Scientists removed the outer lid of OSIRIS-REx’s sample canister on Tuesday (Sept. 26). But a full reveal of the mission’s asteroid sample is still two weeks away.


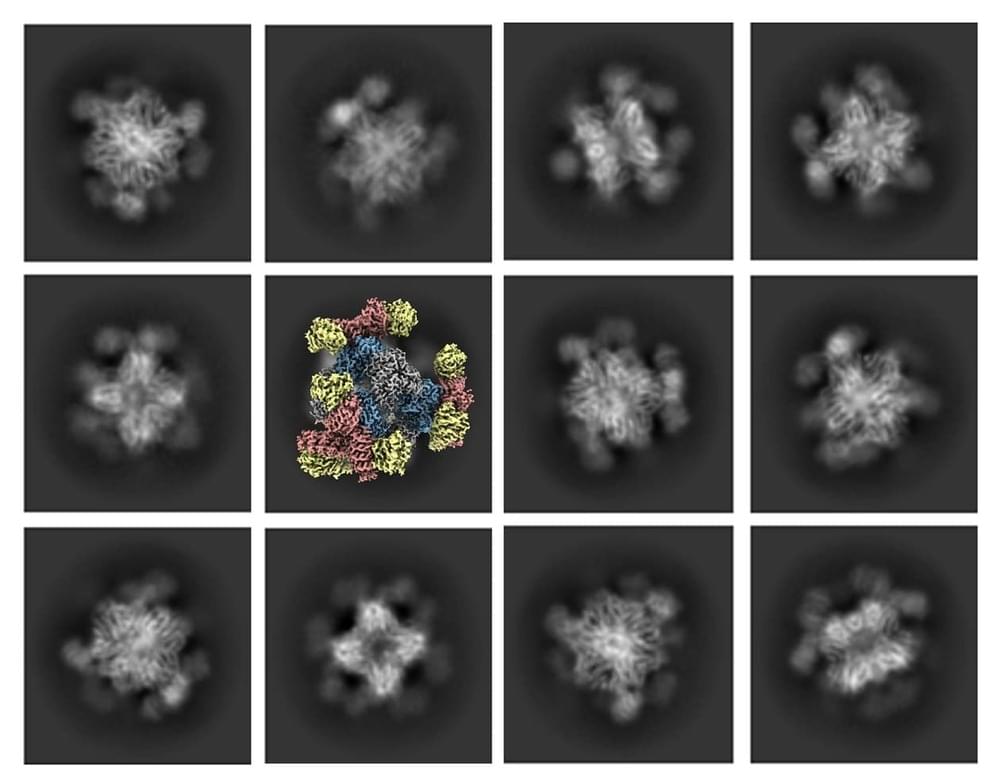
Using their new scaffold with cryo-EM, the UCLA-led team saw the atomic structure of KRAS when it was connected to a drug being studied for lung cancer treatment. This showed that their method can help understand how drugs interact with proteins like KRAS, potentially leading to better medicines.
Castells-Graells said, “The potential applications for the new advance don’t stop with cancer drugs. ” Our modular scaffold can be assembled in any configuration to capture and hold all small protein molecules.”
The UCLA-led team’s essential improvement to cryo-EM technology represents a significant milestone in structural biology and scientific imaging. Their achievement in visualizing small therapeutic protein targets at 3 Å resolution is a testament to the power of innovation and collaboration in pushing the boundaries of scientific discovery. This breakthrough promises to revolutionize drug development and our understanding of complex biological systems, further solidifying Cryo-EM’s place as an invaluable tool in modern research.
Zuby Interviews Elon Musk: https://youtu.be/pjc_oo4ApSY?si=AHD8kdwXqmB1wrjpNeura Pod is a series covering topics related to Neuralink, Inc. Topics such as br…

