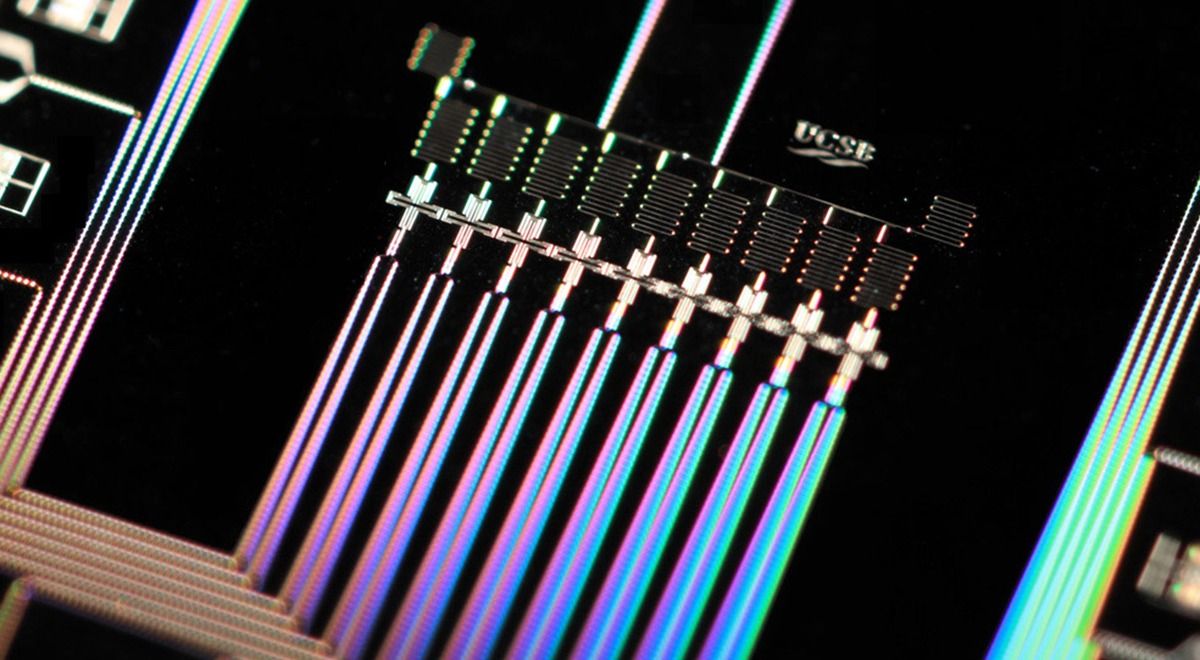
This is a critical step along the way to functional quantum computers that can achieve problems far beyond the capacity of traditional systems.



Flying at 50,000 feet, diving deep in the ocean, or hiking for miles with gear through extreme climates, military service members face conditions that place unique burdens on their individual physiology. The potential exists to develop pharmacological interventions to help service members complete their toughest missions more safely and efficiently, and then recover more quickly and without adverse effects, but those interventions must work on complex physiological systems in the human body. They will not be realized under the prevailing system of drug discovery and development with its focus on engaging single molecular targets. DARPA created the Panacea program to pursue the means of rapidly discovering, designing, and validating new, multi-target drugs that work with the body’s complexity to better support the physiological resilience and recovery of military service members.
The premise of Panacea is that the physiological systems of the human body work in complex and highly integrated ways. Drugs exert effects on our bodies by physically interacting with and changing the functional state of biomolecules that govern the functions of cells and tissues. Most drugs target proteins, which are the principle cellular workhorses. Ideally, drugs would target multiple proteins simultaneously to exert precise, network-level effects.
One major problem facing the drug development community is that the functional proteome — the complete collection of proteins and their roles in signaling networks — is largely dark to science. Despite being able to identify many of the proteins within a cell, researchers do not have a firm grasp on everything those proteins do and how they interact to affect physiology.
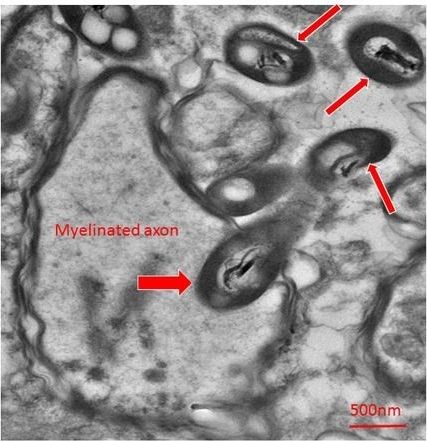
Rosalinda Roberts had gotten used to seeing weird shapes in the brain. Over three decades of looking at brain tissue under an electron microscope, she’d regularly come across “unknown objects”—specks and blobs in her images that weren’t supposed to be there, and didn’t seem to relate to the synapses and structure that she was studying. “I’d just say, ‘well I’m not going to pay attention to that’” she explains. That’s all changed now.
Finding bacteria in the brain is usually very bad news. The brain is protected from the bacterial menagerie of the body by the blood-brain barrier, and is considered a sterile organ. When its borders are breached, things like encephalitis and meningitis can result. Which made it all the more surprising when Roberts, along with Charlene Farmer and Courtney Walker, realized that the unknown objects in their slides were bacteria.
Many of them were caught mid-stride, entering neurons or penetrating axons. Others were in the process of dividing. They were picky, too, strongly preferring some regions of the brain over others. The surrounding brain tissue showed no signs of inflammation. If the bacteria were in the brain while the individual was alive, they were not pathogenic.

