Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.

Scientists are questioning the idea that the human lifespan has a limit
(Al Bello/Getty Images)
Jeanne Calment, the French woman who holds the record for the longest verified lifespan, died in 1997 at 122 years old.
Few people, of course, ever become supercentenarians — 110 years old or older — and even fewer hit 115.


Treating Diabetes
A new approach to treating diabetes sees gene therapy altering other cells in the pancreas so they produce insulin to replace the beta cells that are attacked by the immune system.
Progress has been made towards a potential solution to type 1 diabetes. The novel approach seeks to cure type 1 diabetes and to allow type 2 diabetics to stop using insulin shots by altering other cells in the pancreas so they produce insulin.
The research team based at UT Health San Antonio have found a way to increase the types of pancreatic cells that secrete insulin. The team are now moving towards starting clinical trials in the next three year but they are first testing the approach in larger sized animals, these studies are believed to cost an estimated $5 million.
These studies will pave the way for an application to the FDA for Investigational New Drug (IND) approval which will hopefully see the new therapy moving into clinical trials and ultimately to the people who need it.

Rejuvenation is good for your loved ones
An article discussing the benefits of rejuvenation for your friends and family.
Rejuvenation biotechnologies would bring significant benefits to individuals, but these benefits would indirectly extend to their families and friends too. The ways they can benefit from the rejuvenation of others might be not so obvious, so let’s have a look at them together.
Nearly everyone knows how terrible it is to lose people dear to you. Maybe your grandparents died when you were a child, and that might have been your first encounter with death, at an age when you still couldn’t properly comprehend it. Maybe it happened suddenly, or maybe your grandparents have suffered for long before passing away. Eventually, the moment comes when you start thinking that the same fate awaits your parents, your siblings, your friends. Rejuvenation would spare you seeing your elderly relatives and friends wilt away, suffer and die, because none of that would happen to them. Of course, rejuvenation would spare this pain to your friends and relatives too. Your children and grandchildren would never have to see you become sicker and sicker as you age, and would never—in principle—have to bury you. Today, being 80 means you often have to attend the funeral of a dear friend who passed away. People who have been important parts of your life just keep dying.

Synergy Between Torah and Science: How Far is TOO Far?
This is one of the first articles I’ve seen specifically on #Judiasm and #transhumaism, with input by rabbis. Naturally the article is cautious, but interesting too.
Transhumanism, an intellectual and cultural movement supporting the use of science and technology to improve human mental and physical characteristics and capacities, a concept once limited to the realm of science-fiction, is now becoming more of a reality than ever before. The once outlier philosophy is quickly becoming mainstream, an accepted part of the social conscience that is the new religion for the anti-religious, including its own Messianic vision.
There are many aspects to the transhumanism philosophy, often abbreviated as H+ or h+, including physical longevity through medical breakthroughs and/or merging mankind with machines. Many transhumanists advocate transferring the sum total of a person’s knowledge and experiences into a computer and recreating the individual as a form of artificial intelligence ( AI ) in order to extend an individual’s life.
In its most extreme form, transhumanism advocates limiting human population. This extreme philosophy is criticized for being eugenicist master-race ideology and infringing on basic reproductive rights.
Rabbi Avraham Arieh Trugman, director of Ohr Chadash Torah Institute, noted that as in any social reform, the driving intention behind the movement is the key element, the factor that decides whether it will be a positive or negative influence on human history.

Revita Life Sciences Continues to Advance Multi-Modality Protocol in Attempt to Revive Brain Dead Subjects
Rudrapur, Uttrakhand, India — July 02, 2017
Revita Life Sciences, (http://revitalife.co.in) a biotechnology company focused on translational regenerative therapeutic applications, has announced that it is continuing to advance their novel, multi-modality clinical intervention in the state of brain death in humans.
“We have proactively continued to advance our multi-modality protocol, as an extended treatment before extubation, in an attempt to reverse the state of brain death” said Mr.Pranjal Agrawal, CEO Revita Life Sciences. “This treatment approach has yielded some very encouraging initial outcome signs, ranging from minor observations on blood pressure changes with response to painful stimuli, to eye opening and finger movements, with corresponding transient to permanent reversal changes in EEG patterns.”
This first exploratory study, entitled “Non-randomized, Open-labelled, Interventional, Single Group, and Proof of Concept Study with Multi-modality Approach in Cases of Brain Death Due to Traumatic Brain Injury Having Diffuse Axonal Injury” is ongoing at Anupam Hospital, Rudrapur, Uttrakhand. The intervention primarily involves intrathecal administration of minimal manipulated (processed at point of care) autologous stem cells derived from patient’s fat and bone marrow twice a week.
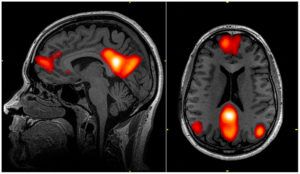
This study was inappropriately removed from the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) database. ICMR has no regulatory oversight on such research in India.
The Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO), Drug Controller General of India, had no objection to the program progressing. Regulatory approval as needed for new drugs, is currently not required when research is conducted on the recently deceased, although IRB and family consent is definitely required. CDSCO, the regulator of such studies, clearly states that “no regulatory requirements are needed for any study with minimal manipulated autologous stem cells in brain death subjects”.
Death is defined as the termination of all biological functions that sustain a living organism. Brain death, the complete and irreversible loss of brain function (including involuntary activity necessary to sustain life) as defined in the 1968 report of the Ad Hoc Committee of the Harvard Medical School, is the legal definition of human death in most countries around the world. Either directly through trauma, or indirectly through secondary disease indications, brain death is the final pathological state that over 60 million people globally transfer through each year.
“We are in process of publishing our initial retrospective results, as well ongoing early results, in a peer reviewed journal. These initial findings will prove invaluable to the future evolution of the program, as well as in progressing the development multi-modality regenerative therapeutics for the full range of the severe disorders of consciousness, including coma, PVS, the minimally conscious state, and a range of other degenerative CNS conditions in humans,” said Dr. Himanshu Bansal, Chief Scientific Officer, Revita Life Sciences and Director of Mother Cell.
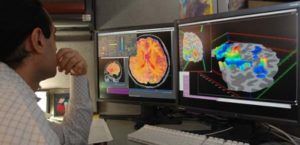
With the maturation of the tools of medical science in the 21st century, especially cell therapies and regenerative medicines, tissues once considered irretrievable, may finally be able to be revived or rejuvenated. Hence many scientists believe that brain death, as presently defined, may one day be reversed. While the very long term goal is to find a solution for “re-infusing life”, the short term purpose of these types of studies is much less dramatic, which is to confirm if the current definition of brain irreversibility still holds true. There have been many anecdotal reports of brain death reversal across the world over the past decades in the scientific literature. Studies of this nature serve to verify and establish this very fact in a scientific and controlled manner. It will also one day give a fair chance to individuals, who are declared brain dead, especially after trauma.
About Revita Life Sciences
Revita Life Sciences is a biotechnology company focused on the development of stem cell therapies and regenerative medicine interventions that target areas of significant unmet medical need. Revita is led by Dr. Himanshu Bansal MD, who has spent over two decades developing novel MRI based classifications of spinal cord injuries as well as comprehensive treatment protocols with autologous tissues including bone marrow stem cells, Dural nerve grafts, nasal olfactory tissues, and omental transposition.
Apocalypse, now? The 10 biggest threats facing civilisation, from asteroids to tyrannical leaders
The team, made up of highly educated academics, lawyers, scholars and philosophers, form the Centre for the Study of Existential Risk (CSER, commonly referred to as “caesar”) and the Leverhulme Centre for the Future of Intelligence. At times of global threat, the experts meet to assess the biggest threats facing Earth and what can be done to save civilisation from the impending apocalypse.

Carbon nanotube reinforce Composites can reduce space vehicle mass
NASA’s Space Technology Mission Directorate (STMD) is keenly interested in nanotechnology – an approach that can reduce the mass and improve the performance of aerospace systems. NASA computer modeling analysis has shown that composites using carbon nanotube reinforcements could lead to a 30 percent reduction in the total mass of a launch vehicle.
“No single technology would have that much of an impact to reduce the mass of a launch vehicle by that much,” explains Michael Meador, Program Element Manager for Lightweight Materials and Manufacturing at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland, Ohio.
Tensile properties of a carbon nanotube fiber-based composite tank were tested in a May 16 test flight.