Last week, it successfully completed a flight of Mira-Light, a scaled-down version of its fourth demonstrator flight Mira, scheduled for its inaugural flight by year-end.


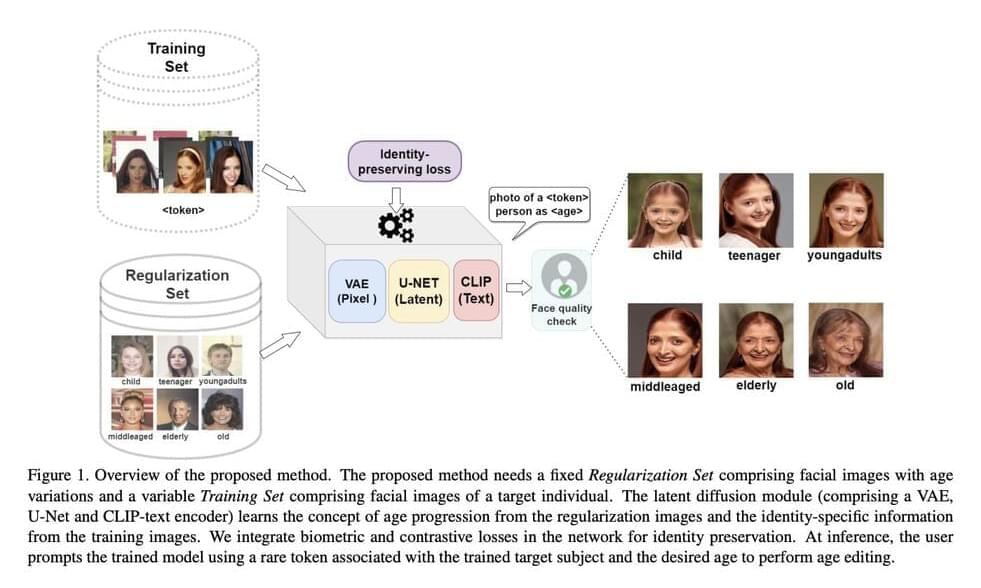
AI systems are increasingly being employed to accurately estimate and modify the ages of individuals using image analysis. Building models that are robust to aging variations requires a lot of data and high-quality longitudinal datasets, which are datasets containing images of a large number of individuals collected over several years.
Numerous AI models have been designed to perform such tasks; however, many encounter challenges when effectively manipulating the age attribute while preserving the individual’s facial identity. These systems face the typical challenge of assembling a large set of training data consisting of images that show individual people over many years.
The researchers at NYU Tandon School of Engineering have developed a new artificial intelligence technique to change a person’s apparent age in images while ensuring the preservation of the individual’s unique biometric identity.
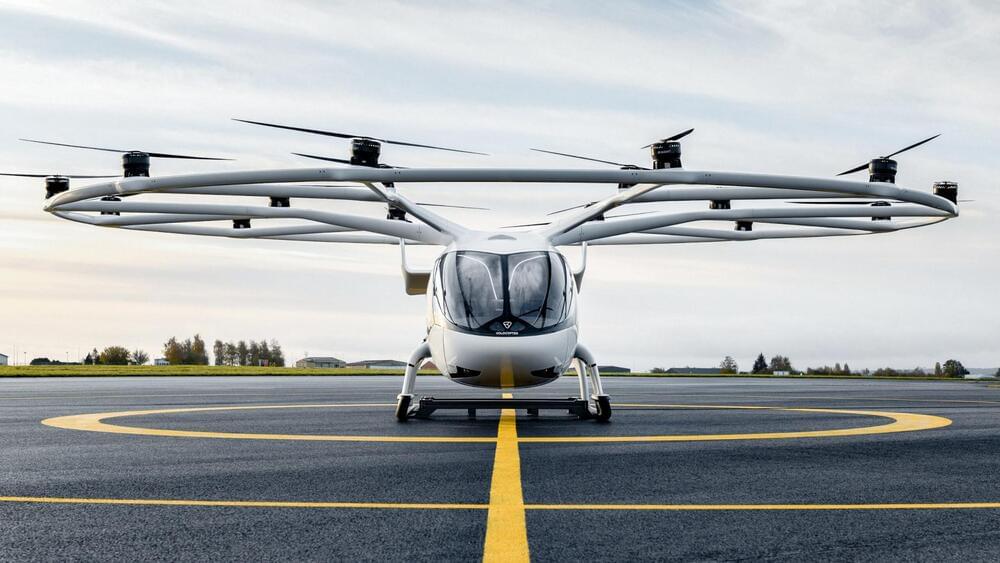


