The move appears to demonstrates a commitment to the public good by the embattled agency.



Floor-to-ceiling bookshelves are lovely, and can act as a robust focal point in any home, though accessing the high shelves can be a problem. The common sidekick has always been ladders which can also add character and charm, but for smaller homes like in Japan they can be a nuisance, occupying too much space for not enough usage. Japanese architect Shinsuke Fujii came up with a simple, yet brilliant solution that solves another problem too: earthquake safety.
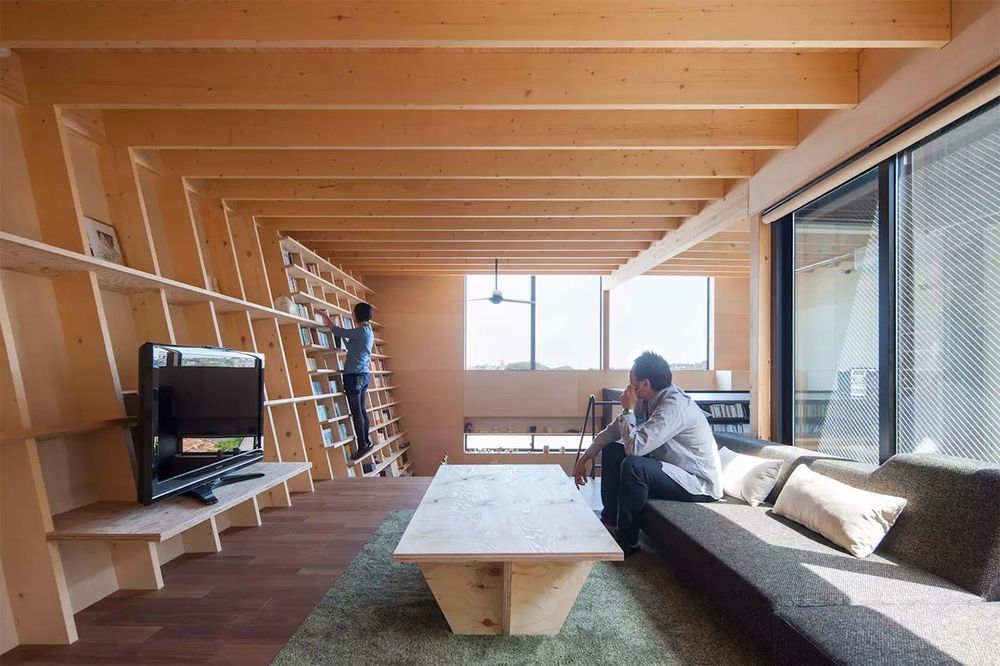

The “House in Shinyoshida,” as it’s called, named for the neighborhood in Yokohama where it stands, was conceived shortly after the 2011 Tohoku Earthquake. The client, who happened to be an avid book lover, approached Fujii with the task to design a home around a large bookshelf that’s both easily accessible but also one that won’t spill all the books if there’s ever a tremor.

