T cell immunity declines with thymic atrophy, but thymic cell grafts rescue T cell function.
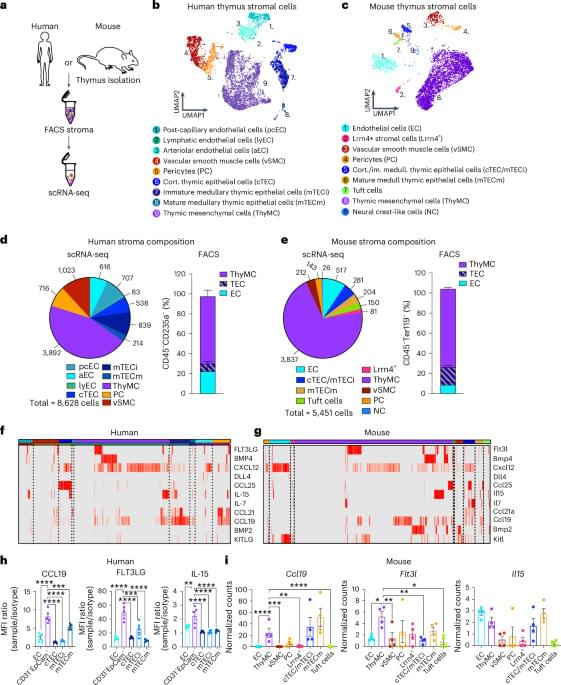

Petitpas et al. dissect the single-cell transcriptome underlying the sequential steps of pre-malignant lesions and early anorectal cancer, mimicking disease evolution seen in patients, at the epithelial and immune level. They reveal a key epithelial-immune cell crosstalk involving IL-17-producing T lymphocytes and neutrophils as essential for the dysplasia-carcinoma progression.
Lex Fridman Podcast full episode: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YDjOS0VHEr4Please support this podcast by checking out our sponsors:- LMNT: https://drinkLM…
Lex Fridman Podcast full episode: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YDjOS0VHEr4Please support this podcast by checking out our sponsors:- LMNT: https://drinkLM…

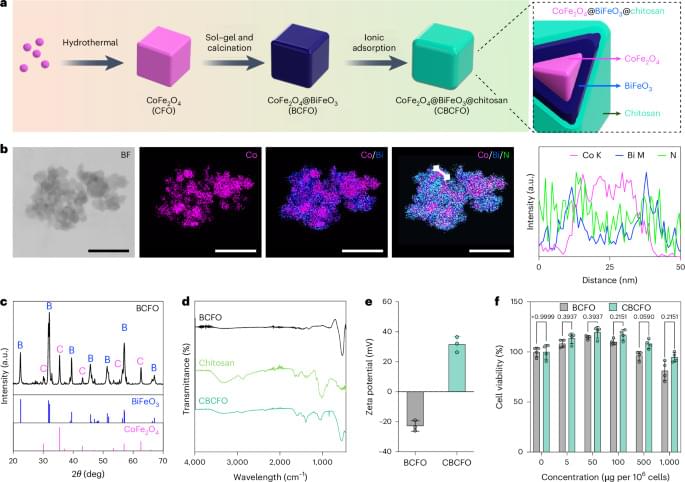
An intriguing paper by Lin et al. where cells were engineered to express a signaling pathway that transcribes a gene of interest upon generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) by CBCFO nanoparticles in response to applied electromagnetic fields. When implanted in a mouse model of diabetes, nanoparticle-treated genetically engineered cells produced insulin and decreased blood glucose levels in the mice after electromagnetic field application.
Wireless magnetic control of gene expression in mammalian cells has been developed based on intracellular nanointerface and ROS-mediated signalling. The approach allows remotely tunable insulin release and regulates blood glucose in diabetic mice.

Uncertainty about a possible future threat disrupts our ability to avoid it or to mitigate its negative impact, and thus results in anxiety. Here, we focus the broad literature on the neurobiology of anxiety through the lens of uncertainty. We identify five processes essential for adaptive anticipatory responses to future threat uncertainty, and propose that alterations to the neural instantiation of these processes results in maladaptive responses to uncertainty in pathological anxiety. This framework has the potential to advance the classification, diagnosis, and treatment of clinical anxiety.

Hair is a signature mammalian characteristic with versatile functions, including thermoregulation, protection from ultraviolet radiation, physical and chemical insults, sensation of pain, vibration and touch, and defence from predators.1–3 Human hair patterns, which feature prominently reduced body hair length combined with extremely long scalp hair,4–8 are an outlier among mammals. The likely original function of long scalp hair was to shield the sun-exposed head of upright-standing human ancestors. Long scalp hair probably reduced the amount of sweat secretion required to counter the total thermal load experienced by individuals from incoming solar radiation in equatorial Africa, and from endogenous muscle-generated heat during exercise.9 Tightly curled scalp hair is more efficacious at reducing heat gains compared with other hair shapes, and such hair probably represents the ancestral scalp hair form (Figure 1).9 Variability in hair shapes increased over time. These variations are thought to be associated with the dispersal of anatomically modern humans (AMHs) and accompanying effects of populational bottlenecks, admixture with Neanderthals and Denisovans, and adaptations to diverse environments at new geographic locations (Figure 1a).10 Extreme scalp hair length was probably universal across all African AMH populations and available for diverse functions, other than thermoregulation. In this sense, long scalp hair is an excellent example of exaptation, a form of evolutionary co-option,11 whereby it acquired secondary essential functions in communicating social cues.12 Under these conditions, unwanted hair loss triggered significant psychological stress in affected individuals.
Despite variations, both across different species and different body regions, hair typically has a finite length. A fully grown hair fibre commonly remains attached within its hair follicle (HF) until a new round of growth replaces it. In a typical adult human, approximately 90% of scalp HFs are in active growth (anagen) at any given time, which lasts for 5–7 years.13,14 This is in contrast to small (vellus) body HFs, which have short-lasting anagen, such as 22–28 days on the upper arm.15 When large (terminal) scalp HFs reduce in size, start growing vellus-like hairs, and/or stop growing for an extended period, they are considered to be entering a pathological state.
Elucidation of long scalp hair roles in human prehistory requires further investigation of its thermoregulatory benefit vs. the physical burden it may have caused by hindering vision and locomotion. Continuous hair growth is also metabolically expensive, requiring synthesis of large quantities of keratins and keratin-associated proteins.1,2,16,17 Conversely, highly visible long scalp hair effectively communicates a good state of fitness, whereas compromised hair growth implies poor nutrition and disease.17,18 Indeed, kwashiorkor, a disease caused by severe dietary protein deficit, features dramatic hair thinning and depigmentation.19 The ornamental potential of long hair enables the use of distinct hairstyles to signify a person’s social position, creativity and manual skills.20 Therefore, in prehistory, hair styling likely became an essential part of social communication, which probably further promoted long-hair trait selection.