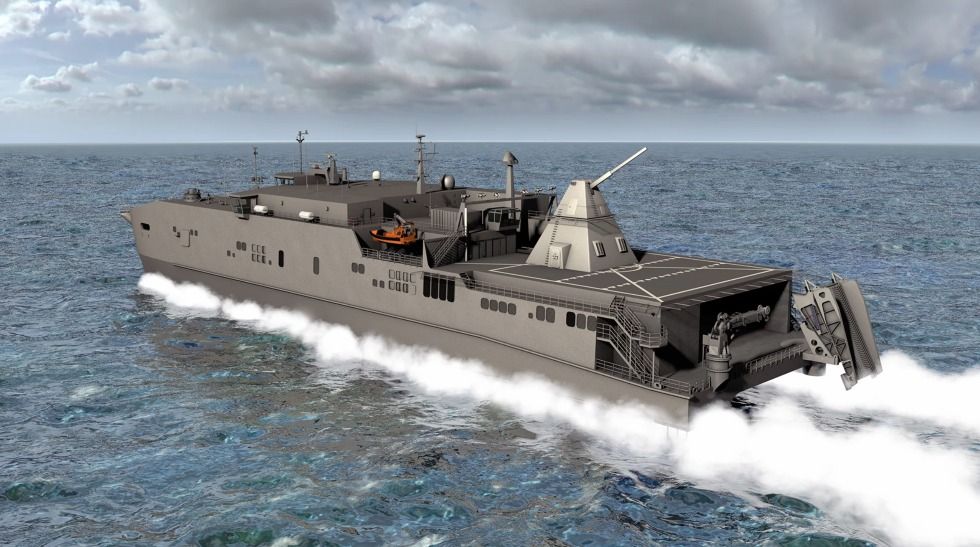
A powerful “mass driver” could launch moon-mined ore into space.



Today, we wish to highlight a new open access publication in which the researchers take a novel approach to the regeneration of the thymus, a small but vitally important organ that is key to our immune system.
The thymus shrinks as we age
The thymus is one of the most important organs in the body, and it is where thymocytes produced in the bone marrow travel to become new T cells before being trained in the lymph nodes to become the defenders of the adaptive immune system. However, as we get older, the thymus increasingly turns to fat and starts to shrink, causing its ability to produce new T cells to fall dramatically. This process is known as thymic involution and actually begins shortly after puberty, so this is one aspect of aging that begins fairly early in life, although it is many decades later before its decline causes serious health issues.


Chinese scientists have found a major lithium deposit in Southwest China’s Yunnan Province, estimated to contain more than 5 million tons.
There are approximately 40 million tons of proven lithium reserves in the world, the Xinhua News Agency’s Globe magazine reported.
A team led by research fellow Wen Hanjie from the Institute of Geochemistry under the Chinese Academy of Sciences found 340,000 tons of lithium oxide in a test site in central Yunnan.
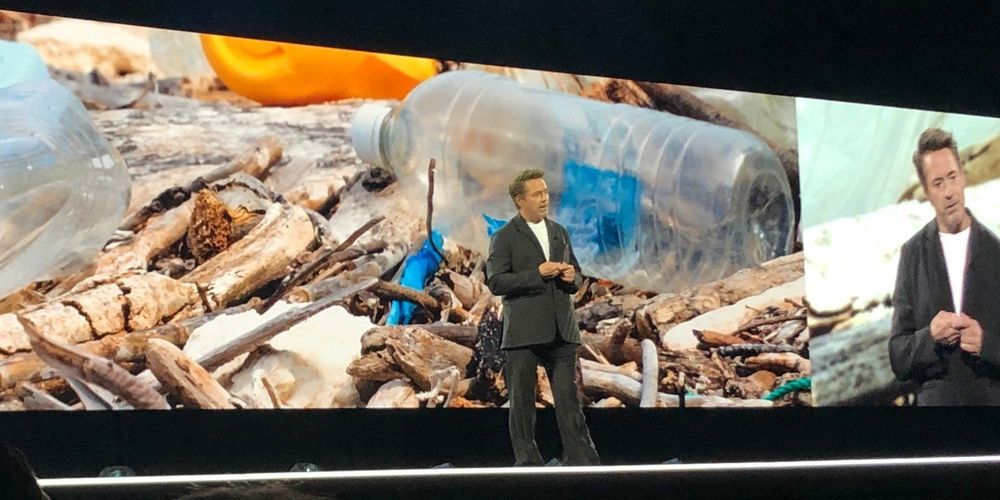

Robert Downey Jr. doesn’t pretend to be a brilliant scientist — even though he’s played Tony Stark, aka Iron Man, for the past 11 years.
But on Tuesday night he attended Amazon’s brand new, premier, open-to-the-public Machine Learning, Automation, Robotics and Space (re: MARS) conference in Las Vegas — a room filled with AI legends, astronauts, and other dignitaries — as a keynote speaker.
He delivered a gag-filled talk that somehow weaved together the history of the Marvel Cinematic Universe, the evolution of Stark’s Iron Man suits, allusions to his own troubled history with drug addiction, the actual history of artificial intelligence and its pioneers, with a bunch of jokes using the Amazon Alexa voice and Matt Damon (including a videotaped guest appearance by Damon).

Researchers, from biochemists to material scientists, have long relied on the rich variety of organic molecules to solve pressing challenges. Some molecules may be useful in treating diseases, others for lighting our digital displays, still others for pigments, paints, and plastics. The unique properties of each molecule are determined by its structure—that is, by the connectivity of its constituent atoms. Once a promising structure is identified, there remains the difficult task of making the targeted molecule through a sequence of chemical reactions. But which ones?
Organic chemists generally work backwards from the target molecule to the starting materials using a process called retrosynthetic analysis. During this process, the chemist faces a series of complex and inter-related decisions. For instance, of the tens of thousands of different chemical reactions, which one should you choose to create the target molecule? Once that decision is made, you may find yourself with multiple reactant molecules needed for the reaction. If these molecules are not available to purchase, then how do you select the appropriate reactions to produce them? Intelligently choosing what to do at each step of this process is critical in navigating the huge number of possible paths.
Researchers at Columbia Engineering have developed a new technique based on reinforcement learning that trains a neural network model to correctly select the “best” reaction at each step of the retrosynthetic process. This form of AI provides a framework for researchers to design chemical syntheses that optimize user specified objectives such synthesis cost, safety, and sustainability. The new approach, published May 31 by ACS Central Science, is more successful (by ~60%) than existing strategies for solving this challenging search problem.