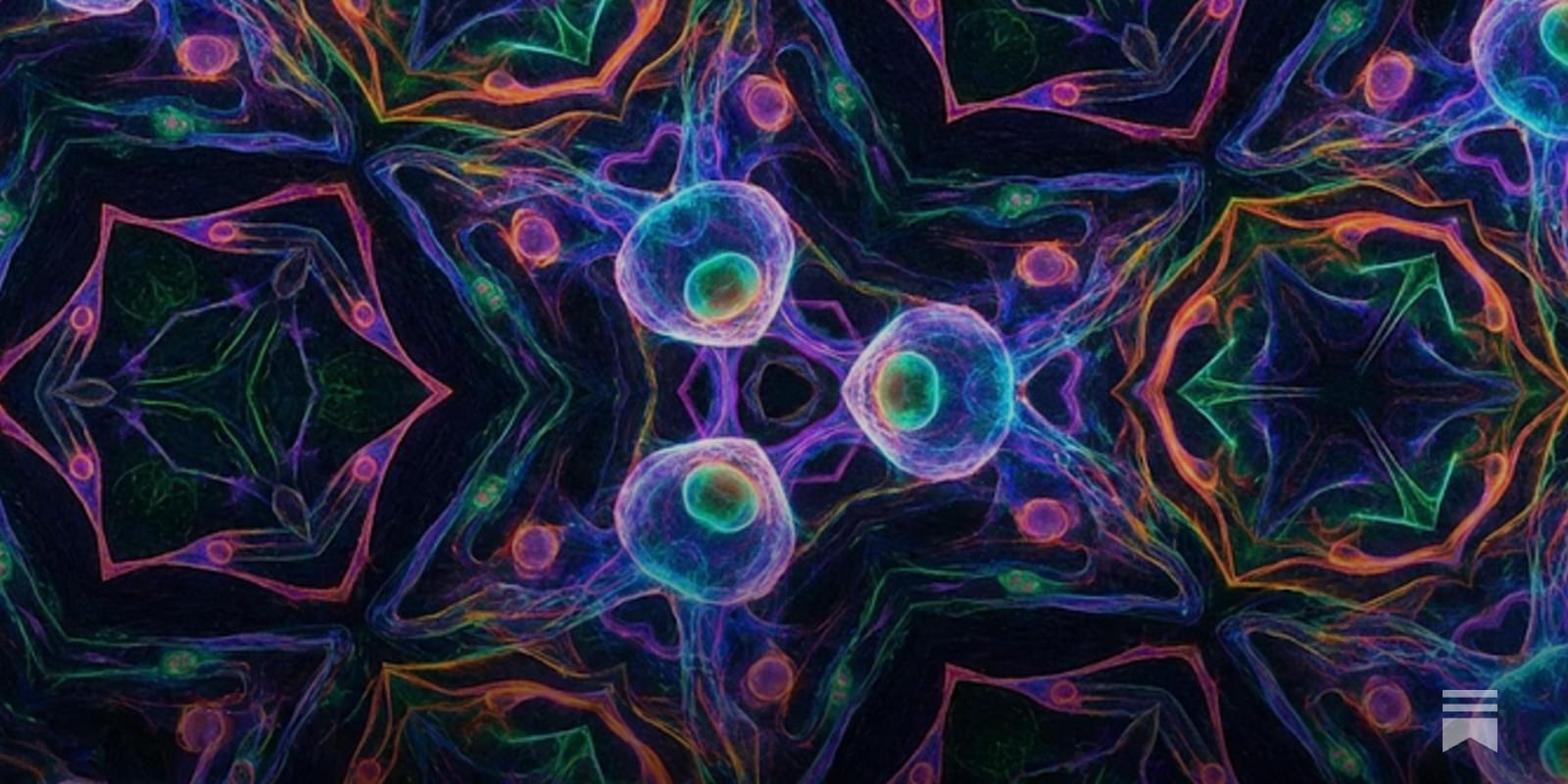
This study shows that non-invasive ultrasound to the human nucleus accumbens can modulate deep brain activity and enhance reward-guided learning, offering a potential alternative to invasive neuromodulation therapies.

In 1885, Michelson began a collaboration with Edward Morley, spending considerable time and money to confirm with higher accuracy Fizeau’s 1851 experiment on Fresnel’s drag coefficient, [ 5 ] to improve on Michelson’s 1881 experiment, [ 1 ] and to establish the wavelength of light as a standard of length. [ 6 ] [ 7 ] John Brashear made the high-quality optics for the Interferometer in his Allegheny-Observatory-affiliated shop. At this time Michelson was professor of physics at the Case School of Applied Science, and Morley was professor of chemistry at Western Reserve University (WRU), which shared a campus with the Case School on the eastern edge of Cleveland. Michelson suffered a mental health crisis in September 1885, from which he recovered by October 1885. Morley ascribed this breakdown to the intense work of Michelson during the preparation of the experiments. In 1886, Michelson and Morley successfully confirmed Fresnel’s drag coefficient—this result was also considered as a confirmation of the stationary aether concept. [ A 2 ]
This result strengthened their hope of finding the aether wind. Michelson and Morley created an improved version of the Michelson experiment with more than enough accuracy to detect this hypothetical effect. The experiment was performed in several periods of concentrated observations between April and July 1887, in the basement of Adelbert Dormitory of WRU (later renamed Pierce Hall, demolished in 1962). [ A 11 ] [ A 12 ]
As shown in the diagram to the right, the light was repeatedly reflected back and forth along the arms of the interferometer, increasing the path length to 11 m (36 ft). At this length, the drift would be about 0.4 fringes. To make that easily detectable, the apparatus was assembled in a closed room in the basement of the heavy stone dormitory, eliminating most thermal and vibrational effects. Vibrations were further reduced by building the apparatus on top of a large block of sandstone (Fig. 1), about a foot thick and five feet (1.5 m) square, which was then floated in a circular trough of mercury. They estimated that effects of about 0.01 fringe would be detectable.
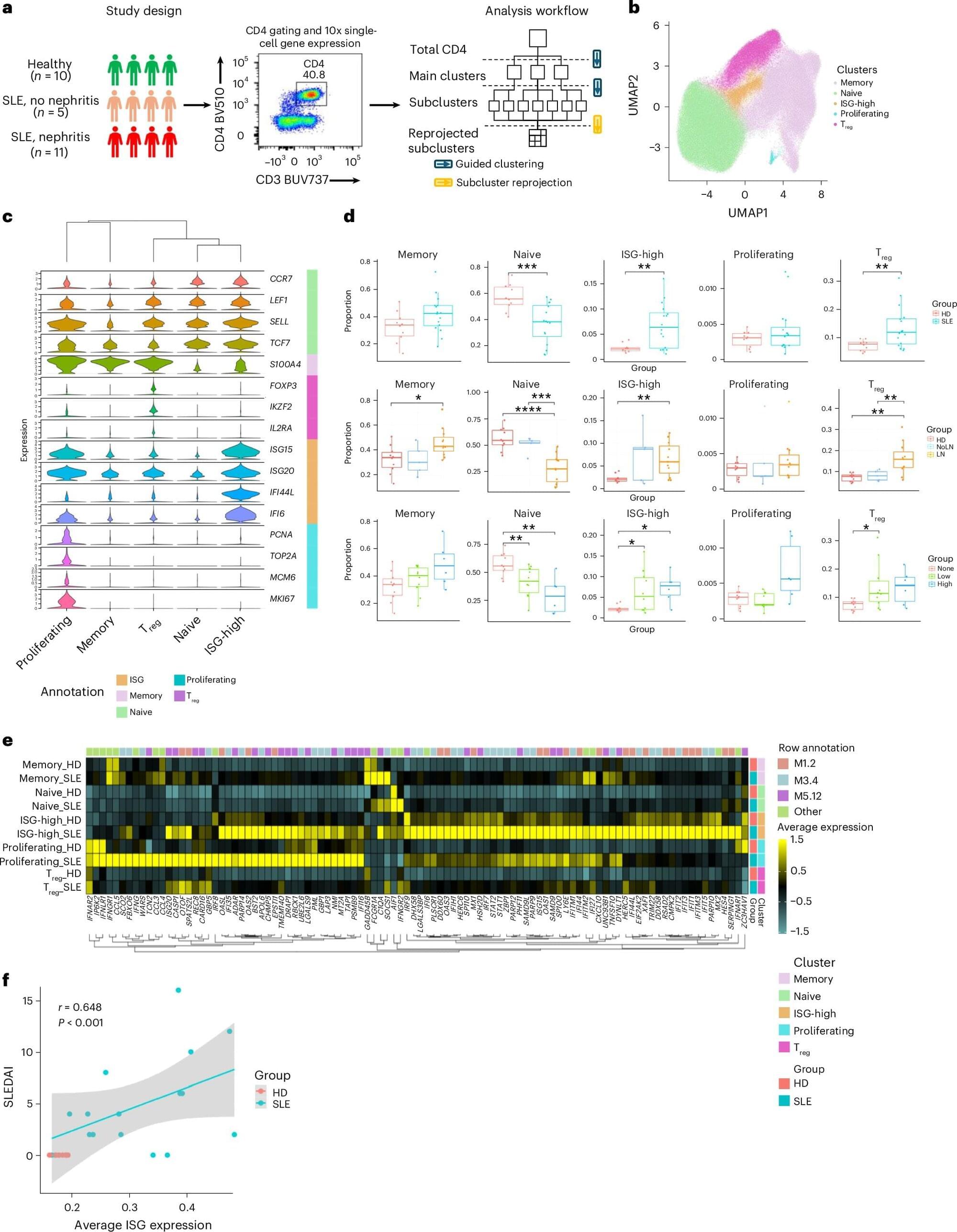
Detailed mapping of CD4⁺ T cells from children with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) has revealed distinct immune cell subsets with likely roles in disease pathogenesis, according to a study led by Weill Cornell Medicine investigators. The findings are poised to redirect lupus research and open the door to more precise therapies that avoid broad immune suppression.
