Haidar el Ali’s reforestation project has planted 152 million mangrove buds in southern Senegal over the past decade!
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.

Judge rules against Johnson & Johnson in landmark opioid case in Oklahoma
Oklahoma Attorney General Mike Hunter had claimed that J&J and its pharmaceutical subsidiary Janssen aggressively marketed to doctors and downplayed the risks of opioids as early as the 1990s. The state said J&J’s sales practices created an oversupply of the addictive painkillers and “a public nuisance” that upended lives and would cost the state $12.7 billion to $17.5 billion. The state was seeking more than $17 billion from the company.
J&J, which marketed the opioid painkillers Duragesic and Nucynta, has denied any wrongdoing. Lawyers for the company disputed the legal basis Oklahoma used to sue J&J, relying on a “public nuisance” claim. They said the state has previously limited the act to disputes involving property or public spaces.
Investors were expecting J&J to be fined between $500 million and $5 billion, according to Evercore ISI analyst Elizabeth Anderson.
Disappearing act: Device vanishes on command after military missions
A polymer that self-destructs? While once a fictional idea, new polymers now exist that are rugged enough to ferry packages or sensors into hostile territory and vaporize immediately upon a military mission’s completion. The material has been made into a rigid-winged glider and a nylon-like parachute fabric for airborne delivery across distances of a hundred miles or more. It could also be used someday in building materials or environmental sensors.
The researchers will present their results today at the American Chemical Society (ACS) Fall 2019 National Meeting & Exposition.
“This is not the kind of thing that slowly degrades over a year, like the biodegradable plastics that consumers might be familiar with,” says Paul Kohl, Ph.D., whose team developed the material. “This polymer disappears in an instant when you push a button to trigger an internal mechanism or the sun hits it.” The disappearing polymers were developed for the Department of Defense, which is interested in deploying electronic sensors and delivery vehicles that leave no trace of their existence after use, thus avoiding discovery and alleviating the need for device recovery.
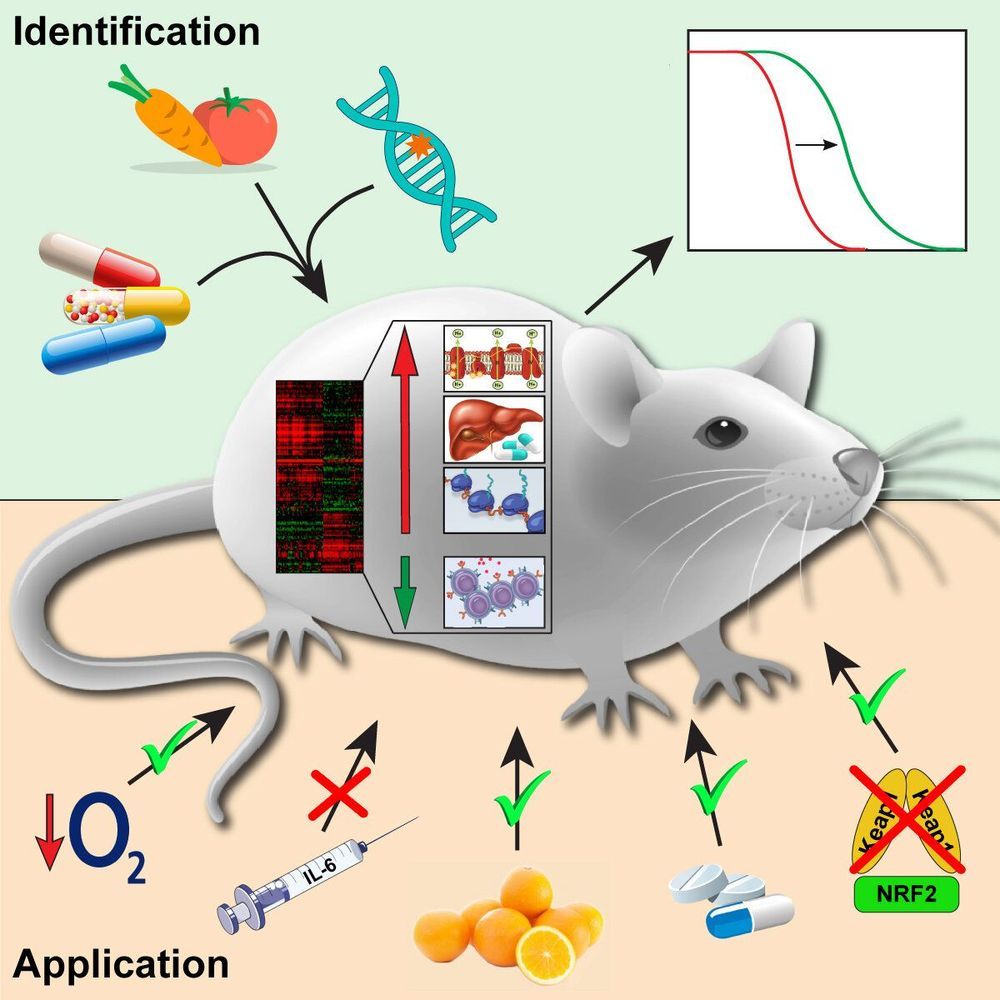
Scientists find longevity biomarkers
An international group of scientists studied the effects of 17 lifespan-extending interventions on gene activity in mice and discovered genetic biomarkers of longevity. The results of their study were published in the journal Cell Metabolism.
Nowadays, dozens of interventions are known that extend the lifespan of various living organisms ranging from yeast to mammals. They include chemical compounds (e.g. rapamycin), genetic interventions (e.g. mutations associated with disruption of growth hormone synthesis), and diets (e.g. caloric restriction). Some targets of these interventions have been discovered. However, there is still no clear understanding of the systemic molecular mechanisms leading to lifespan extension.
A group of scientists from Skoltech, Moscow State University and Harvard University decided to fill this gap and identify crucial molecular processes associated with longevity. To do so, they looked at the effects of various lifespan-extending interventions on the activity of genes in a mouse, a commonly used model organism closely related to humans.



