To help put the first generation of space colonists on the right footing, Purdue University’s Resilient ExtraTerrestrial Habitats (RETH) Institute is building a one-quarter-scale space habitat similar to ones that may one day be built on the Moon and Mars. It is hoped habitats boasting a combination of “resilience, intelligence, and autonomy” will stand up to the many hazards space can throw at them.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
The World’s First Flying Car Skyport Is Under Construction in Miami
Future residents of Paramount Miami World Center, a 600-unit condominium building now under construction, may be the first in the world with a private skyport for their use, television station WSVN reports.
Infrastructure matters. Flying cars will never, um, get off the ground if they don’t have places to land. Helicopter landing pads and heliports are apparent answers to the question of where to touch down. However, landing spots or sky ports built specifically for flying cars could offer convenience and amenities specifically applicable for or adapted to flying cars.
“Ever since ‘The Jetsons’ came out, America’s been talking about flying cars,” Daniel Kodsi, Paramount Miami World Center’s CEO and developer, said in a statement. “It’s something that inspires you, something that you think about when you’re building a project. You’re saying, ‘Well, what is the future? What’s going to happen in the future?’”

An Interview with Jose Cordeiro
Jose Cordeiro is promoting the development of rejuvenation biotechnologies in Spain and the integration of Latin American immigrants into Spain’s aging society to maintain the country’s productivity. He was at the recent Undoing aging conference in Berlin and gave us an interview about his political goals.
At Undoing Aging 2019, jointly organized by SENS Research Foundation and Forever Healthy Foundation, there was a session focused on the ways to make healthy life extension and medical progress a greater part of the global agenda. Among the speakers there was Jose Cordeiro, the vice chair of Humanity Plus, director of The Millennium Project, fellow of the World Academy of Art and Science, and board member of the Lifeboat Foundation.
Jose earned his Bachelor’s and Master’s degrees in Mechanical Engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in Cambridge, Massachusetts. His thesis was focused on the modeling of the International Space Station. Jose has also studied International Economics and Comparative Politics at Georgetown University in Washington, D.C., and received his MBA in France at INSEAD, where he focused on Finance and Globalization.
Last year, Jose decided to begin his political activities in order to foster the development of rejuvenation biotechnologies in Spain and to work on the integration of Latin American immigrants into Spain’s aging society and thus maintain the country’s productivity. He kindly agreed to give me an interview to discuss more about his ambitious initiative.

Subscribe To Our Emails
May 17–20, 2021 Detroit Michigan. Automation is helping companies in every industry become stronger global competitors. To succeed, you need the right solution providers, the right technology, and the right expertise. Automate 2019 will provide it all and more!
This biennial show held in Detroit, Michigan is North America’s largest showcase of robot, machine vision, motion control and other automation technologies.

Hahn showcases ‘broad spectrum’ of automation solutions at Automate
Hahn says it is showcasing a “broad spectrum” of automation solutions which can help manufacturers around the world to automate more than ever before.
At the ongoing Automate Show, in Chicago April 8–11, 2019, experts of the Hahn Group are giving insights about industrial automation and robot solutions at booth #7372.
Hahn Automation, Rethink Robotics, and Walther Systemtechnik will be present at the show.