How well that translation occurs remains to be seen while the patient learns and adapts to the new system. “The implant procedures involving the Onward ARC-IM and Clinatec BCI went smoothly,” Dr. Bloch said in an press release. “We are now working with the patient to use this cutting-edge innovation to recover movement of his arms, hands, and fingers. We look forward to sharing more information in due course.”
“If the therapy continues to show promise, it is possible it could reach patients by the end of the decade,” Onward CEO Dave Marver said in a statement to Engadget. “It is important to note that we do not expect people with spinal cord injury to wait that long for Onward to commercialize an impactful therapy — we hope to commercialize our external spinal cord stimulation solution, ARC-EX Therapy, to restore hand and arm function in the second half of 2024.”
Onward Medical among a quickly expanding field of BCI-based startups working to apply the fledgling technology to a variety of medical maladies. Those applications include loss of limb and self-regulatory function due to stroke, traumatic brain or spinal cord injury, physical rehabilitation from those same injuries, as well as a critical means of communication for people living with Locked-In Syndrome.
Risk for community-onset C. difficile infection varies widely with choice of antibiotic.
The rising incidence of hospital-and community-acquired Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) reinforces the need for more-effective prevention. Researchers performed a retrospective case-control study to examine relative risk for community-acquired CDI (CA-CDI) in patients receiving different oral antibiotics. Using administrative claims databases from 2001–2021 that included commercial, Medicare, and Medicaid records, they matched each CA-CDI case with five control patients for a total of 159,404 cases and 797,020 controls.
For cases occurring within 30 days of antibiotic exposure, the highest risk for CA-CDI occurred with clindamycin (adjusted odds ratio, 25.4) and the lowest with minocycline (AOR, 0.79; the only 1 of 27 oral antibiotics with an AOR 1.0). Other high-risk antibiotics were cefixime (AOR, 12.0), cefdinir (11.0), cefuroxime (9.6), cefpodoxime (9.2), amoxicillin-clavulanate (8.5), and ciprofloxacin (6.8). Older beta-lactams were lower risk (penicillin AOR, 1.8; amoxicillin, 2.0; cephalexin, 2.9; cefadroxil, 2.8). The lowest-risk antibiotic classes were the macrolides, sulfonamides, and tetracyclines. For all antibiotic classes, different agents had discernible differences in AOR for CA-CDI. A sensitivity analysis assessing relative risk for CA-CDI over multiple exposure periods up to 180 days found that the relative hierarchy of risk for the different antibiotics remained the same for each exposure period, and that overall risk progressively declined with time.
The authors acknowledge multiple limitations of their analysis, including use of administrative claims data to identify CA-CDI and outpatient claims data to identify antibiotic exposure and lack of information on inpatient antibiotic usage. Still, the large study population allowed for a more-precise definition of relative risk than in prior studies, not only showing a wide variation among beta-lactam antibiotics but also indicating that the risk associated with fluoroquinolone antibiotics falls between that of the older and newer cephalosporin classes.
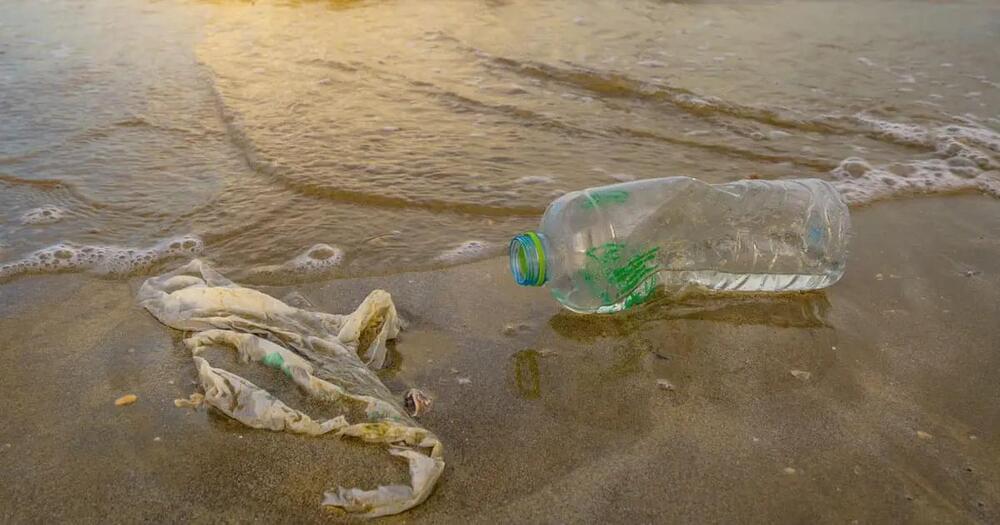


A genetically engineered marine microorganism is shown to break down polyethylene terephthalate (PET) in saltwater. This plastic, used in everything from water bottles to clothing, is a significant contributor to microplastic pollution in oceans.
“This is exciting because we need to address plastic pollution in marine environments,” says Nathan Crook, corresponding author of a paper on the work and an assistant professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering at North Carolina State University.
An exploration of the idea Black Holes from Before The Universe Existed, and other black hole oddities.
My Patreon Page:
https://www.patreon.com/johnmichaelgodier.
My Event Horizon Channel:
Music: