In 2018, AI bested humans at following fauna, diagnosing disease, mapping the moon and more.


https://paper.li/e-1437691924#/
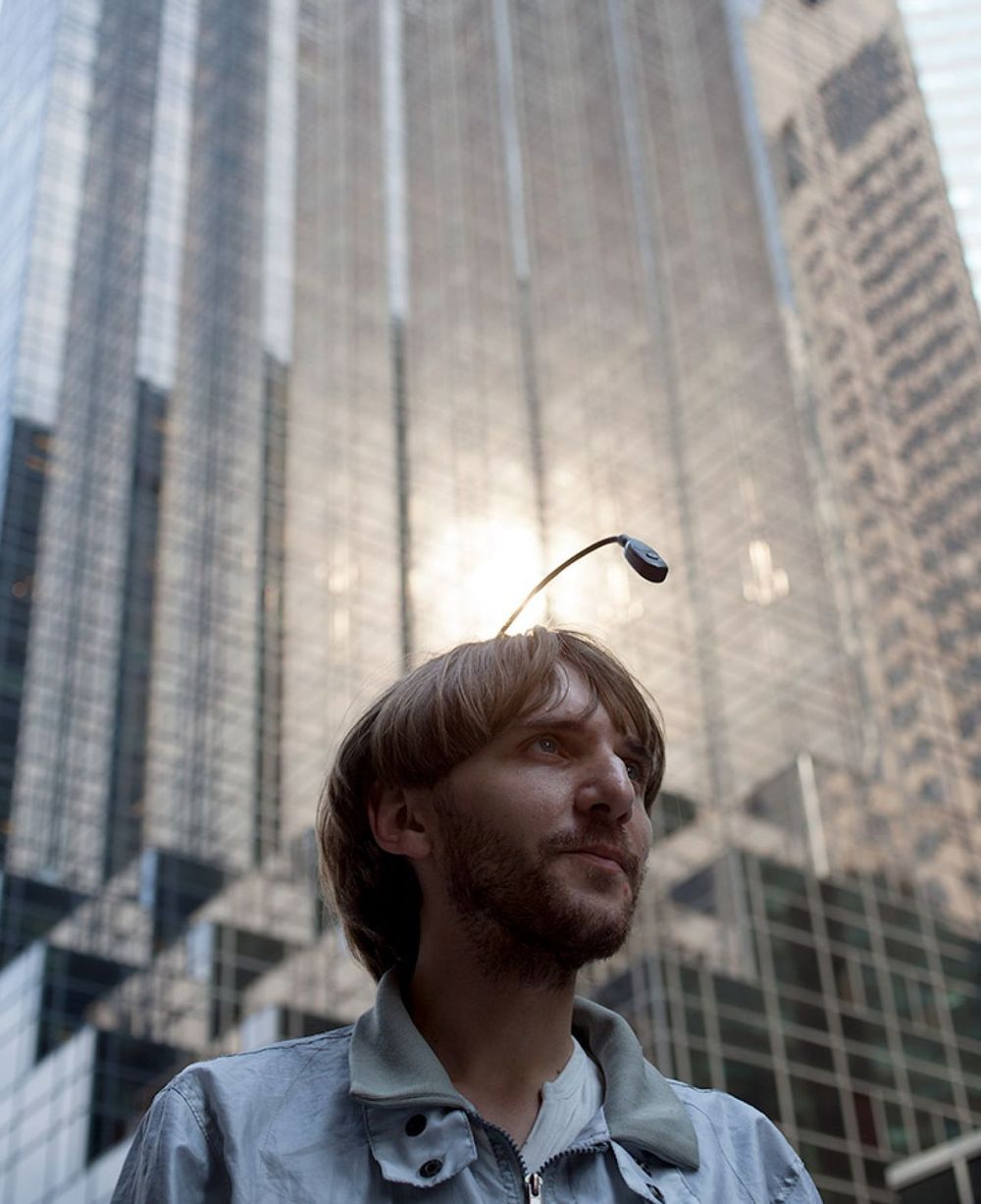
On the second balmy day of the year in New York, Neil Harbisson, a Catalan artist, musician, and self-professed “cyborg,” walked into a café in the Nolita district of Manhattan. The actor Gabriel Byrne was sitting at a table in the corner. Harbisson approached. “May I do a sound portrait of you? It will just take one minute. For nine years, I’ve been listening to colors,” he explained.
Byrne eyed his questioner from under raised eyebrows. On a slight frame, the 30-year-old Harbisson wore a white T-shirt, deep-pink jeans and black-and-white showman’s brogues. His face was angular, with an aquiline nose and a chin smudged with grown-out stubble. A small plastic oval floated in front of his forehead, attached to the end of a flexible stem that reached around from the back of his head and over a sandy pageboy mop, like the light on the head of an angler fish. This “eyeborg,” as Harbisson calls it, converts light into audible sound, with a pitch that varies according to the color of the light.
With a good-natured shrug, Byrne relented. Harbisson darted down next to his quarry, intent, but with a boyish smile that betrayed his excitement. He pointed the eyeborg first at Byrne’s ear, then his lips, then his left eye, then the bridge of his nose, and finally his salt-and-pepper hair, scribbling down musical notes on the back of a cardboard coffee-holder. Byrne gave him his agent’s email. When Harbisson got back to a computer, he would make a sound file that combined the notes from each bit of Byrne’s anatomy, and send it back to the actor. Harbisson’s collection already included Prince Charles, Nicole Kidman, and Al Gore.

Replication is nature’s greatest magic trick. Watch closely, and before your very eyes you’ll see a single cell blur into two virtually identical copies. Presto.
After more than half a century of research on molecular genetics, it would be easy to assume we’ve had this biological sleight-of-hand all figured out — but it’s not the case.
Now, by applying cutting edge technology, researchers have uncovered crucial details showing how DNA times its own replication.

This particular region is located over 66,000 light years from Earth and at on opposite side of the Milky Way, relative to our Solar System. The previous record for a parallax measurement was about 36,000 light-years, roughly 11,000 light years farther than the distance between our Solar System and the center of our galaxy. As Sanna explained, this accomplishment in radio astronomy will enable surveys that reach much farther than previous ones:
“Most of the stars and gas in our Galaxy are within this newly-measured distance from the Sun. With the VLBA, we now have the capability to measure enough distances to accurately trace the Galaxy’s spiral arms and learn their true shapes.”
Hundreds of star-forming regions exist within the Milky Way. But as Karl Menten – a member of the MPIfR and a co-author on the study – explained, this study was significant because of where this one is located. “So we have plenty of ‘mileposts’ to use for our mapping project,” he said. “But this one is special: Looking all the way through the Milky Way, past its center, way out into the other side.”


The team at Jetpack Aviation (JPA) has just completed test flights in which two pilots flew close enough together to playfully boop each other on the nose. Next step: the world’s first jetpack race series, starting in 2019, and yes, the jetboards and jet suits of the world are invited to participate!

China could emerge as the world’s biggest spender on research and development, after adjusting for the purchasing power of its currency, once countries publish their 2018 spending data in late 2019. Outlays on science in China have accelerated since 2003, although the country still trails behind the United States on measures of research quality. Over in Europe, officials will try to agree on how to disburse a proposed €100 billion (US$110 billion) through the European Union’s next research-funding programme, Horizon Europe, which begins in 2021. It’s unclear how fully UK researchers will be able to participate, as uncertainty over Brexit continues to plague the country.
Gene-editing, open access and a biosafety rethink are set to shape research.

2019 is featuring five eclipses, a rare planet transit, one of the best meteor showers and a super blood wolf moon, but the fun doesn’t stop there.
The new year will also bring three supermoons, a blue moon, multiple meteor showers, close approach by the moon and Jupiter and several rocket launches.
Although we would love to talk about all of the extraordinary occurrences, these are our top events to watch for in the sky in 2019: