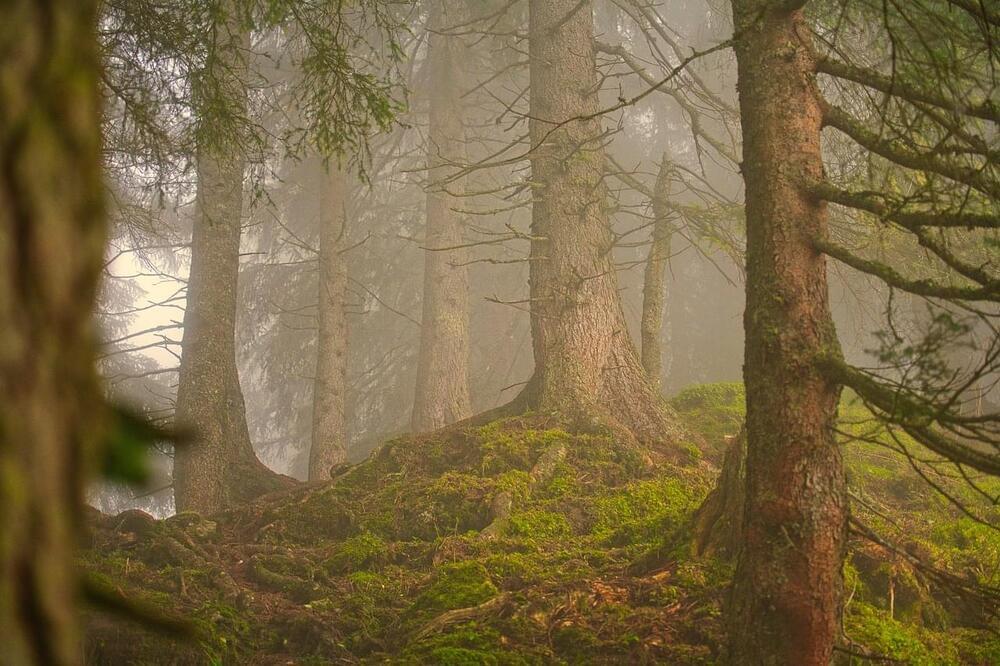
How can older trees help combat climate change? This is what a recent study published in Nature Climate Change hopes to address as an international team of researchers investigated changes in woody biomass in older trees that have been while exposed to free-air CO2 enrichment (FACE) resulting from climate change. This study holds the potential to help researchers, climate scientists, and the public better understand the steps that can be taken to decrease CO2 emissions and combat climate change worldwide.
For the study, the researchers, led by the University of Birmingham’s Institute of Forest Research (BIFoR), conducted a FACE experiment through a combination of canopy laser scanning and tree-ring analysis to examine the 180-year-old Quercus robur L. woodland in central England between 2021and 2022. The goal was ascertaining the effectiveness of older trees compared to younger trees regarding their consumption of CO2, also known as CO2 storage. In the end, the researchers found increased levels of CO2 compared to ambient conditions in 2021 and 2022, respectively, equivalent to 1.7 tons of dry matter per hectare per year.
“Our findings refute the notion that older, mature forests cannot respond to rising levels of atmospheric CO2, but how they respond will likely depend on the supply of nutrients from the soil,” said Dr. Richard Norby from the University of Birmingham, who is lead author of the study. “Evidence from BIFoR FACE of a significant increase in woody biomass production supports the role of mature, long-established, forests as natural climate solutions in the coming decades while society strives to reduce its dependency on carbon.”