OpenAI team illiegaly used more than one million hours of YouTube videos, here is why.


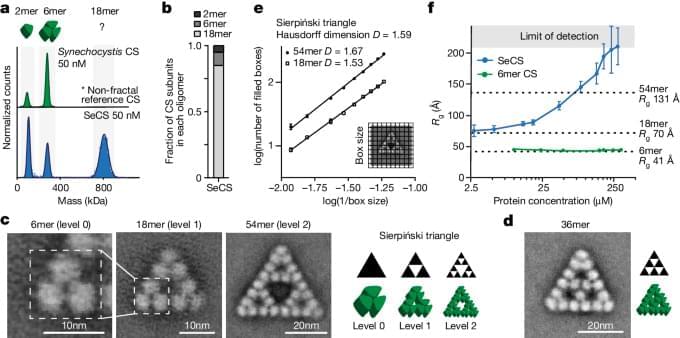
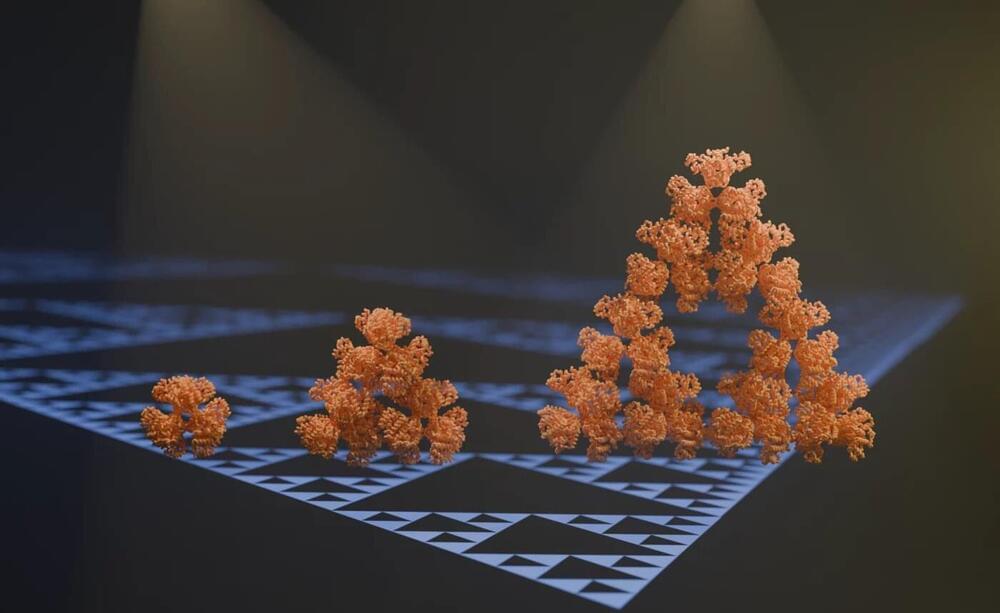
An international team of researchers led by groups from the Max Planck Institute in Marburg and Phillips University in Marburg has now discovered the first regular molecular fractal in nature. They discovered a microbial enzyme—citrate synthase from a cyanobacterium—that spontaneously assembles into a regular fractal pattern known as the Sierpiński triangle. This is an infinitely repeating series of triangles made up of smaller triangles.
“We stumbled on this structure completely by accident and almost couldn’t believe what we saw when we first took images of it using an electron microscope,” says first author Franziska Sendker.
“The protein makes these beautiful triangles and as the fractal grows, we see these larger and larger triangular voids in the middle of them, which is totally unlike any protein assembly we’ve ever seen before,” she continues.
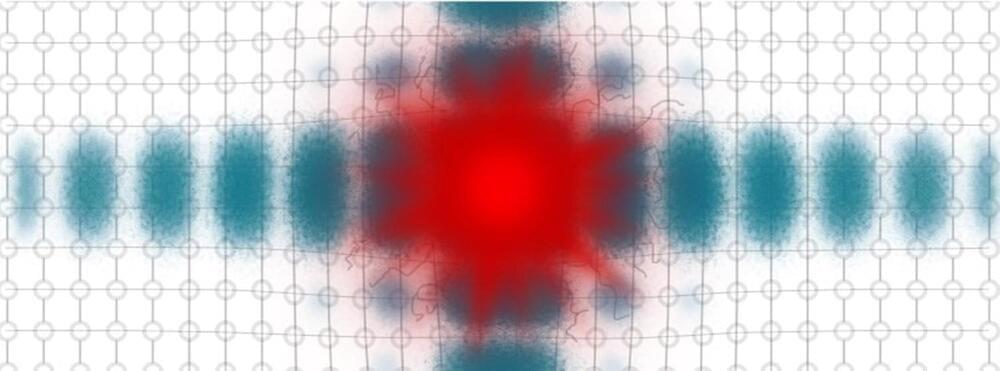
Notably, while other scientists have observed similar phenomena in their laboratory data, the mechanisms behind these observations remained elusive until now. Allan Johnson and his collaborators have elucidated the underlying processes, highlighting the formation of polarons and their ordering in specific directions as a key factor in reducing the energy penalty to the metallic phase. Driving the phase transition by exciting this disordered state of motion can be achieved with less energy.
Furthermore, the dynamic barrier lowering means that scientists are able to selectively reduce the energy required for the laser driven phase transition without increasing the probability of thermal switching, in contrast to other methods for improving the efficiency.
The results have been published in Nature Physics. The implications of this research extend beyond fundamental science, offering new avenues for precise material control and technological innovation. As the team continues to optimize the method and explore new materials, the potential for transformative advancements in material science and optical control remains high.
The use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in education has seen an increase in recent years. The rapid development of this new technology is having a major impact on education. In this edition of Edtech Mondays we will talk about the applications and benefits of AI in the education sector, the necessary implementation frameworks, the policy support and also seek to hear from the end users on the impact AI has or would have.
In physics, quintessence is a hypothetical form of dark energy, more precisely a scalar field, postulated as an explanation of the observation of an accelerating rate of expansion of the universe. The first example of this scenario was proposed by Ratra and Peebles (1988)[1] and Wetterich (1988).[2][3] The concept was expanded to more general types of time-varying dark energy, and the term “quintessence” was first introduced in a 1998 paper by Robert R. Caldwell, Rahul Dave and Paul Steinhardt.[4] It has been proposed by some physicists to be a fifth fundamental force.[5][6][7][8] Quintessence differs from the cosmological constant explanation of dark energy in that it is dynamic; that is, it changes over time, unlike the cosmological constant which, by definition, does not change. Quintessence can be either attractive or repulsive depending on the ratio of its kinetic and potential energy. Those working with this postulate believe that quintessence became repulsive about ten billion years ago, about 3.5 billion years after the Big Bang.[9]
A group of researchers argued in 2021 that observations of the Hubble tension may imply that only quintessence models with a nonzero coupling constant are viable.[10].
