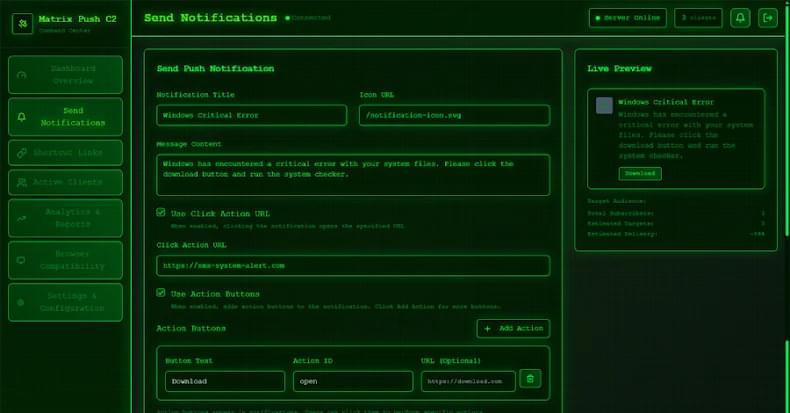
That’s not all. Since the attack plays out via the web browser, it’s also a cross-platform threat. This essentially turns any browser application on any platform that subscribes to the malicious notifications to be enlisted to the pool of clients, giving adversaries a persistent communication channel.
Matrix Push C2 is offered as a malware-as-a-service (MaaS) kit to other threat actors. It’s sold directly through crimeware channels, typically via Telegram and cybercrime forums, under a tiered subscription model: about $150 for one month, $405 for three months, $765 for six months, and $1,500 for a full year.
“Payments are accepted in cryptocurrency, and buyers communicate directly with the operator for access,” Dr. Darren Williams, founder and CEO of BlackFog, told The Hacker News. “Matrix Push was first observed at the beginning of October and has been active since then. There’s no evidence of older versions, earlier branding, or long-standing infrastructure. Everything indicates this is a newly launched kit.”