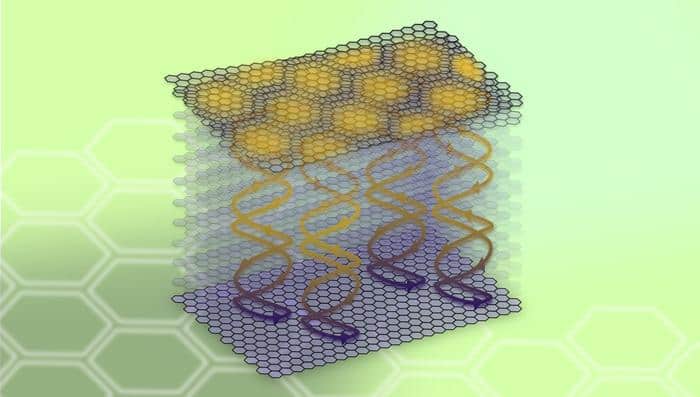
When two sheets of graphene are placed on top of each other and slightly twisted, their atoms form a moiré pattern, or superlattice. At the so-called “magic” twist angle of 1.08°, something unusual happens: the weak van der Waals (vdW) coupling between atoms in adjacent layers modifies the atoms’ electronic states and transforms the material from a semimetal to a superconductor. The study of such twist-related electronic effects is known as “twistronics”, and it also includes phenomena such as correlated insulator states that appear at different degrees of misalignment.
Because the moiré pattern that underlies twistronics appears only at the interface between two thin sheets, it was assumed that twistronic effects could only occur in structures containing just a few layers. Although it is possible to produce a moiré pattern at a two-dimensional interface within a three-dimensional structure, it was thought that this pattern would not substantially modify the properties of the bulk material. After all, the 2D moiré region would only comprise a small fraction of the total 3D crystal volume.
New work by two research groups – one at the University of Washington in the US and Osaka University in Japan, the other at the University of Manchester in the UK – shows that this picture is not always correct. In fact, rotating a single layer of a 2D material by a small twist angle within a three-dimensional graphite film can cause the properties of the moiré interface to become inextricably mixed with those of the graphite. The result is a new class of hybrid 2D-3D moiré materials that substantially alters our understanding of how twistronics works.




 עברית (Hebrew)
עברית (Hebrew)