The FAA made a big splash when it unveiled its Innovate28 plan for advanced air mobility (AAM) operations with electric vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) aircraft at scale by 2028. But while Innovate28 is just that—a plan—the agency’s friend across the Atlantic is already proposing hard requirements for AAM certification, operations, and maintenance.
The European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) on Thursday shared its final opinion on rules and regulations for eVTOL air taxis, drones, and other emerging aircraft with the European Commission. Now, the ball is in the Commission’s court as it determines whether to accept EASA’s policy recommendations.
Opinion No 03/2023 lays out a comprehensive regulatory framework for safe operations of new aircraft types. It introduces requirements for piloted electric air taxi operations, flight crew licensing, air traffic management, and standardized European rules of the air (SERA). The proposal also suggests a criteria and process for the certification and maintenance of remotely piloted drones.

Images of the new, refreshed Tesla Model 3 electric vehicle (EV) has been revealed ahead of the model’s official debut in Europe and China. This is the first time Tesla has chosen to launch a new vehicle outside the United States.
The new Model 3 will produced in China and sold in Europe, China and the Middle East.
It looks similar to the current Model 3, with this new design being akin to a mid-generation refresh that traditional automakers would push forward. It comes with a revised front bumper with a reimagined LED signature, has new aerodynamic wheels and is said to have a more streamlined body, which has lead to more all-electric range.
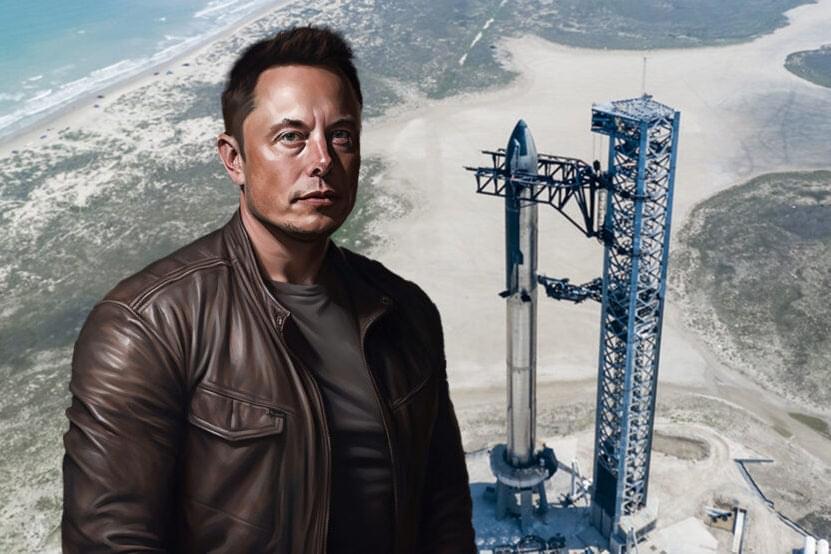

Elon Musk’s rocket manufacturing company SpaceX has completed 60 launches this year, much to the CEO’s excitement.
What Happened: SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket launched 22 Starlink satellites to low-Earth orbit from Florida on Thursday at about 10:21 p.m. ET, marking the company’s 60th launch this year.
“Congrats to the SpaceX team on launch 60 of 2023!” Musk wrote.

