Some people ask what they’re supposed to do while waiting for their EV to charge. Tesla has just added a new option in Germany. It’s time for a swim.
Scientists from the University of Virginia School of Medicine and collaborators used the building blocks of life to potentially revolutionize electronics.
The scientists utilized DNA to guide a chemical reaction that would overcome the barrier to Little’s superconductor, which was once thought to be “insurmountable”, a press statement reveals.
A new study proposes a possible solution to the Fermi Paradox, suggesting why we may not detect advanced alien civilizations.
A new study offers a possible solution to the Fermi Paradox. * The Fermi Paradox wonders why we haven’t encountered aliens yet. * Advanced alien civilizations may be pulling back from space exploration to avoid collapse, predict the researchers.
With the sheer vastness of space, it seems quite conceivable that there should be more intelligent civilizations out there besides us. After all, some estimates peg the observable universe to contain at least 2 trillion galaxies, with each such galaxy having approximately 100 million stars on average but with some like our Milky Way Galaxy estimated as having as many as 200 billion stars and 100 billion planets. We are talking astonishing numbers in quintillions or sextillions for the total number of planets in the universe. new study by Dr. Michael Wong of the Carnegie Institution for Science and Caltech’s Dr. Stuart Bartlett proposes a possible solution to the Fermi Paradox.
A breakthrough from Deakin University researchers could help address a major obstacle in the development of environmentally-friendly, cost effective, polymer-based batteries.
The team from Deakin’s Institute for Frontier Materials (IFM) used computer modeling and simulations to design a new type of solid-state polymer electrolyte, showing its potential use in various types of polymer-based solid-state batteries, particularly sodium and potassium batteries.
Polymer-based batteries are able to support high-energy density metals in an all solid-state batteries. They use polymer as the ion conductor rather than flammable organic liquid solvents in current lithium-ion batteries. Therefore, a polymer-based solid-state battery offers an energy storage option that is greener, safer and providing a higher capacity, meaning more energy.
“Augmented books, or a-books, can be the future of many book genres, from travel and tourism to education. This technology exists to assist the reader in a deeper understanding of the written topic and get more through digital means without ruining the experience of reading a paper book.”
Power efficiency and pre-printed conductive paper are some of the new features which allow Surrey’s augmented books to now be manufactured on a semi-industrial scale. With no wiring visible to the reader, Surrey’s augmented reality books allow users to trigger digital content with a simple gesture (such as a swipe of a finger or turn of a page), which will then be displayed on a nearby device.
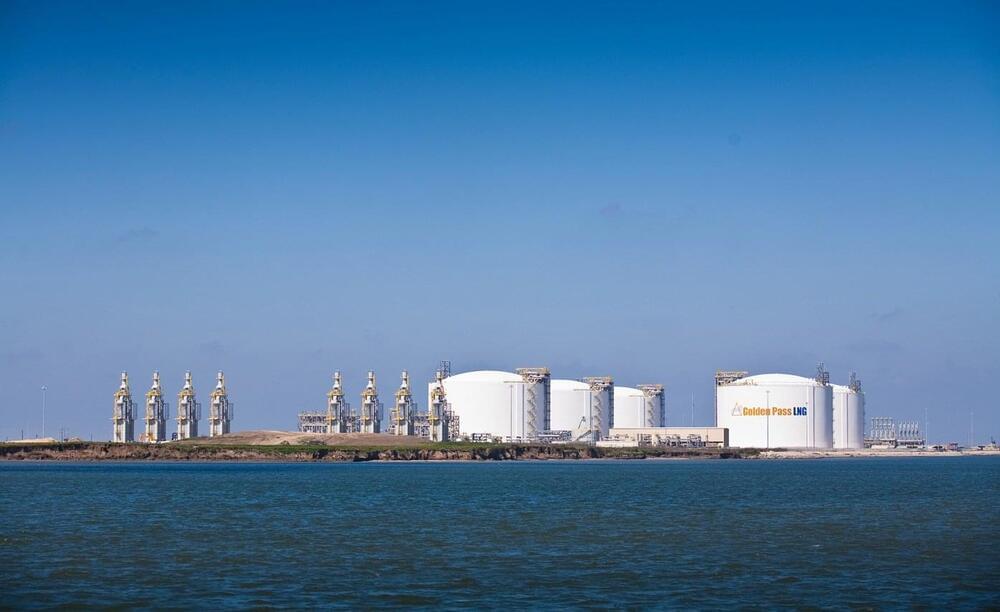
U.S. oil and gas company Chesapeake Energy has entered into a term gas supply agreement (GSA) with Golden Pass LNG Terminal, a joint venture of QatarEnergy and ExxonMobil.
Under the deal, Chesapeake is to deliver 300 milllion cubic feet per day of gas from Haynesville to Golden Pass’s LNG terminal on the Gulf Coast near Sabine Pass, Texas.
The GSA is to start in 2024 with a 36-month term at an NYMEX-based price less a fixed differential.
Knowing how strong a piece of steel is, especially the stainless steel used in everything from cars to buildings, is vitally important for the people who make and use it. This information helps to keep people safe during crashes and to prevent buildings from collapsing.
Accurately predicting the strength of a steel prototype based on its microstructure and composition would be indispensable when designing new types of steel, but it has been nearly impossible to achieve—until now.
“Designing/making the best-strength steel is the hardest task,” said Dr. Harishchandra Singh, an adjunct professor at NANOMO and the Centre for Advanced Steels Research at the University of Oulu in Finland.