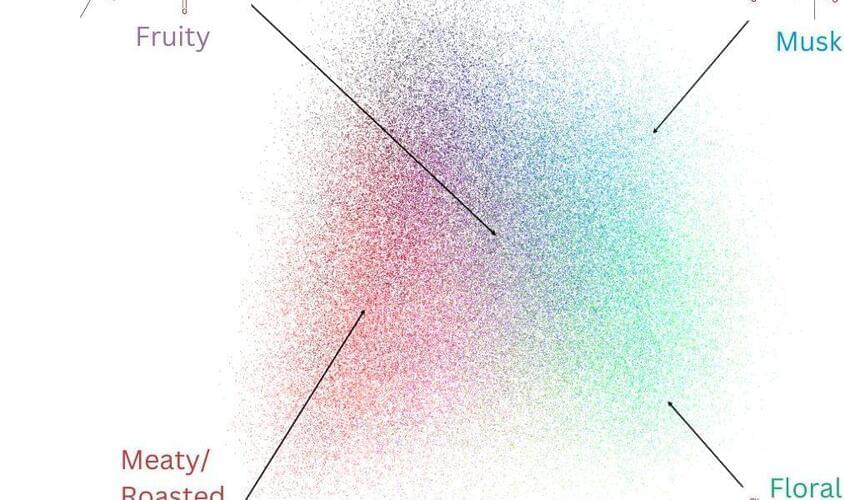
Our immune system is made of various cell types responsible for fighting pathogens and disease that enter the body. There are two distinct arms or responses of the immune system: innate and adaptive. The innate immune response is the first line of defense that includes immune cells that are not specific to the invading pathogen, but recognize it is foreign and tries to kill it. Cells that are included in this response are neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, monocytes, macrophages, mast cells, and natural killer cells. The adaptive immune response is the second line of defense and made up of cells that are more specific to the invading pathogen. The adaptive immune system includes dendritic cells, T cells, and B cells. T cells specifically have different subsets and function differently to effectively kill invading pathogens.
Although scientists know a lot about the immune system, there is still much unknown about how the cells that make up these immune responses completely function. One unclear phenomenon includes the mechanism by which immune cells know which way to travel to the site of infection. Researchers lead by Drs. Michael Sixt and Edouard Hannezo at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) recently reported in Science Immunology that immune cells generate their own path to navigate environments throughout the body.
One particular immune cell type, dendritic cells, are not exclusively part of the adaptive immune system. They work to bridge the innate and adaptive immune systems to help cohesively deliver a response that will efficiently kill the pathogen. More specifically, dendritic cells detect pathogens and then travel to the lymph nodes to coordinate a systemic attack. Dendritic cells move according to chemokines, or small proteins that help cells migrate to specific locations. Previously, it was believed that the chemokines produce a gradient and it was this gradient that allowed cells to migrate to specific locations. However, Sixt, Hannezo, and colleagues reported that this gradient might not be the only way for migrating cells.



 עברית (Hebrew)
עברית (Hebrew)