According to today’s conventional scientific wisdom, time flows strictly forward — from the past to the future through the present. We can remember the past, and we can predict the future based on the past (albeit imperfectly) — but we can’t perceive the future.
But if the recent data from the lab of Prof. Daryl Bem at Cornell University is correct, conventional scientific wisdom may need some corrections on this particular point.
In a research paper titled Feeling the Future, recently accepted for publication in the prestigious Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, Bem presents some rather compelling empirical evidence that in some cases — and with weak but highly statistically significant accuracy – many human beings can directly perceive the future. Not just predict it based on the past.
A team from the University of Chicago has announced the first evidence for “quantum superchemistry” – a phenomenon where particles in the same quantum state undergo collective accelerated reactions. The effect had been predicted, but never observed in the laboratory.
The findings, published July 24 in Nature Physics, open the door to a new field. Scientists are intensely interested in what are known as “quantum-enhanced” chemical reactions, which could have applications in quantum chemistry, quantum computing, and other technologies, as well as in better understanding the laws of the universe.
Breakthrough could point way to fundamental insights, new technology.
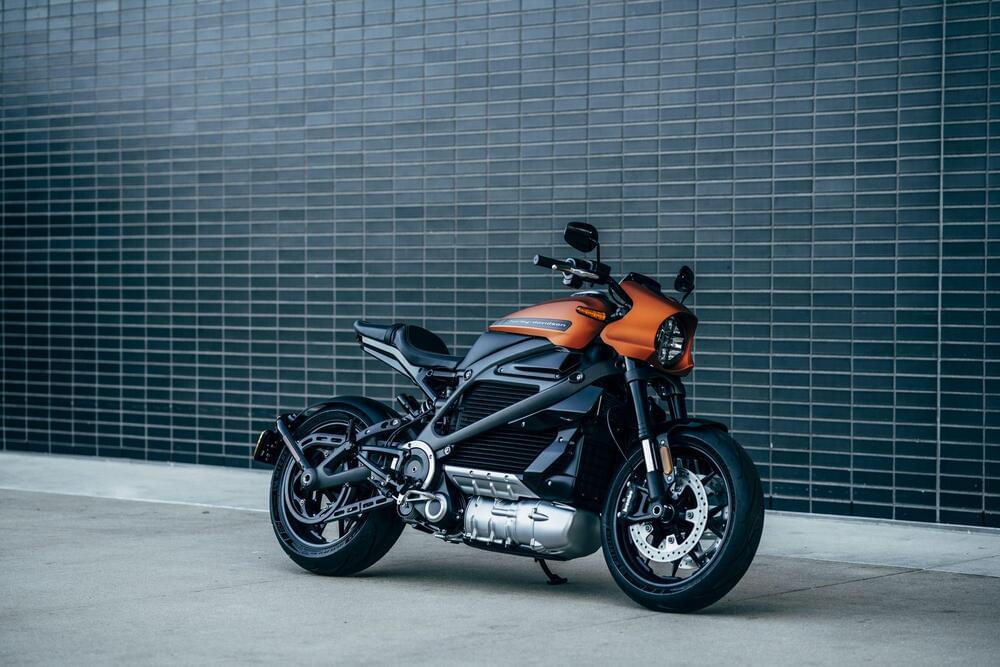

In response to rising fuel prices, Uber has introduced electric motorbikes in Kenya, initially available only in Nairobi. Uber has unveiled an electric motorbike named “One Electric” for the Kenyan market.
This introduction is pivotal as the global automotive sector is shifting towards electric vehicles, with nations like the U.K. intending to eliminate vehicles powered by internal combustion engines. This announcement is Uber’s third significant product introduction in Kenya this year, preceded by the launch of an audio recording feature for safety and the incorporation of M-PESA into its payment methods.
Frans Hiemstra, the director and regional general manager for Uber in the Middle East and Africa, emphasized the company’s commitment to sustainable practices. He mentioned that introducing the Electric Boda on their platform showcases their dedication to offering an emissions-free transportation option in Kenya. This move also aligns with Uber’s global ambition to achieve a zero-emissions platform by 2040.
That’s why we were struck to see a team of scientists that includes researchers from the name-brand Harvard Medical School and Massachusetts Institute of Technology sounding off about what they say are promising new leads, published this month in the journal Aging.
“We identify six chemical cocktails, which, in less than a week and without compromising cellular identity, restore a youthful genome-wide transcript profile and reverse transcriptomic age,” reads the paper. “Thus, rejuvenation by age reversal can be achieved, not only by genetic, but also chemical means.”
Sounds big, right? The researchers claim they pinpointed six treatments that can reverse aging in cells and turn them into a more “youthful state,” according to a press release from Aging’s publisher, without causing dangerous unregulated cell growth.