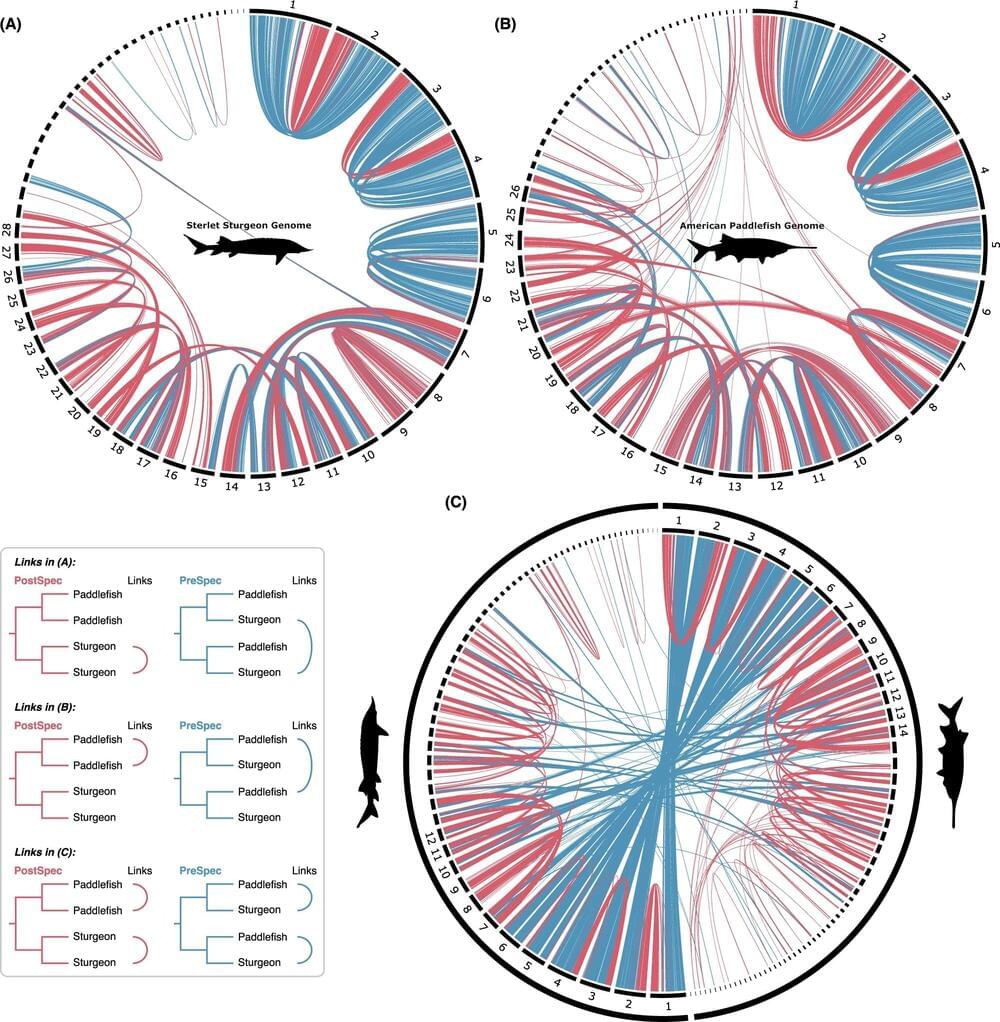
Geneticists have unearthed a major event in the ancient history of sturgeons and paddlefish that has significant implications for the way we understand evolution. They have pinpointed a previously hidden “whole genome duplication” (WGD) in the common ancestor of these species, which seemingly opened the door to genetic variations that may have conferred an advantage around the time of a major mass extinction some 200 million years ago.
The big-picture finding suggests that there may be many more overlooked, shared WGDs in other species before periods of extreme environmental upheaval throughout Earth’s tumultuous history.
The research, led by Professor Aoife McLysaght and Dr. Anthony Redmond from Trinity College Dublin’s School of Genetics and Microbiology, has just been published in Nature Communications.