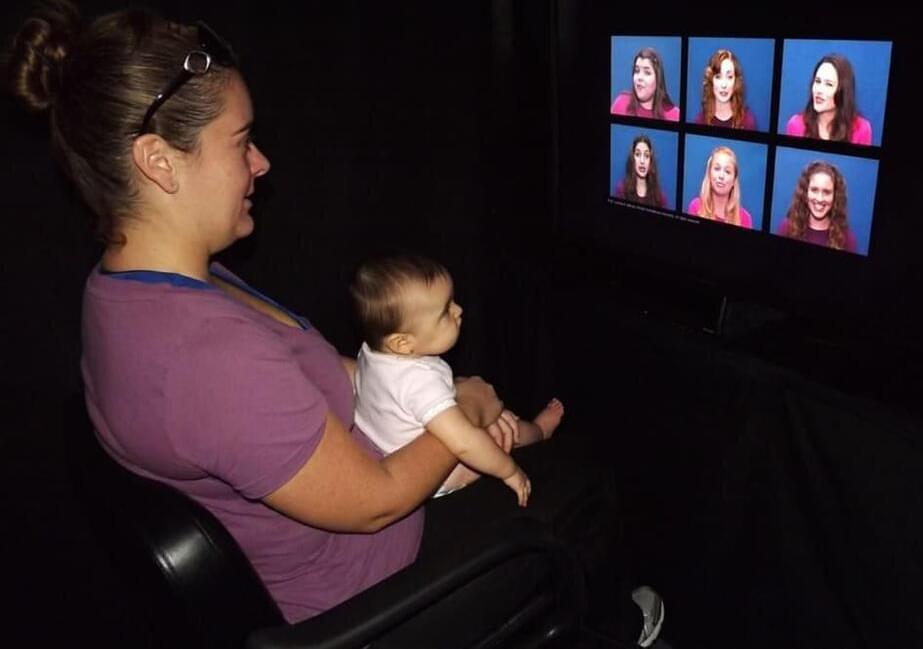
Matching the sight and sound of speech—a face to a voice—in early infancy is an important foundation for later language development.
This ability, known as intersensory processing, is an essential pathway to learning new words. According to a recent study published in the journal Infancy, the degree of success at intersensory processing at only 6 months old can predict vocabulary and language outcomes at 18 months, 2 years and 3 years old.
“Adults are highly skilled at this, but infants must learn to relate what they see with what they hear. It’s a tremendous job and they do it very early in their development,” said lead author Elizabeth V. Edgar, who conducted the study as an FIU psychology doctoral student and is now a postdoctoral fellow at the Yale Child Study Center. “Our findings show that intersensory processing has its own independent contribution to language, over and above other established predictors, including parent language input and socioeconomic status.”