The treatment was unusual in that alongside talk therapy, May underwent several sessions in a sensory-deprivation chamber: a dark, soundproof room where she floated in a shallow pool of water heated to match the temperature of her skin and saturated with Epsom salts to make her more buoyant. The goal was to blunt May’s external senses, enabling her to feel from within—focusing on the steady thudding of her heart, the gentle flow of air in and out of her lungs, and other internal bodily signals.
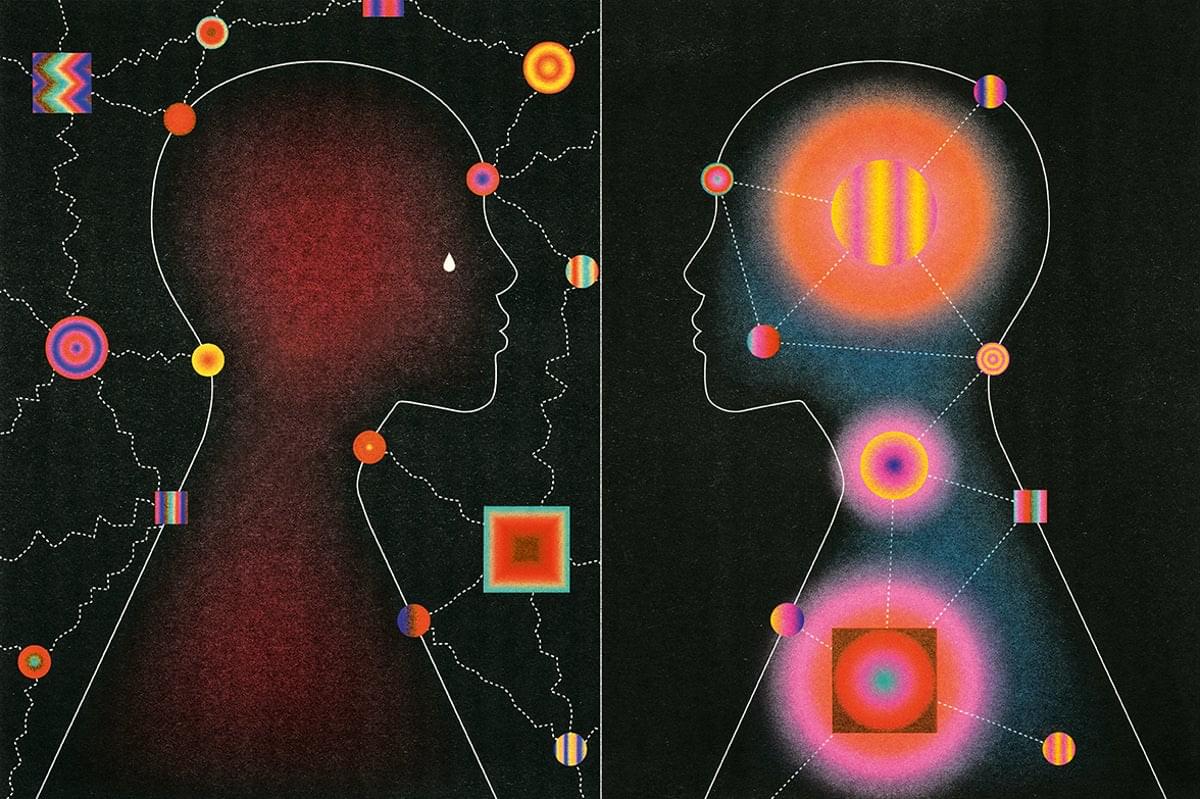
The ability to connect with the body’s inner signals is called interoception. Some people are better at it than others, and one’s aptitude for it may change. Life events can also bolster or damage a person’s interoceptive skills. Sahib Khalsa, a psychiatrist and neuroscientist at the University of California, Los Angeles, and his colleagues think a disrupted interoception system might be one of the driving forces behind anorexia nervosa. So they decided to repurpose a decades-old therapy called flotation-REST (for “reduced environmental stimulation therapy”) and launched a trial with it in 2018. They. hypothesized that in people with anorexia and some other disorders, an underreliance on internal signals may lead to an overreliance on external ones, such as how one looks in the mirror, that ultimately causes distorted body image, one of the key factors underlying these conditions. “When they’re in the float environment, they experience internal signals more strongly,” Khalsa says. “And having that experience may then confer a different understanding of the brain-body relationship that they have.”
Disruptions in interoception may underlie anxiety, eating disorders, and other mental health ailments.
By Diana Kwon edited by Jeanna Bryner.