SpaceFund Venture Capital
SpaceFund is a new type of venture capital firm, providing near-term liquidity through security tokens and informed investing in a diversified portfolio of space companies.
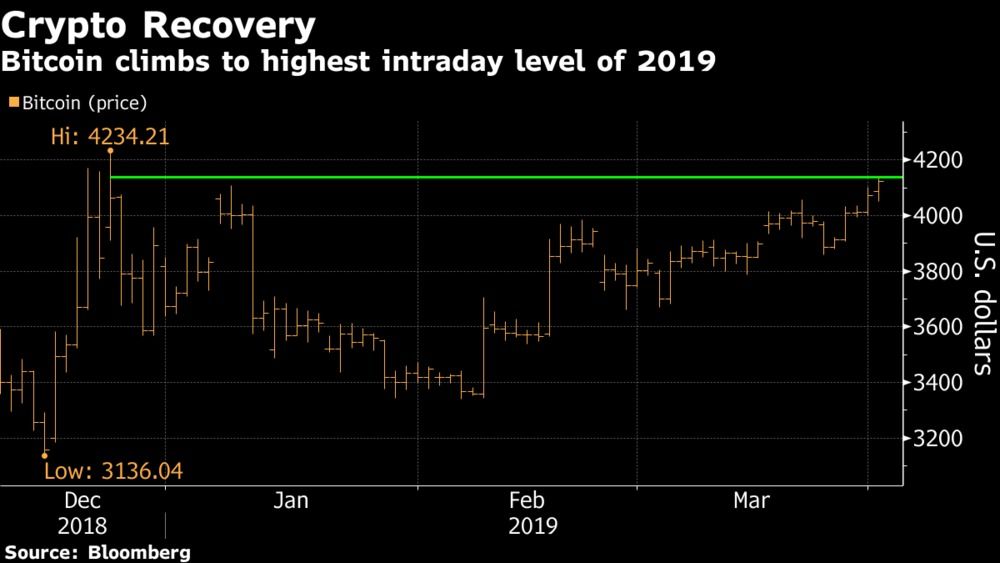
Bitcoin Climbs to Highest This Year as Volatility Recedes
Bitcoin advanced to the highest level of 2019, the latest milestone for cryptocurrencies as they claw back from a year that saw three-quarters of their market value wiped out.
The biggest digital coin on Monday rose as much as 1.6 percent to $4,135.60, the top intraday level since Dec. 24, according to weekday trading data compiled by Bloomberg. So-called alternative coins rallied more, with Dash jumping as much as 31 percent and Monero increasing as much as 10 percent.
Bitcoin is close to breaking above an intraday level set on Christmas Eve. That day marked the end of a U.S. stocks selloff, after which the S&P 500 Index started a rally that continued through March and reversed most of the fourth-quarter rout.
Will Artificial Intelligence Enhance or Hack Humanity?
THIS WEEK, I interviewed Yuval Noah Harari, the author of three best-selling books about the history and future of our species, and Fei-Fei Li, one of the pioneers in the field of artificial intelligence. The event was hosted by the Stanford Center for Ethics and Society, the Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence, and the Stanford Humanities Center. A transcript of the event follows, and a video is posted below.
Historian Yuval Noah Harari and computer scientist Fei-Fei Li discuss the promise and perils of the transformative technology with WIRED editor in chief Nicholas Thompson.
Cold Plasma Torch Produces a Cleansing Flame that Never Consumes
It’s basically a lightsaber. Except smaller. And with an invisible blade. And cold to the touch. But other than that, this homebrew cold plasma torch (YouTube, embedded below) is just like the Jedi’s choice in elegant weaponry.
Perhaps we shouldn’t kid [Justin] given how hard he worked on this project – seventeen prototypes before hitting on the version seen in the video below – but he himself notes the underwhelming appearance of the torch without the benefit of long-exposure photography. That doesn’t detract from how cool this build is, pun intended. As [Justin] explains, cold plasma or non-equilibrium plasma is an ionized stream of gas where the electron temperature is much hotter than the temperature of the heavier, more thermally conductive species in the stream. It’s pretty common stuff, seen commercially in everything from mercury vapor lamps to microbial sterilization.
It’s the latter use that piqued [Justin]’s interest and resulted in a solid year of prototyping before dialing in a design using a flyback transformer to delivery the high voltage to a stream of argon flowing inside a capillary tube. The quartz tube acts as a dielectric that keeps electrons from escaping and allows argon to be ionized and wafted gently from the tube before it can reach thermal equilibrium. The result is a faint blue glowing flame that’s barely above room temperature but still has all the reactive properties of a plasma. The video shows all the details of construction and shows the torch in action.