Researchers Created AI That Hides Your Emotions From Other AI
Humans can communicate a range of nonverbal emotions, from terrified shrieks to exasperated groans. Voice inflections and cues can communicate subtle feelings, from ecstasy to agony, arousal and disgust. Even when simply speaking, the human voice is stuffed with meaning, and a lot of potential value if you’re a company collecting personal data.
Now, researchers at the Imperial College London have used AI to mask the emotional cues in users’ voices when they’re speaking to internet-connected voice assistants. The idea is to put a “layer” between the user and the cloud their data is uploaded to by automatically converting emotional speech into “normal” speech. They recently published their paper “Emotionless: Privacy-Preserving Speech Analysis for Voice Assistants” on the arXiv preprint server.
Our voices can reveal our confidence and stress levels, physical condition, age, gender, and personal traits. This isn’t lost on smart speaker makers, and companies such as Amazon are always working to improve the emotion-detecting abilities of AI.
Study: Blood test detects concussion and subconcussive injuries in children and adults
In one of the largest studies of its kind, researchers at Orlando Health are making new progress in finding ways to detect a traumatic yet sinister brain injury—and getting closer to preventing further damage.
Subconcussive injuries often show no symptoms or immediate effects, but can cause wear and tear on the brain over time with repeated injuries. The latest study, published in the journal BMJ Paediatrics Open, includes more than 700 emergency room patients—children and adults. The study gets us closer to developing a standard blood test to spot these injuries as early as possible.
“A unique feature of this study is that it includes patients who hit their heads but have no symptoms,” said Linda Papa, MD, lead author of the study and emergency medicine doctor at Orlando Health. “This group is rarely—if ever—included in biomarker studies.”


Rejuvenation Research Is Now a Mainstream Topic
It is a sure sign that the tide has turned when mainstream news outlets and magazines start publishing positive articles about aging research and the prospects of rejuvenation.
A refreshing change
Today, I want to highlight an article in MIT Technology Review in which the author, David Adam, gives a sensible and measured overview of what is happening in the field and manages to sidestep the usual negativity and misconceptions that often plague popular science pieces.