by a universal charger after a tussle with the European Union.
The European bloc is insisting that all phones and other small devices must be compatible with the USB-C charging cables from the end of next year, a move it says will reduce waste and save money for consumers.
The firm had long argued that its cable was more secure than USB-C chargers, which are already deployed by Apple on other devices and widely used by rivals including the world’s biggest smartphone maker Samsung.