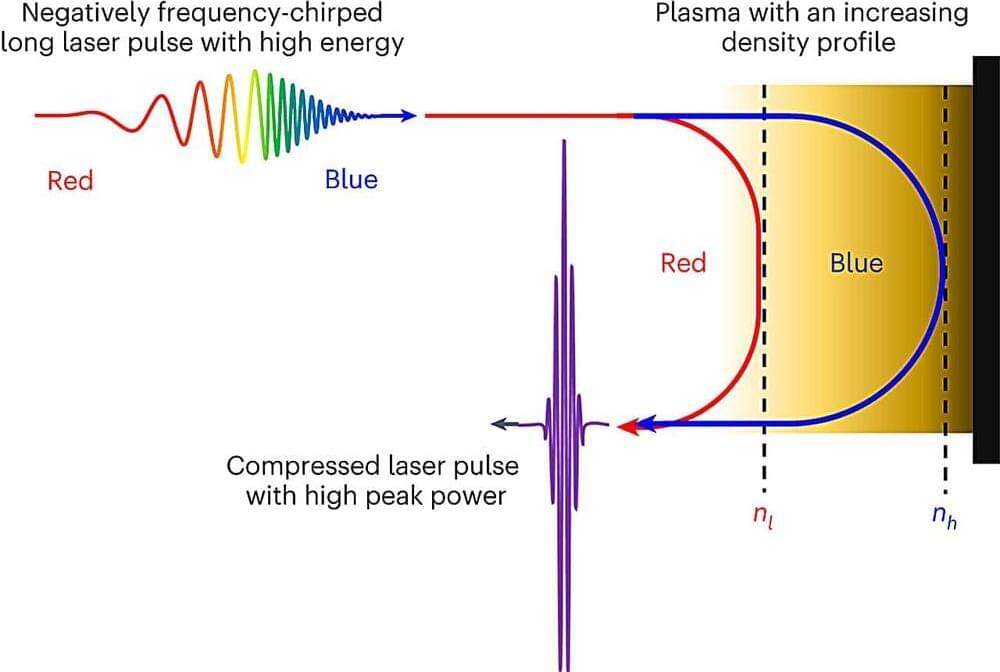
Are you ready to bring more awareness to your brand? Consider becoming a sponsor for The AI Impact Tour. Learn more about the opportunities here.
A new hallucination index developed by the research arm of San Francisco-based Galileo, which helps enterprises build, fine-tune and monitor production-grade large language model (LLM) apps, shows that OpenAI’s GPT-4 model works best and hallucinates the least when challenged with multiple tasks.
Published today, the index looked at nearly a dozen open and closed-source LLMs, including Meta’s Llama series, and assessed each of their performance at different tasks to see which LLM experiences the least hallucinations when performing different tasks.