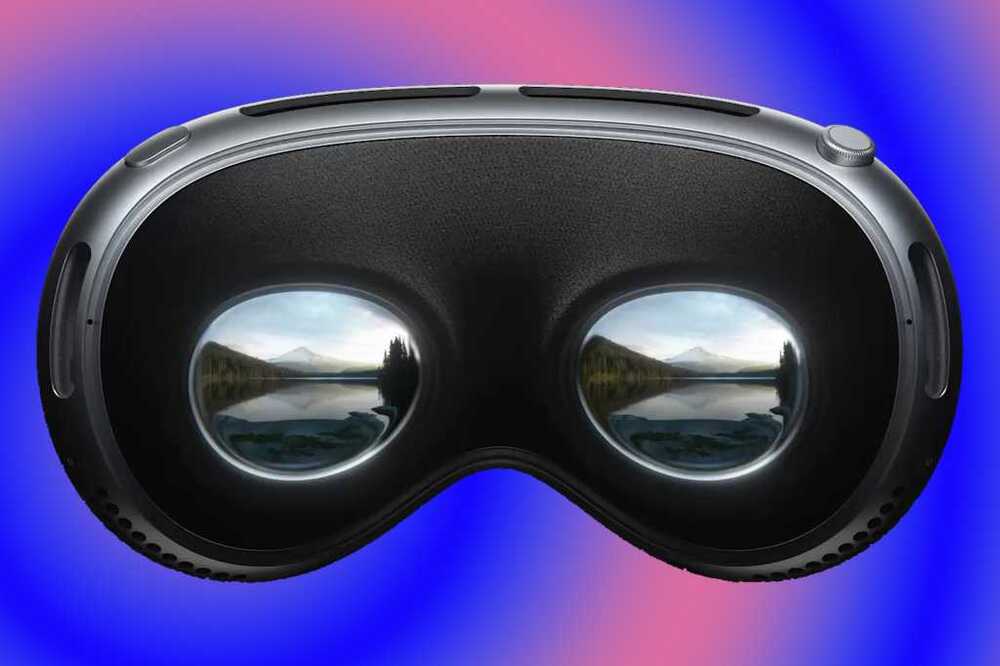
At Apple’s WWDC23, I think I saw the future. [Pausing to ponder.] Yeah, I’m pretty sure I saw the future–or at least Apple’s vision of the future of computing. On Tuesday morning, I got to try the Apple Vision Pro, the new $3,499 mixed-reality headset that was announced this week and ships next year.
I’m here to tell you the major details of my experience, but the overall impression I have is that the Vision Pro is the most impressive first-gen product I’ve seen from Apple–more impressive than the 1998 iMac, or the 2007 iPhone. And I’m fully aware that other companies have made VR headsets, but Apple does that thing that it does, where it puts its understanding of what makes a satisfying user experience and creates a new product in an existing market that sets a higher bar of excellence.
Yes, it’s expensive, and yes, this market hasn’t proven that it can move beyond being niche. Those are very important considerations to discuss in other articles. For now, I’ll convey my experiences and impressions here, from a one-hour demonstration at Apple Park. (I was not allowed to take photos or record video; the photos posted here were supplied by Apple.) The device I used is an early beta, so it’s possible—likely even—that the hardware or software could change before next year.


 עברית (Hebrew)
עברית (Hebrew)