The universe is almost devoid of antimatter, and physicists haven’t yet figured out why. Discovering any slight difference between the behaviour of antimatter and matter in Earth’s gravitational field could shed light on this question. Positronium atoms, which consist of an electron and a positron, are one type of atimatter atoms being considered to test whether antimatter falls at the same rate as matter in Earth’s gravitational field. But they are short-lived, lasting a mere 142 nanoseconds – too little to perform an antimatter gravity experiment. Researchers are therefore actively seeking tricks to make sources of positronium atoms that live longer. In a paper published today in the journal Physical Review A, the AEgIS collaboration at CERN describes a new way of making long-lived positronium.
To be useful for antimatter gravity experiments, a source of positronium atoms needs to produce long-lived atoms in large numbers, and with known velocities that can be controlled and are unaffected by disturbances such as electric and magnetic fields. The new AEgIS source ticks all of these boxes, producing some 80 000 positronium atoms per minute that last 1140 nanoseconds each and have a known velocity (between 70 and 120 kilometres per second) that can be controlled with a high precision (10 kilometres per second).
The trick? Using a special positron-to-positronium converter to produce the atoms and a single flash of ultraviolet laser light that kills two birds with one stone. The laser brings the atoms from the lowest-energy electronic state to a long-lived higher-energy state and can select among all of the atoms only those with a certain velocity.
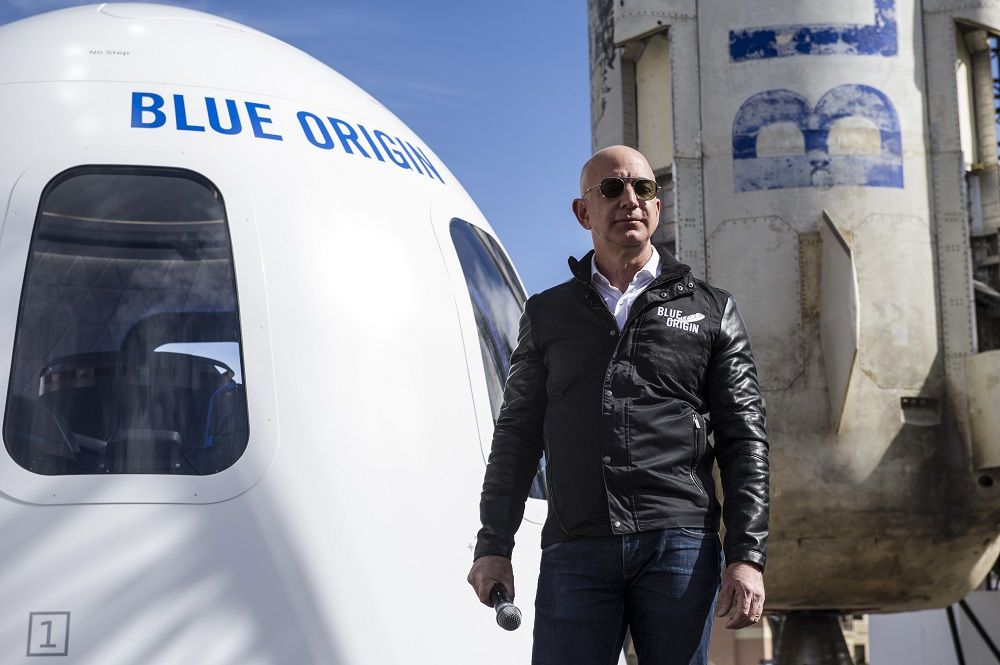



Blue Origin’s founder explains how New Shepard and New Glenn enable humanity’s future in the solar system.
This article originally appeared in the Feb. 25, 2019 issue of SpaceNews magazine.
Jeff Bezos is not a man of little dreams. The world’s richest person, with an estimated net worth of more than $130 billion, is spending some of his wealth on his space startup, Blue Origin. Much of the attention that the company has received has focused on the billions he’s invested into the company, its plans to fly tourists on its suborbital New Shepard vehicle and its entry into the orbital launch market with its New Glenn rocket.
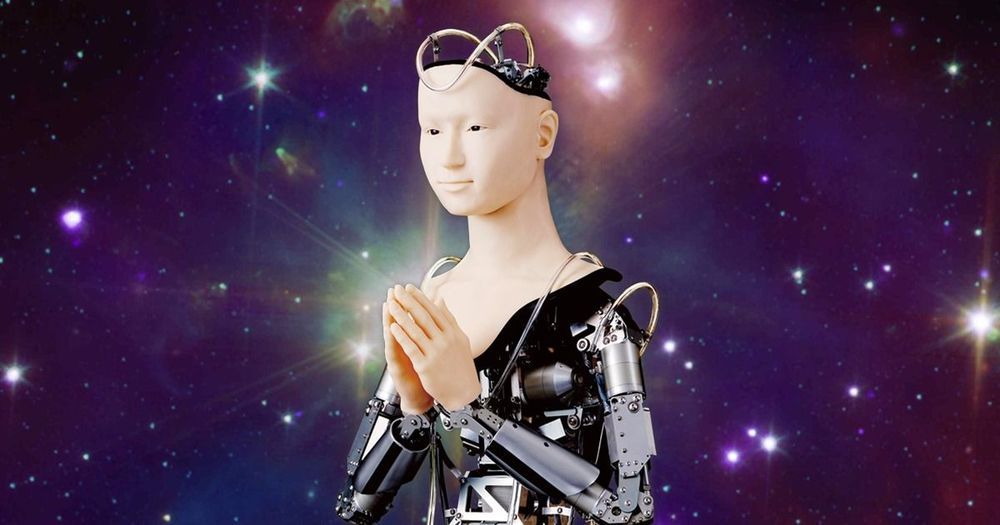

