SEC files charges over a $14M crypto scam using fake AI investment tips, WhatsApp groups, and bogus trading platforms to defraud U.S. investors.



OpenAI has quietly rolled out ‘formatting blocks,’ which tweak GPT’s layout to match the UI of the task it is supposed to execute.
ChatGPT has different use cases, including writing emails or blogs. Up until now, if you asked GPT to write an email for you, it would show the content of the email in the same way as a typical response.
That does not make GPT worse than any other LLM, but it’s not the best experience, and OpenAI wants to fix it with a new feature that automatically adapts the UI.

Google will finally allow you to change your @gmail address or create a new alias, according to a new support document.
As spotted in a Telegram group, Google says that it’s already rolling out a feature that lets you change your email address, and it’s not just for your custom emails.
Up until now, Google has allowed you to switch between different aliases for your emails, but you couldn’t change your “@gmail.com” address.

A typosquatted domain impersonating the Microsoft Activation Scripts (MAS) tool was used to distribute malicious PowerShell scripts that infect Windows systems with the ‘Cosmali Loader’
BleepingComputer has found that multiple MAS users began reporting on Reddit [1, 2] yesterday that they received pop-up warnings on their systems about a Cosmali Loader infection.
You have been infected by a malware called ‘cosmali loader’ because you mistyped ‘get.activated.win’ as ‘get.activate[.]win’ when activating Windows in PowerShell.
Explore CUDA resources including libraries, tools, integrations, tutorials, and more.
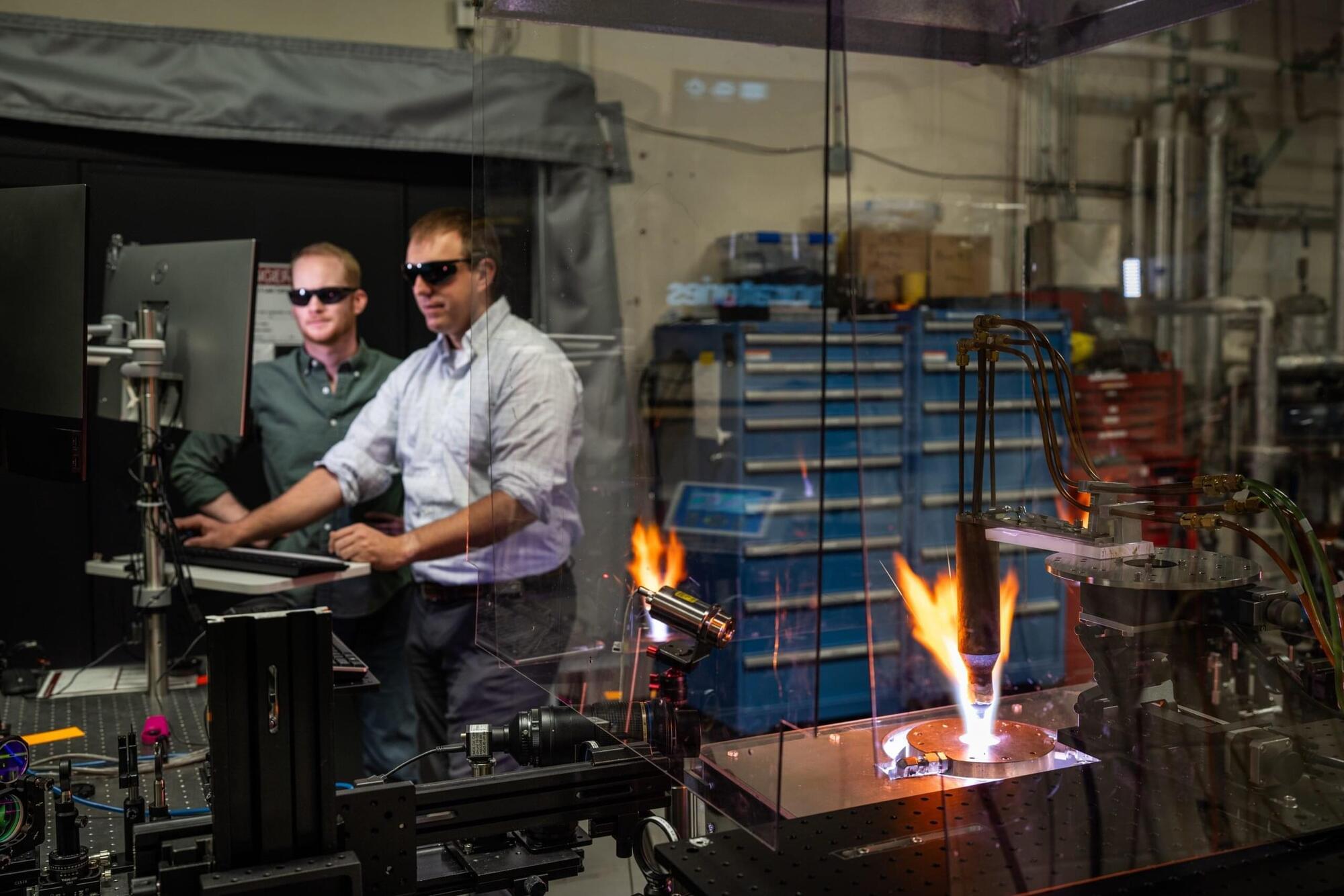

From the tragedy of the space shuttle Columbia disaster in 2003 to the now-routine return of commercial spacecraft, heat shields—formally called thermal protection systems—are critical for protecting vehicles from the intense heat and friction of atmospheric reentry or traveling at many times the speed of sound.
Now, a team of engineers at Sandia National Laboratories have developed ways to rapidly evaluate new thermal protection materials for hypersonic vehicles. Their three-year research project combined computer modeling, laboratory experiments and flight testing to better understand how heat shields behave under extreme temperatures and pressures, and to predict their performance much faster than before.
Hypersonic flight means traveling at speeds of at least five times faster than the speed of sound, or more than 3,800 miles per hour. Other vehicles, such as ballistic missiles, can travel this fast, but hypersonic vehicles are far more maneuverable and unpredictable, making them harder to intercept. Unlike reusable spacecraft, the thermal protection systems used on U.S. hypersonic missiles—which solely deliver conventional weapons—are designed for a single use.

The secret to a healthier and “younger” heart lies in the vagus nerve. A recent study coordinated by the Sant’Anna School of Advanced Studies in Pisa and published in Science Translational Medicine has shown that preserving bilateral cardiac vagal innervation is an anti-aging factor. In particular, the right cardiac vagus nerve emerges as a true guardian of cardiomyocyte health, helping to preserve the longevity of the heart independently of heart rate.
The study is characterized by a strongly multidisciplinary approach, integrating experimental medicine and bioengineering applied to cardiovascular research. Specifically, the research was led by the Translational Critical Care Unit (TrancriLab) of the Interdisciplinary Research Center Health Science, under the responsibility of Professor Vincenzo Lionetti, and by the laboratory of the Biorobotics Institute led by Professor Silvestro Micera, which contributed to the development of the bioabsorbable nerve conduit used to facilitate vagal regeneration.
The study involved a broad network of Italian and international institutions of excellence, including the Scuola Normale Superiore, the University of Pisa, the Fondazione Toscana G. Monasterio, the Institute of Clinical Physiology of the CNR, the University of Udine, GVM Care & Research, Al-Farabi Kazakh National University, the Leibniz Institute on Ageing in Jena and the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne.