And it got the idea from NASA.


A spot of sunshine is all it could take to get your washing done, thanks to pioneering nano research into self-cleaning textiles.
Researchers at RMIT University in Melbourne, Australia, have developed a cheap and efficient new way to grow special nanostructures—which can degrade organic matter when exposed to light—directly onto textiles.
The work paves the way towards nano-enhanced textiles that can spontaneously clean themselves of stains and grime simply by being put under a light bulb or worn out in the sun.
TABLE OF CONTENTS —————
0:00–17:57 : Introduction (Meaning of Life)
17:58–37:45 CHAPTER 1: Longevism and Life Extension
—————————————————————————————–
WHY DOES AGING HAPPEN?
—————————————————————————————–
37:46–54:39 CHAPTER 2 : Gerontonology and Aging a. Free Radical Theory of Aging b. Waste Accumulation Theory of Aging c. Stem Cell Theory of Aging d. DNA Damage Theory of Aging.
—————————————————————————————–
HOW DO WE CURE AGING?
—————————————————————————————–
54:39–1:08:39 : CHAPTER 3 :The Biochemical Solution (#1)
a. mitoSENS
b. oncoSENS
c. lysoSENS
d. amyloSENS
e. apoptoSENS
f. repliSENS
g. glycoSENS
1:08:40–2:13:12 CHAPTER 4 : The Physiological Solution (#2)
a. Parabiosis and Biovampirism b. Regeneration and Stem Cells c. Lab Grown Organs and Bioprinting d. Head Transplants and Doppleganger Bodies.
2:13:12–2:33:19 CHAPTER 5 : The Genetic Solution (#3)
a. TALEN genetic engineering b. Zinc-Finger gene tailoring c. CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing.
—————————————————————————————–
WILL WE CURE AGING GENETICALLY?
—————————————————————————————–
2:33:20–2:49:58 : CHAPTER 6 : Genomics and DNA
2:49:59–3:05:48 : CHAPTER 7 : Transcriptomics and RNA
3:05:49–3:22:08 : CHAPTER 8 : Proteomics and TNA
3:22:09–3:39:38 : CHAPTER 9 : Xenobiology and XNA
a. alien proteins b. alien base pairs c. alien DNA
3:39:39–3:54:58 : CHAPTER 10 : Vectors and Gene Therapy (Gene Editing #1)
3:54:59–4:14:57 : CHAPTER 11 : Synthetic Biology (Gene Editing #2)
4:14:58–4:32:14 : CHAPTER 12 : Chimeras, Rianths, and Splices (Gene Editing #3)
4:32:15–4:48:35 : CHAPTER 13 : Ouroborology and Immortal Chimeras (Gene Editing #4)
4:48:36-:5:03:52 : CHAPTER 14 : Kleptoplasty and Photosynthesis (Gene Editing #5)
—————————————————————————————-
HOW TO SURVIVE UNTIL AGING IS CURED
—————————————————————————————-
5:03:53–5:14:27 : CHAPTER 15 : Survive to the Singularity a. the breakeven point b. longevity escape velocity c. the longevity dividend.
5:14:28–5:30:16 : CHAPTER 16 : Centennarians and Blue Zones (Survival Method #0)
a. loma linda b. ikaria c. sardinia d. okinawa.
5:30:17–5:42:26 : CHAPTER 17 : Risk Aversion and Micromorts (Survival Method #1)
a. micromorts
b.microlives
5:42:27–5:58:18 : CHAPTER 18 : Nutraceuticals and Geroprotectors (Survival Method #2)
a. rapamycin b. metformin c. selegilene d. nicotinamide riboside e. resverratrol.
5:58:19–6:12:51 : CHAPTER 19 : Caloric Restriction (Survival Method #3)
a. endocrine b. epigenetic c. genetic
6:12:52–6:51:57 : CHAPTER 20 : Cryonics & Cryogenics (Survival Method #4)
a. the efficacy question b. the cost question c. the resurrection question d. the identity question e. the legal question f. the catastrophe question g. the culture question.
—————————————————————————————–
CAN WE BE IMMORTAL WITHOUT CURING AGING?
—————————————————————————————–
_______________________________________________________
6:51:58–7:04:08 : CHAPTER 21 : Genetic Immortality — Test Tube Babies
7:04:09–7:24:02 : CHAPTER 22 : Genetic Immortality — Designer Babies
7:24:03–7:41:55 : CHAPTER 23 : Genetic Immortality — Clone Babies
7:41:56–7:53:08 : CHAPTER 24 : Genetic Immortality — Artificial Wombs
7:53:08–7:53:09 CHAPTER 25 : Immortalism and Ethics a. the crime argument b. the natural argument c. the boredom argument d. the inequality argument e. the overpopulation argument f. the gerontocracy argument g. the economic argument h. EPILOGUE
Patreon https://www.patreon.com/transhumania
KEYWORDS :
Immortology, Athanophy, Biotechnology, Biotech, Bioviva, Alcor, Calico, Nanotechnology, Nanotech, Reverse Aging, Live Forever, Caloric Restriction, Blue Zone, Centenarian, Singularity, Nutraceuticals, Geroprotectors, Metformin, Seligiline, Rapamycin, Nikolai Fedorov, Aubrey De Grey, Immortalism, Peter Thiel, Gerontology, Telomere, Elizabeth Blackburn, Free Radicals, Oxidative Stress, SENS, Bioinformatic, Transcriptomics, Proteonomics, Genomics, CRISPR Cas9, Synthetic Biology, Craig Venter, Retrovirus, Gene Therapy, Gene Editing, Xenobiology, Epigenetics, RNAi interference, C2C2, David Sinclair, Resveratrol, Sirtuin, Gene, Kleptoplasty, Splice, Spidergoat, Rianth, Chimera, IVF, Test Tube Designer Baby, Cloning South Korea, Artificial Womb, Ectogenesis, Human Cloning, Panyotis Zavos, Stem Cell, Parabiosis, 3D Bioprinting, Regenerative Medicine, Thomas Rando, Sergio Canavero, Head Transplant, Biostasis, Cryopreservation, Cryonics, Vitrification, Extropianism.

What is needed as a cocktail is the Gerevivify Algorithms Serum Elixir. An Elixir that enters the body that then goes into battle fighting the infection that is aging. I search for strong-minded partners and investors to join me in the growth and development of the specially grown 13 ingredients that make up the powerful serum. Respect r.p.berry & AEWR https://gerevivify.blogspot.com/
“Fahy’s fascination with the thymus goes back to 1986, when he read a study in which scientists transplanted growth-hormone-secreting cells into rats, apparently rejuvenating their immune systems,” Nature reported. “He was surprised that no one seemed to have followed up on the result with a clinical trial. A decade later, at age 46, he treated himself for a month with growth hormone and DHEA, and found some regeneration of his own thymus.”
The thymus is located in the chest between the lungs and the breastbone and is crucial for efficient immune function. “White blood cells are produced in bone marrow and then mature inside the thymus, where they become specialized T-cells that help the body to fight infections and cancers,” Nature reported. “But the gland starts to shrink after puberty and increasingly becomes clogged with fat. Evidence from animal and some human studies shows that growth hormone stimulates regeneration of the thymus. But this hormone can also promote diabetes, so the trial included two widely used anti-diabetic drugs, dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and metformin, in the treatment cocktail.”
The TRIIM trial showed regenerated thymus tissue had replaced accumulated fat in seven of the nine participants. Horvath was charged with analyzing the effect of the drugs on the participants’ epigenetic clocks after the trial was finished.
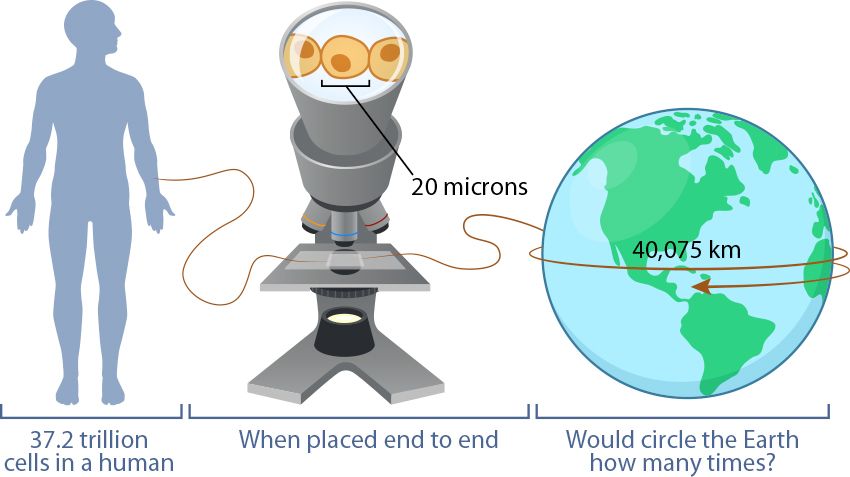
All living beings are made up of cells. Some of them are made up of only one cell and others have many cells. The average adult human body has around 37.2 trillion cells. WOW, that’s a lot of cells. So many, in fact, that it’s hard to picture. But let’s try to imagine it: If we lined up all the cells in a human body end to end, could the line reach around the Earth? If so, how many times?
Heart problems are more likely for people taller than 5ft 7 inches, a new study suggests, with the risk increasing with every inch.
Scientists in the US found that height is linked to an increased chance of developing atrial fibrillation, an irregular and often rapid heartbeat that can lead to stroke and heart failure.
Researchers studied more than 600,000 people involved in the Penn Medicine Biobank, of whom 65,446 (12.5 per cent) had atrial fibrillation.
Beyond cortical and limbic systems, the company Neuralink could add a third layer of digital superintelligence to humans and avoid artificial intelligence enslavement, its founder Elon Musk claimed Tuesday. The brain-computer linkup firm is working to treat medical conditions using its implanted chip as early as next year, but during a podcast appearance, Musk reiterated his belief that the technology could avoid some of the worst consequences of advanced machines.
“It’s important that Neuralink solves this problem sooner rather than later, because the point at which we have digital superintelligence, that’s when we pass the singularity and things become just very uncertain,” Musk said during an interview with MIT professor Lex Fridman.
Musk was keen to note that the singularity, a hypothesized point where machines grow so advanced that humanity slips into an irreversible change, may not necessarily be good or bad. He did state, however, that “things become extremely unstable” after that point, which means Neuralink would need to achieve its human-brain linkup either before or not long after “to minimize the existential risk for humanity and consciousness as we know it.”
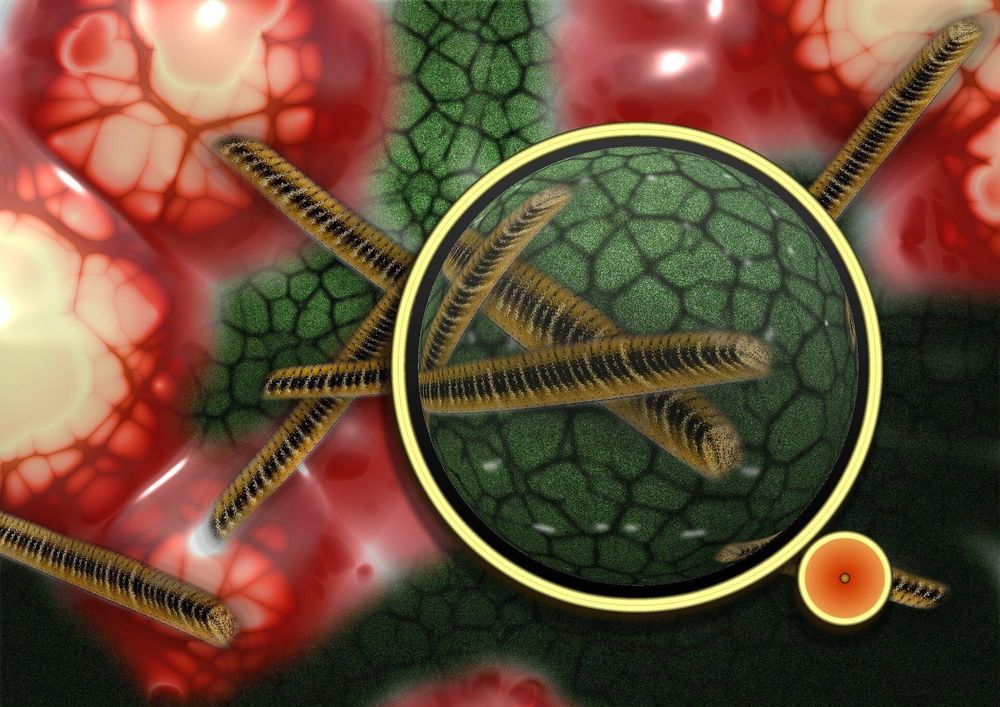
An international team based in Austria has unearthed a previously unknown type of virus in samples of human bodily fluids. The researchers were looking for viruses that infect bacteria, known as bacteriophages, with an emphasis on those that attack the Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacterium found in the human gut. The team identified a total of 43 bacteriophages in samples of human bodily fluids, particularly in blood samples. The discovery of such phages in the human body is especially significant because they can pass antibiotic resistance genes on to bacteria. Consequently, information about the prevalence and frequency of phages in humans, as well as the relationships between them, is urgently needed. The findings of a team from Karl Landsteiner University of Health Sciences under the lead of University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna, which have now been published in an international journal, will make a major contribution in this regard.
The human body is teeming with countless fungi, bacteria and viruses. Bacteriophages are one of the great unknowns in this human ecosystem. Interest in them has grown rapidly in light of research carried out in Austria, which highlighted the prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes in bacteria. A team of researchers from Karl Landsteiner University of Health Sciences (KL Krems), the University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna and the University of Lisbon has now isolated 43 bacteriophages from samples of human bodily fluids, including one which is thought to be a previously unknown type.
“We examined 111 samples of blood, urine and other human body fluids to see if they contained phages. And we found them in almost one in seven samples,” explained Dr. Cátia Pacífico, scientist at KL Krems and lead author of the study. “We also found a new kind of phage from the Tunavirinae subfamily. The presence of phages in so many samples and the discovery of a new form show just how little we know about phages in the human body.”
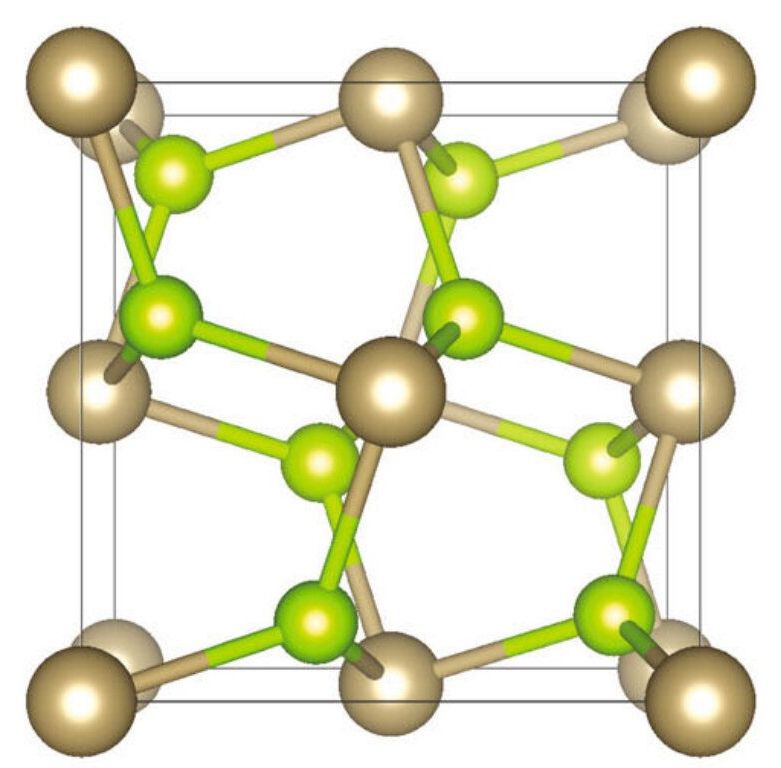
A Monash University study revealing new spin textures in pyrite could unlock these materials’ potential in future spintronics devices.
The study of pyrite-type materials provides new insights and opportunities for selective spin control in topological spintronics devices.
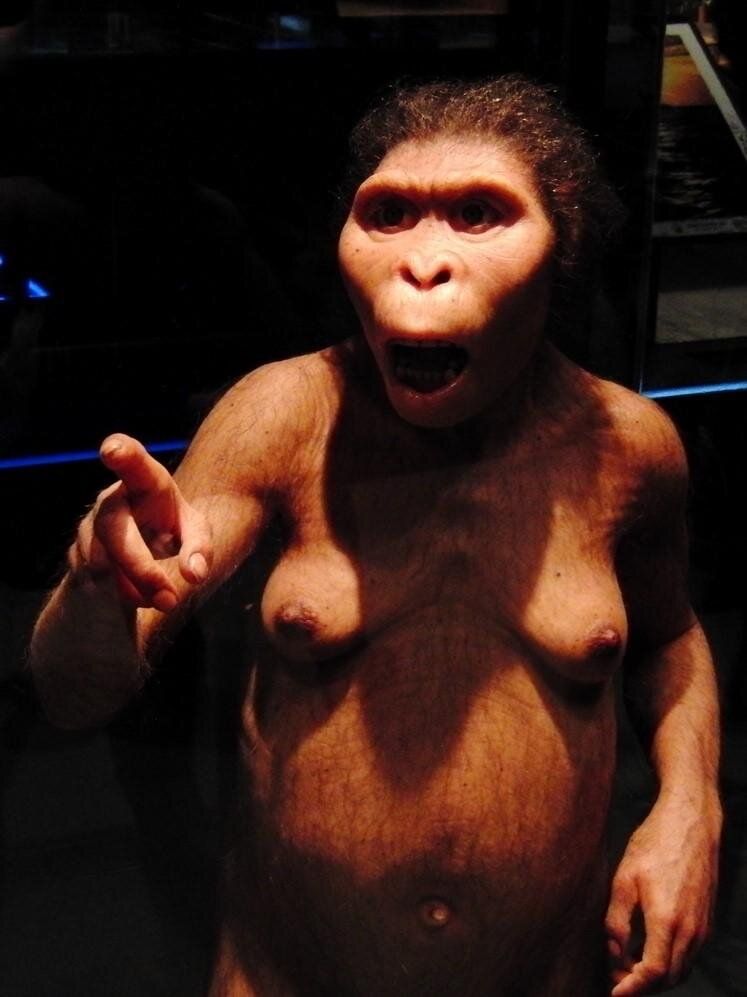

New research from the University of Adelaide suggests living great apes are smarter than our pre-human ancestor Australopithecus, a group that included the famous “Lucy.”
The study, conducted in partnership with the Evolutionary Studies Institute of the University of the Witwatersrand and published today in the Proceedings of the Royal Society B, challenges the long-held idea that, because the brain of Australopithecus was larger than that of many modern apes, it was smarter.
The new research measured the rate of blood flow to the cognitive part of the brain, based on the size of the holes in the skull that passed the supply arteries. This technique was calibrated in humans and other mammals and applied to 96 great ape skulls and 11 Australopithecus fossil skulls.