The competition aims to incorporate modern tools and data science into practice to enhance patients’ quality of life.



“My hope is that this finding will encourage materials researchers to consider that, under the right circumstances, materials can do things we never expected,” Demkowicz concluded.
The study is published in the journal Nature.
Self-healing metals are an exciting area of research in the field of materials science. The term refers to metals that have the ability to heal themselves after being damaged or degraded.
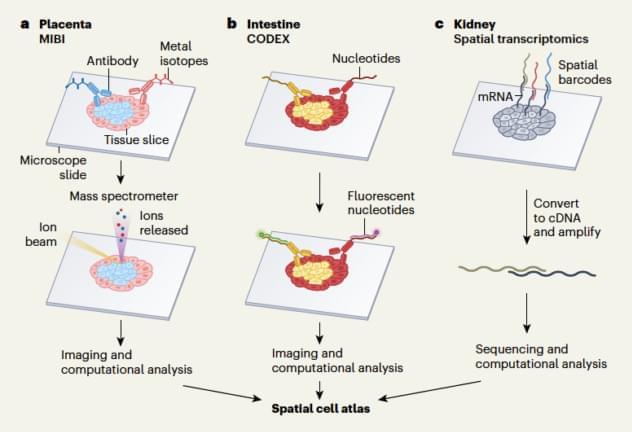
A consortium of scientists has just published an atlas of remarkable images of three human organs, each vital in their own way, showing how cell types are arranged and interact.
The result: Glittering, kaleidoscopic blueprints lit up by fluorescent dyes that reveal new intimacies about our bodies and reshape our understanding of human biology and disease like never before.
As you can see in the diagram below, researchers generated the cell atlases in three ways.
Duke University professor Sultan Meghji joined ‘Fox & Friends Weekend’ to discuss artificial intelligence and scientists’ latest efforts to combine the technology with brain cells. #foxnews.
Watch more Fox News Video: http://video.foxnews.com.
Watch Fox News Channel Live: http://www.foxnewsgo.com/
FOX News Channel (FNC) is a 24-hour all-encompassing news service delivering breaking news as well as political and business news. The number one network in cable, FNC has been the most-watched television news channel for 18 consecutive years. According to a 2020 Brand Keys Consumer Loyalty Engagement Index report, FOX News is the top brand in the country for morning and evening news coverage. A 2019 Suffolk University poll named FOX News as the most trusted source for television news or commentary, while a 2019 Brand Keys Emotion Engagement Analysis survey found that FOX News was the most trusted cable news brand. A 2017 Gallup/Knight Foundation survey also found that among Americans who could name an objective news source, FOX News was the top-cited outlet. Owned by FOX Corporation, FNC is available in nearly 90 million homes and dominates the cable news landscape, routinely notching the top ten programs in the genre.
Watch full episodes of your favorite shows.
The Five: https://www.foxnews.com/video/shows/the-five.
Special Report with Bret Baier: https://www.foxnews.com/video/shows/special-report.
Jesse Watters Primetime: https://www.foxnews.com/video/shows/jesse-watters-primetime.
Hannity: https://www.foxnews.com/video/shows/hannity.
The Ingraham Angle: https://www.foxnews.com/video/shows/ingraham-angle.
Gutfeld!: https://www.foxnews.com/video/shows/gutfeld.
Fox News @ Night: https://www.foxnews.com/video/shows/fox-news-night.
Follow Fox News on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/FoxNews/
Follow Fox News on Twitter: https://twitter.com/FoxNews/
Follow Fox News on Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/foxnews/

In a ground-breaking experiment, researchers from the University of Groningen collaborated with their peers from Nijmegen and Twente universities in the Netherlands, and the Harbin Institute of Technology in China. Together, they confirmed the existence of a superconductive state that was first predicted in 2017.
Their findings, which demonstrate evidence for a unique form of the FFLO superconductive state, were recently published in the journal Nature. This breakthrough has the potential to be impactful, particularly within the field of superconducting electronics.

The study also confirmed past research showing that superagers have a greater volume of gray matter associated with memory in parts of the brain.
In an editorial commentary accompanying the study, researchers Dr. Alexandra Touroutoglous, Dr. Bonnie Wong, and Dr. Joseph M Andreano of Harvard Medical School said this finding primarily focused on the medial temporal lobe of the brain, “which is consistent with previous research.”
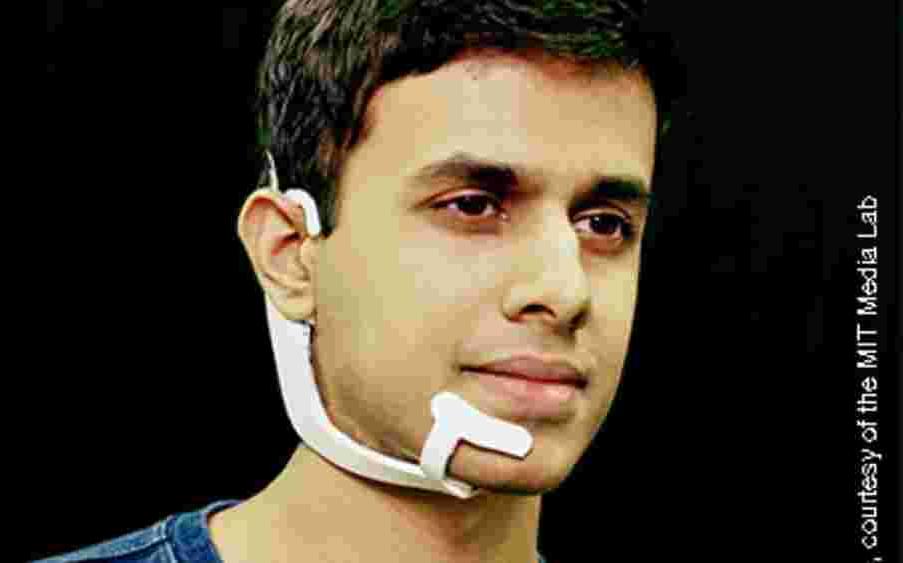
A student of the prestigious Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) has invented an artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled device that helps people to converse in a natural language with machines, AI assistants, services, and other people without any voice. People don’t have to open their mouths and don’t have to make any externally observable movements. They can simply converse articulating words internally.

Ear infections in babies and toddlers are extremely common. In fact, according to the National Institutes of Health, five out of six children will experience an ear infection before their third birthday.
“Many parents are concerned that an ear infection will affect their child’s hearing irreversibly—or that an ear infection will go undetected and untreated,” says David Tunkel, M.D., Johns Hopkins Medicine pediatric otolaryngologist (ENT). “The good news is that most ear infections go away on their own, and those that don’t are typically easy to treat.”
Ear infections happen when there is inflammation— usually from trapped bacteria—in the middle ear, the part of the ear connects to the back of the nose and throat. The most common type of ear infection is otitis media, which results when fluid builds up behind the eardrum and parts of the middle ear become infected and swollen.
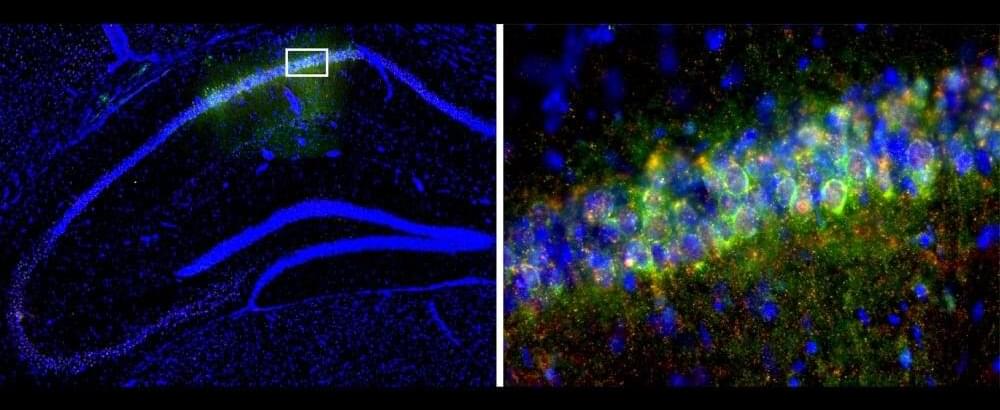
A gene that plays a key role in regulating how bodies change across the 24-hour day also influences memory formation, allowing mice to consolidate memories better during the day than at night. Researchers at Penn State tested the memory of mice during the day and at night, then identified genes whose activity fluctuated in a memory-related region of the brain in parallel with memory performance.
Experiments showed that the gene, Period 1, which is known to be involved in the body’s circadian clock, is crucial for improved daytime memory performance. A paper describing the research was published online in the journal Neuropsychopharmacology.
The research demonstrates a link between the circadian system and memory formation and begins to piece together the molecular mechanisms that help form and keep memories. Understanding these mechanisms and the influence of time of day on memory formation could help researchers to determine how and when people learn best.
Credit: Hyundai Motor Group.
During a press conference held yesterday in Seoul, South Korea, Hyundai Motor Group revealed plans for a new generation of high-tech cars incorporating nanoscale features, which it hopes to begin mass producing by 2025–2026.
Nanotechnology is defined as materials or devices that work on a scale smaller than one hundred nanometres (nm). A nanometre is one billionth of a metre or about 100,000 times narrower than a human hair. Individual atoms, for comparison, tend to range in size from 0.1 to 0.5 nm. Many interesting and unique physical effects become possible at this level of detail, making nanotechnology a highly promising technology of the future.