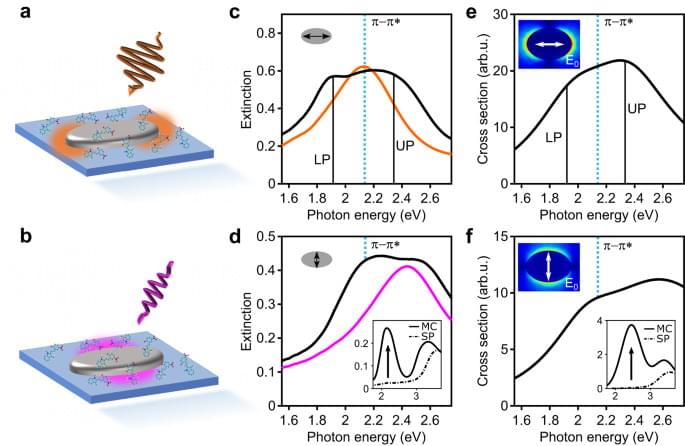
Scientists at Leipzig University, in collaboration with colleagues at Vilnius University in Lithuania, have developed a new method to measure the smallest twists and torques of molecules within milliseconds. The method makes it possible to track the gene recognition of CRISPR-Cas protein complexes, also known as “genetic scissors”, in real time and with the highest resolution. With the data obtained, the recognition process can be accurately characterised and modelled to improve the precision of the genetic scissors. The results obtained by the team led by Professor Ralf Seidel and Dominik Kauert from the Faculty of Physics and Earth Sciences have now been published in the prestigious journal Nature Structural and Molecular Biology.
When bacteria are attacked by a virus, they can defend themselves with a mechanism that fends off the genetic material introduced by the intruder. The key is CRISPR-Cas protein complexes. It is only in the last decade that their function for adaptive immunity in microorganisms has been discovered and elucidated. With the help of an embedded RNA, the CRISPR complexes recognize a short sequence in the attacker’s DNA. The mechanism of sequence recognition by RNA has since been used to selectively switch off and modify genes in any organism. This discovery revolutionized genetic engineering and was already honored in 2020 with the Nobel Prize in Chemistry awarded to Emmanuelle Charpentier and Jennifer A. Doudna.
Occasionally, however, CRISPR complexes also react to gene segments that differ slightly from the sequence specified by the RNA. This leads to undesirable side effects in medical applications. “The causes of this are not yet well understood, as the process could not be observed directly until now,” says Dominik Kauert, who worked on the project as a PhD student.