“Monks don’t discuss the true meaning of the Heart Sutra to worshippers; they just read it like poetry,” Kohei Ogawa, a robotics professor at the University of Osaka who worked on the robot, told The Diplomat. “But this doesn’t work. The monks are like robots.”
Androgynous Android
The Mindar android also bends gender, according to The Diplomat, with its human-like face and chest designed to evoke both male and female characteristics.
Testing a rail gun in the middle of a field has never been so fun! This rail gun includes 9-volt batteries as a portable source of power to charge the capacitors. The capacitors provide instantaneous amperage to the rail gun. When triggered, the rail gun fires an aluminum projectile.
And, it’s a success! The first test, run at 350 volts, successfully fires the projectile. The team will have to make some modifications for the next phase. Any suggestions for making the capacitors or the cables more stable?

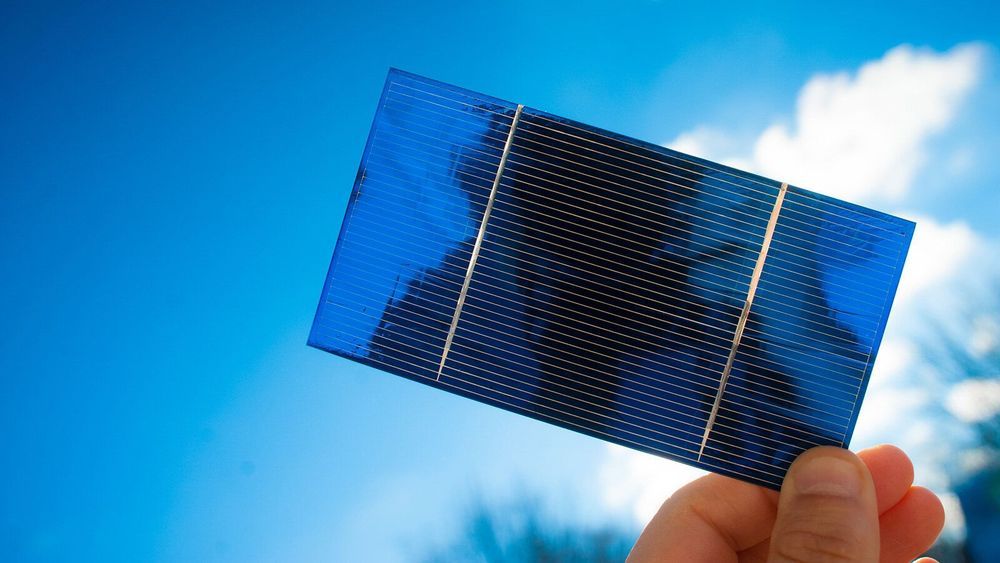
Finding the best light-harvesting chemicals for use in solar cells can feel like searching for a needle in a haystack. Over the years, researchers have developed and tested thousands of different dyes and pigments to see how they absorb sunlight and convert it to electricity. Sorting through all of them requires an innovative approach.
Now, thanks to a study that combines the power of supercomputing with data science and experimental methods, researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory and the University of Cambridge in England have developed a novel “design to device” approach to identify promising materials for dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs). DSSCs can be manufactured with low-cost, scalable techniques, allowing them to reach competitive performance-to-price ratios.
The team, led by Argonne materials scientist Jacqueline Cole, who is also head of the Molecular Engineering group at the University of Cambridge’s Cavendish Laboratory, used the Theta supercomputer at the Argonne Leadership Computing Facility (ALCF) to pinpoint five high-performing, low-cost dye materials from a pool of nearly 10,000 candidates for fabrication and device testing. The ALCF is a DOE Office of Science User Facility.