Published in Nature Immunology, the study used single-cell RNA sequencing to profile CD4⁺ T-cell subtypes from children with SLE and healthy controls. Although CD4⁺ T cells have long been implicated in lupus, their full diversity and the identity of disease-driving subsets had not been fully defined. The authors note that the results likely apply not only to pediatric lupus but also to adult disease.
“Modulation of a particular CD4⁺ T-cell subset called Th10 might be a good strategy for treating patients with lupus, and we are following up with that goal in mind,” said study co–senior author Dr. Virginia Pascual, the Ronay Menschel Professor of Pediatrics and Gale and Ira Drukier Director of Children’s Health Research at Weill Cornell Medicine.

Their findings have been published in the journal Advanced Functional Materials in an article titled “Long-Lasting Moisture Energy Scavenging in Dry Ambient Air Empowered by a Salt Concentration-Gradient Cationic Hydrogel.”
How the new MEG technology works These moisture-activated generators (or MEGs) work by creating a flow of ions—charged particles—inside a special gel, generating power naturally. But current versions face challenges: they don’t last long (less than 16 hours), have high internal resistance, and only work well in very humid conditions.
Professor Shin and his team have overcome those hurdles. They developed a salt-concentration-gradient cationic hydrogel for MEG, promising lower energy loss and higher output even in conditions of low relative humidity.
Key findings from the study include:
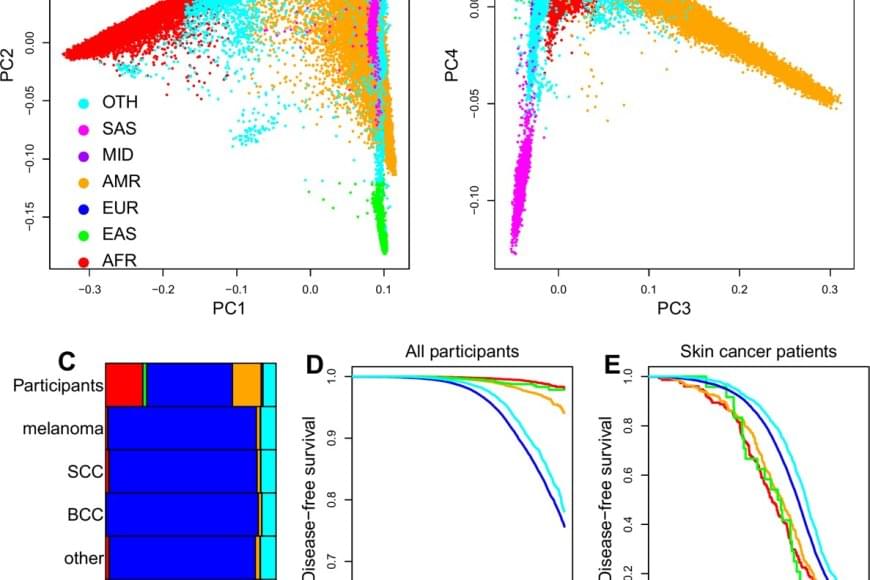
Researchers have developed a new approach for identifying individuals with skin cancer that combines genetic ancestry, lifestyle and social determinants of health using a machine learning model. Their model, more accurate than existing approaches, also helped the researchers better characterize disparities in skin cancer risk and outcomes.
Skin cancer is among the most common cancers in the United States, with more than 9,500 new cases diagnosed every day and approximately two deaths from skin cancer occurring every hour. One important component of reducing the burden of skin cancer is risk prediction, which utilizes technology and patient information to help doctors decide which individuals should be prioritized for cancer screening.
Traditional risk prediction tools, such as risk calculators based on family history, skin type and sun exposure, have historically performed best in people of European ancestry because they are more represented in the data used to develop these models. This leaves significant gaps in early detection for other populations, particularly those with darker skin, who are less likely to be of European ancestry. As a result, skin cancer in people of non-European ancestry is frequently diagnosed at later stages when it is more difficult to treat. As a consequence of later stage detection, people of non-European ancestry also tend to have worse overall outcomes from skin cancer.
