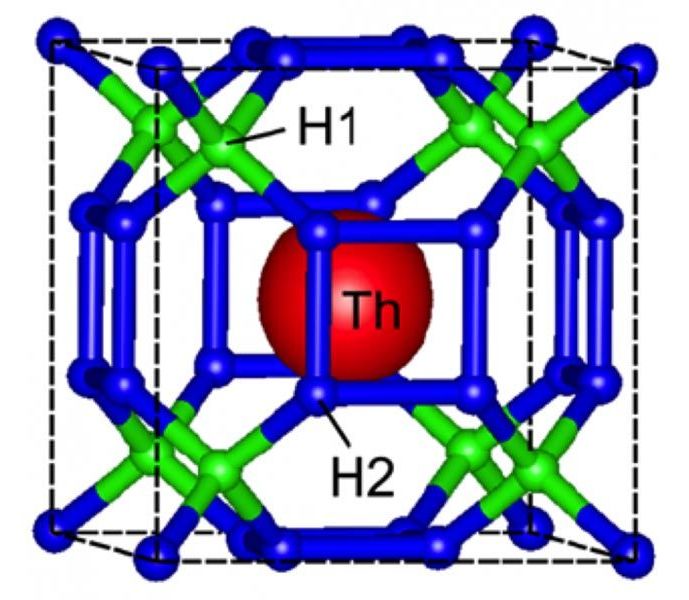
A group of scientists led by Artem Oganov of Skoltech and the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology, and Ivan Troyan of the Institute of Crystallography of RAS has succeeded in synthesizing thorium decahydride (ThH10), a new superconducting material with the very high critical temperature of 161 kelvins. The results of their study, supported by a Russian Science Foundation grant, were published in the journal Materials Today on November 6, 2019.
A truly remarkable property of quantum materials, superconductivity is the complete loss of electrical resistance under quite specific, and sometimes very harsh, conditions. Despite the tremendous potential for quantum computers and high-sensitivity detectors, the application of superconductors is hindered by the fact that their valuable properties typically manifest themselves at very low temperatures or extremely high pressures.
Until recently, the list of superconductors was topped by a mercury-containing cuprate, which becomes superconducting at 135 kelvins, or −138 degrees Celsius. This year, lanthanum decahydride, LaH10, set a new record of −13 C, which is very close to room temperature. Unfortunately, that superconductor requires pressures approaching 2 million atmospheres, which can hardly be maintained in real-life applications. Scientists, therefore, continue their quest for a superconductor that retains its properties at standard conditions.