Scientists look around the universe and see amazing structure. There are objects and processes of fantastic complexity. Every action in our universe follows exact laws of nature that are perfectly expressed in a mathematical language. These laws of nature appear fine-tuned to bring about life, and in particular, intelligent life. What exactly are these laws of nature and how do we find them?
The universe is so structured and orderly that we compare it to the most complicated and exact contraptions of the age. In the 18th and 19th centuries, the universe was compared to a perfectly working clock or watch. Philosophers then discussed the Watchmaker. In the 20th and 21st centuries, the most complicated object is a computer. The universe is compared to a perfectly working supercomputer. Researchers ask how this computer got its programming.
How does one explain all this structure? Why do the laws seem so perfect for producing life and why are they expressed in such exact mathematical language? Is the universe really as structured as it seems?

“Graham is another speaker who has been a key member of the “SENS family” since its earliest days. He is one of the few eminent biogerontologists who can proudly claim to have spoken out regularly in favour of intervention in aging during the dark days when such talk was widely viewed by colleagues as misguided or even irresponsible. He continues to be a world leader in the study of immunosenescence, elucidating key aspects of why older people are so bad at fighting off infections, and I’m really looking forward to hearing his latest findings.” says Aubrey de Grey.
https://www.undoing-aging.org/news/dr-graham-pawelec-to-spea…aging-2019
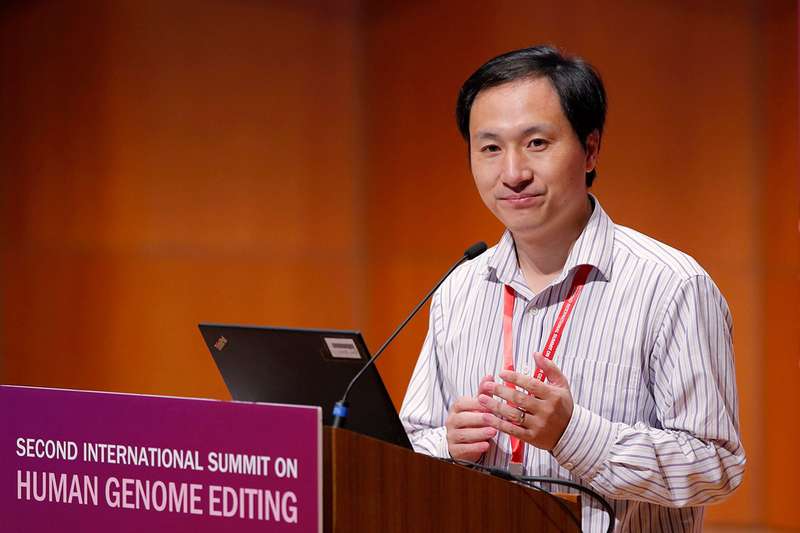

A woman is already pregnant with the next CRISPR baby, according to He Jiankui, the Chinese scientist who claims to have already created the world’s first genetically edited babies.
Bombshell: He made the claim about the early-stage pregnancy on the second day of an international gene-editing summit at the University of Hong Kong. “There is another one, another potential pregnancy,” he said on stage. He defended his work, saying he feels “proud” to have used gene-editing techniques to make the twin girls HIV resistant. “This is not just for this case, but for millions of children. They need this protection. [An] HIV vaccine is not available,” he said.
Irresponsible: After his presentation, He was quizzed by audience members about his work. Nobel laureate David Baltimore said that proceeding with germ-line editing in this way was “irresponsible” and criticized He for not being more open. “I think there has been a failure of self-regulation by the scientific community because of the lack of transparency,” he said. It also emerged that none of He’s presentation slides had contained information about the implanted embryos—or the babies—when they were submitted to the conference organizers.
In a new book published this week titled Architects of Intelligence, writer and futurist Martin Ford interviewed 23 of the most prominent men and women who are working in AI today, including DeepMind CEO Demis Hassabis, Google AI Chief Jeff Dean, and Stanford AI director Fei-Fei Li. In an informal survey, Ford asked each of them to guess by which year there will be at least a 50 percent chance of AGI being built.
Short answer: maybe within our lifetimes, but don’t hold out.

Artificial intelligences are about to get a place to call their own — and it’s located somewhere humans are unlikely to want to visit.
According to a story published Monday in the South China Morning Post, scientists from the Chinese Academy of Sciences plan to construct a research base deep in the South China Sea, and they want artificially intelligent robots to run it.
This base could be the “first artificial intelligence colony on Earth,” those involved in the project told the SCMP.