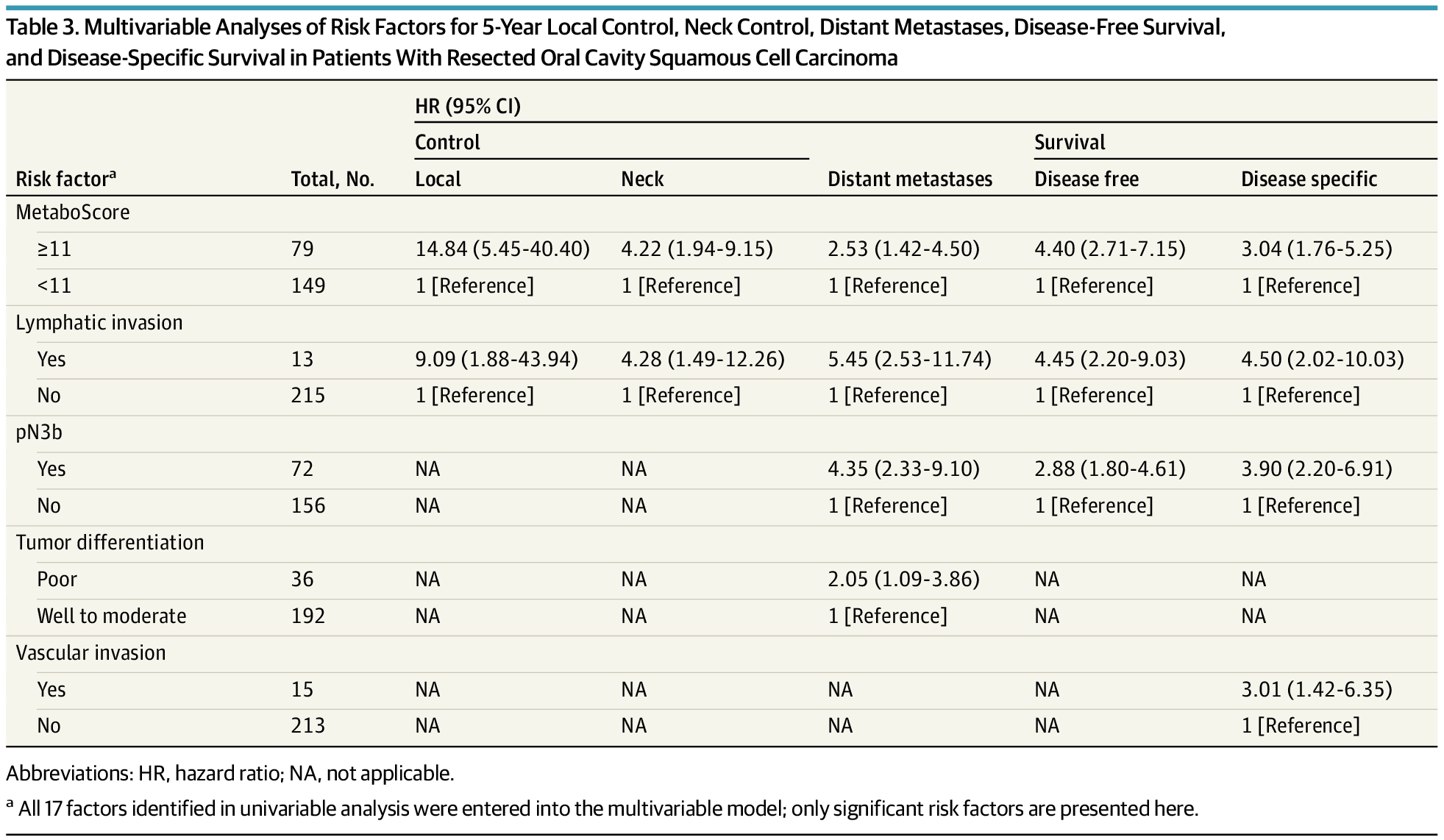
A cohort study developed and validated a serum metabolite-based prognostic scoring system (MetaboScore) to predict recurrence risk in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma (OCSCC) among patients with resected, advanced-stage disease and high betel quid exposure.
The MetaboScore, comprising 19 metabolites, was independently associated with increased risk of local, regional, and distant recurrence, as well as lower disease-free and disease-specific survival, beyond conventional staging.
Importance Improved methods are needed to predict recurrence in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma (OCSCC). However, to date, no metabolome studies have fully explored the prediction of OCSCC relapse patterns and survival.
Objective To identify serum metabolites associated with OCSCC recurrence and develop and validate a prognostic scoring system.
Design, Setting, and Participants This retrospective cohort study was conducted at a single tertiary academic center and enrolled patients with histologically confirmed, surgically resected first primary advanced-stage OCSCC from betel quid–chewing areas. Patients underwent primary surgery between February 2007 and May 2018, with follow-up data systematically collected through a prospectively maintained institutional registry. Data were analyzed from December 2024 to September 2025.