Page 4927
Apr 22, 2022
A new genome reference index could save the gene diversity of humans
Posted by Gemechu Taye in categories: biotech/medical, genetics
Apr 22, 2022
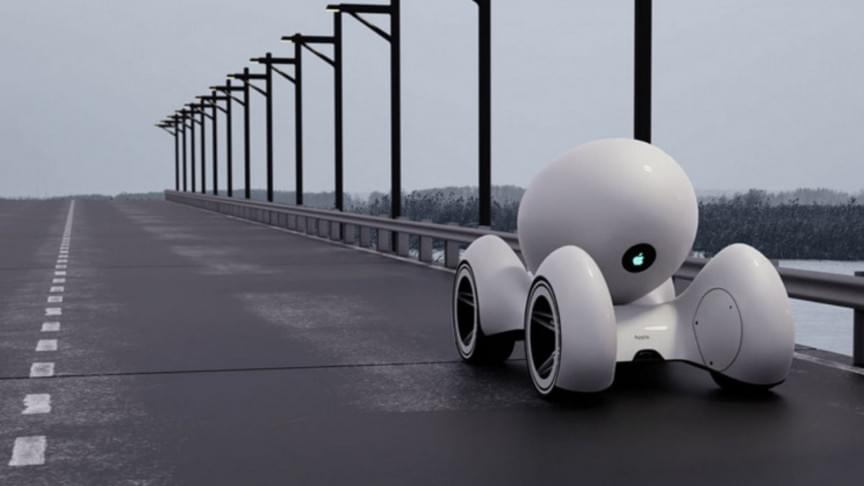
Here’s everything we know about the next-gen Apple Car
Posted by Gemechu Taye in category: transportation
Apr 22, 2022
Carmakers and Countries Come Together to Ban ICE Vehicles by 2040
Posted by Gemechu Taye in categories: climatology, sustainability
Apr 22, 2022
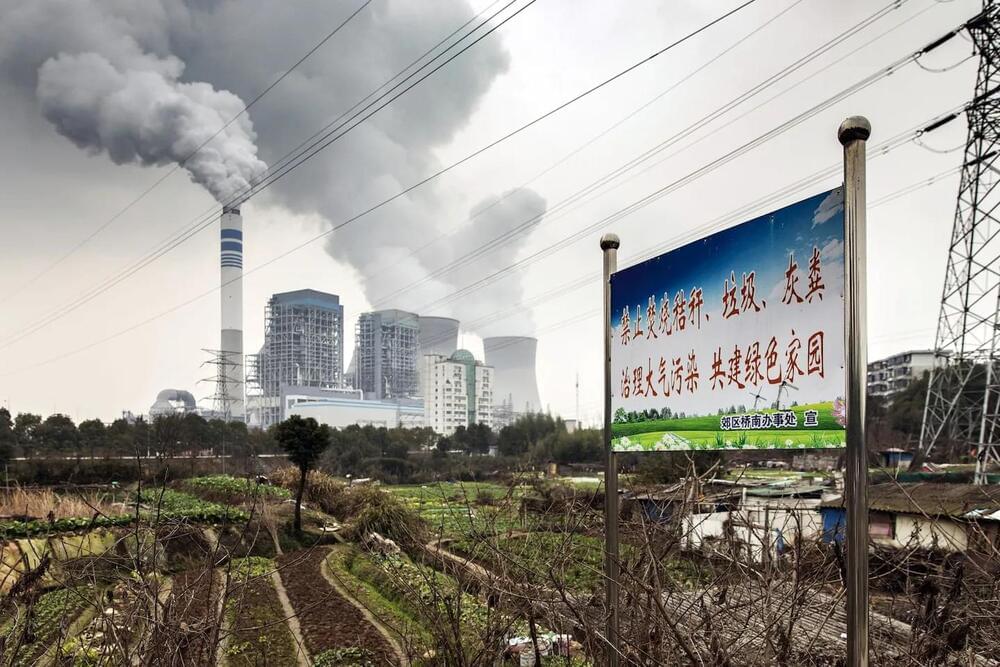
With coal surge, China puts energy security and growth before climate
Posted by Len Rosen in category: climatology
China is using loopholes in climate agreements to continue to build and operate coal-fired power plants.
China produces and consumes half the world’s coal and despite recent climate pledges, it remains deeply bound to continuing to use this energy source.
Apr 22, 2022
Quantum Physics of Consciousness
Posted by Jose Ruben Rodriguez Fuentes in categories: neuroscience, quantum physics

Are quantum events required for consciousness in a very special sense, far beyond the general sense that quantum events are part of all physical systems? What would it take for quantum events, on such a micro-scale, to be relevant for brain function, which operates at the much higher level of neurons and brain circuits? What would it mean?
Free access to Closer to Truth’s library of 5,000 videos: http://bit.ly/376lkKN
Apr 22, 2022
Largest study of whole genome sequencing data reveals ‘treasure trove’ of clues about causes of cancer
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: biotech/medical, genetics
DNA analysis of thousands of tumors from NHS patients has found a ‘treasure trove’ of clues about the causes of cancer, with genetic mutations providing a personal history of the damage and repair processes each patient has been through.
