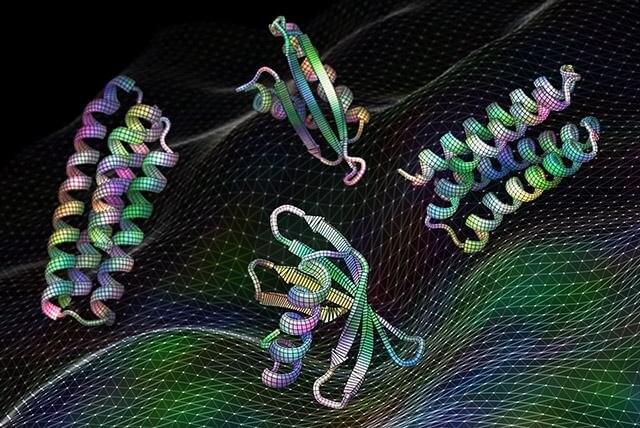
Scientists have developed artificial intelligence software that can create proteins that may be useful as vaccines, cancer treatments, or even tools for pulling carbon pollution out of the air.
This research, reported today in the journal Science, was led by the University of Washington School of Medicine and Harvard University. The article is titled “Scaffolding protein functional sites using deep learning.”
“The proteins we find in nature are amazing molecules, but designed proteins can do so much more,” said senior author David Baker, an HHMI Investigator and professor of biochemistry at UW Medicine. “In this work, we show that machine learning can be used to design proteins with a wide variety of functions.”