A Human Rights Watch review finds that mistreatment by guards, including the use of chemical sprays and electronic stun guns, has led to a number of deaths.


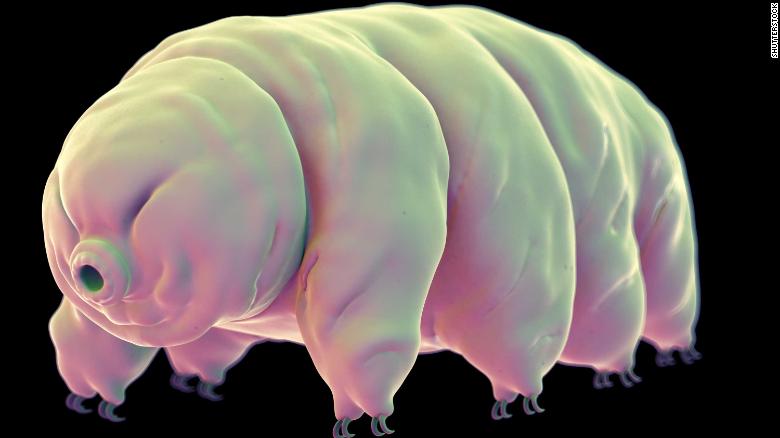
(CNN)You’ve heard of men on the moon — but what about moss piglets?
Source: https://www.cnn.com/2019/08/07/world/water-bear-space-intl-scli-scn/index.html
IBM recently developed three artificial intelligence tools that could help medical researchers fight cancer.
Now, the company has decided to make all three tools open-source, meaning scientists will be able to use them in their research whenever they please, according to ZDNet. The tools are designed to streamline the cancer drug development process and help scientists stay on top of newly-published research — so, if they prove useful, it could mean more cancer treatments coming through the pipeline more rapidly than before.

Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an autosomal recessive disease caused by mutations in the CFTR gene. The 3272–26AG and 3849+10kbCT CFTR mutations alter the correct splicing of the CFTR gene, generating new acceptor and donor splice sites respectively. Here we develop a genome editing approach to permanently correct these genetic defects, using a single crRNA and the Acidaminococcus sp. BV3L6, AsCas12a. This genetic repair strategy is highly precise, showing very strong discrimination between the wild-type and mutant sequence and a complete absence of detectable off-targets. The efficacy of this gene correction strategy is verified in intestinal organoids and airway epithelial cells derived from CF patients carrying the 3272–26AG or 3849+10kbCT mutations, showing efficient repair and complete functional recovery of the CFTR channel. These results demonstrate that allele-specific genome editing with AsCas12a can correct aberrant CFTR splicing mutations, paving the way for a permanent splicing correction in genetic diseases.


A study on animals with autoimmune myocarditis was recently released in the journal Cell Reports [1], showing the impact of heart inflammation on the types of immune cell that are formed in the heart. This could have a significant impact on our understanding of cardiac aging.
What is myocarditis and how is it relevant to aging?
Myocarditis is a disease involving inflammation of the heart. It mainly influences people between the ages of 20 and 51 [2] [3]; however, the elderly are still affected to some degree. The disease has been known to cause serious complications, such as heart attack and heart failure.

ABOVE: © ISTOCK.COM, CYNOCLUB
Genetics hold far more sway over the mouse microbiome than transient environmental exposures, researchers reported July 26 in Applied and Environmental Microbiology. The results appear to contradict previous studies in humans that have found environmental factors to be more influential than genetics, and they add to an ongoing dialogue in the microbiome research community over how much control we hold over the bacterial communities in our guts.
Hila Korach-Rechtman, a microbiologist at the Israel Institute of Technology in Haifa, set out to identify the microbes in mice that become a fixture in the gut after being introduced through the environment. “We really wanted to find these bacteria that can be transferred and remain in the host, even though they have different genetics,” she says.

The Defense Department is looking to build tools that can quickly detect deepfakes and other manipulated media amid the growing threat of “large-scale, automated disinformation attacks.”
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency on Tuesday announced it would host a proposers day for an upcoming initiative focused on curbing the spread of malicious deepfakes, shockingly realistic but forged images, audio and videos generated by artificial intelligence. Under the Semantic Forensics program, or SemaFor, researchers aim to help computers use common sense and logical reasoning to detect manipulated media.
As global adversaries enhance their technological capabilities, deepfakes and other advanced disinformation tactics are becoming a top concern for the national security community. Russia already showed the potential of fake media to sway public opinion during the 2016 election, and as deepfake tools become more advanced and readily available, experts worry bad actors will use the tech to fuel increasingly powerful influence campaigns.

Low-grade inflammation is the hallmark of metabolic disorders such as obesity, type 2 diabetes and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Emerging evidence indicates that these disorders are characterized by alterations in the intestinal microbiota composition and its metabolites, which translocate from the gut across a disrupted intestinal barrier to affect various metabolic organs, such as the liver and adipose tissue, thereby contributing to metabolic inflammation. Here, we discuss some of the recently identified mechanisms that showcase the role of the intestinal microbiota and barrier dysfunction in metabolic inflammation. We propose a concept by which the gut microbiota fuels metabolic inflammation and dysregulation.