In the biggest study of its kind, a team of scientists led by Professor Serena Nik-Zainal from Cambridge University Hospitals (CUH) and University of Cambridge, analyzed the complete genetic make-up or whole-genome sequences of more than 12,000 NHS cancer patients.
Because of the vast amount of data provided by whole genome sequencing, the researchers were able to detect patterns in the DNA of cancer—or ‘mutational signatures’—that provide clues about whether a patient has had a past exposure to environmental causes of cancer such as smoking or UV light, or has internal, cellular malfunctions.
Apr 22, 2022
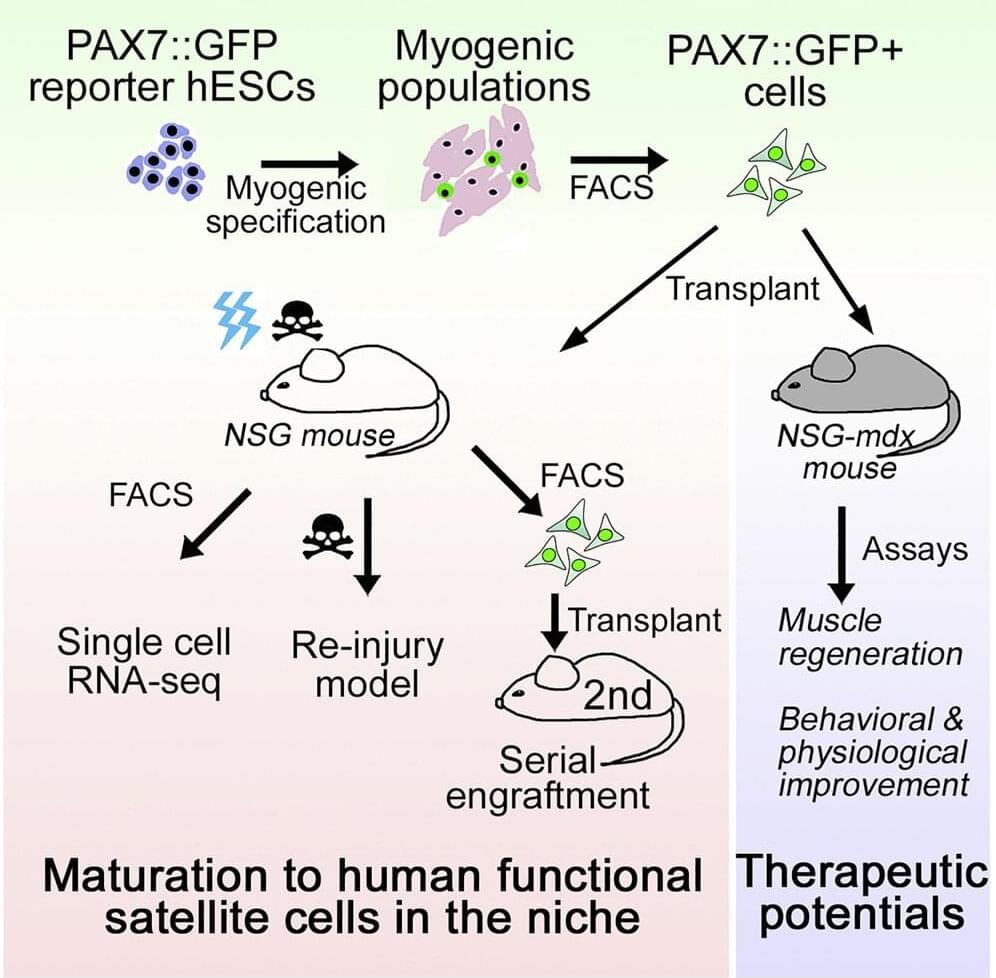
Lab grown, self-sustainable muscle cells repair injury and disease, mouse study shows
Posted by Josh Seeherman in categories: biotech/medical, genetics
In proof-of-concept experiments, Johns Hopkins Medicine scientists say they have successfully cultivated human muscle stem cells capable of renewing themselves and repairing muscle tissue damage in mice, potentially advancing efforts to treat muscle injuries and muscle-wasting disorders in people.
A report on the experiments was published April 7 in Cell Stem Cell.
To make the self-renewing stem cells, the scientists began with laboratory-grown human skin cells that were genetically reprogrammed to a more primitive state in which the cells have the potential to become almost any type of cell in the body. At this point, the cells are known as induced pluripotent stem (IPS) cells, and they are mixed with a solution of standard cell growth factors and nutrients that nudge them to differentiate into specific cell types.
Apr 22, 2022
Feeling Sensations, Including Ones Connected to Sadness, May Be Key to Depression Recovery
Posted by Kelvin Dafiaghor in category: neuroscience
Summary: Suppressing or blocking out physical sensations related to emotions such as sadness can hinder recovery from depression symptoms and may cause a relapse into depression.
Source: University of Toronto.
The physical sensations that accompany sadness can feel as undesirable as they are intense—a constriction of the chest, watery eyes and a raw throat, to name a few.
Apr 22, 2022
Artificial fingertip gives robots nearly humanlike touch
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: biotech/medical, robotics/AI
3D printed skin reacts to texture and shape like our skin.
The optical properties of mitochondrial bundles in the retina may improve how efficiently the eye captures light.