
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.


‘Immortality, Inc.’ Review: Birthdays Without End
Amid today’s technological wizardry, it’s easy to forget that several decades have passed since a single innovation has dramatically raised the quality of life for millions of people. Summoning a car with one’s phone is nifty, but it pales in comparison with discovering penicillin or electrifying cities. Artificial intelligence is being heralded as the next big thing, but a cluster of scientists, technologists and investors are aiming higher. In the vernacular of Silicon Valley, where many of them are based, their goal is nothing less than disrupting death, and their story is at the center of “Immortality, Inc.” by science journalist Chip Walter.
The efforts of scientists and investors to defy the aging process—and extend the human life span—are still in their infancy.

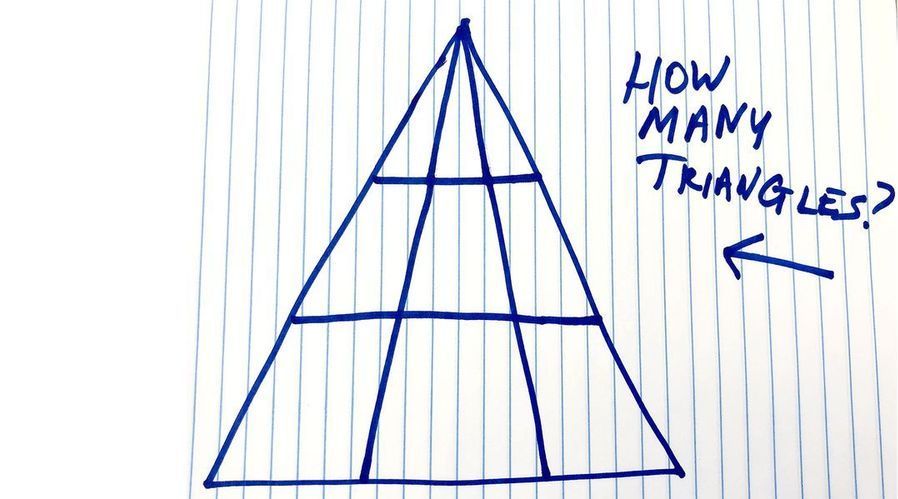
We Spent All Day Arguing About This Triangle Brain Teaser. Can You Solve It?
There’s nothing quite like a maddening math problem, mind-bending optical illusion, or twisty logic puzzle to halt all productivity in the Popular Mechanics office. We’re curious people by nature, but we also collectively share a stubborn insistence that we’re right, dammit, and so we tend to throw work by the wayside whenever we come upon a problem with several seemingly possible solutions.
This triangle brain teaser isn’t new—shoutout to Popsugar for unearthing it a couple years ago—but based on some shady Internet magic, the tweet below reappeared in my feed today and kick-started a new debate on our staff-wide Slack channel, a place traditionally reserved for workshopping ideas, but instead mostly used for yelling about other stuff that we occasionally turn into content.
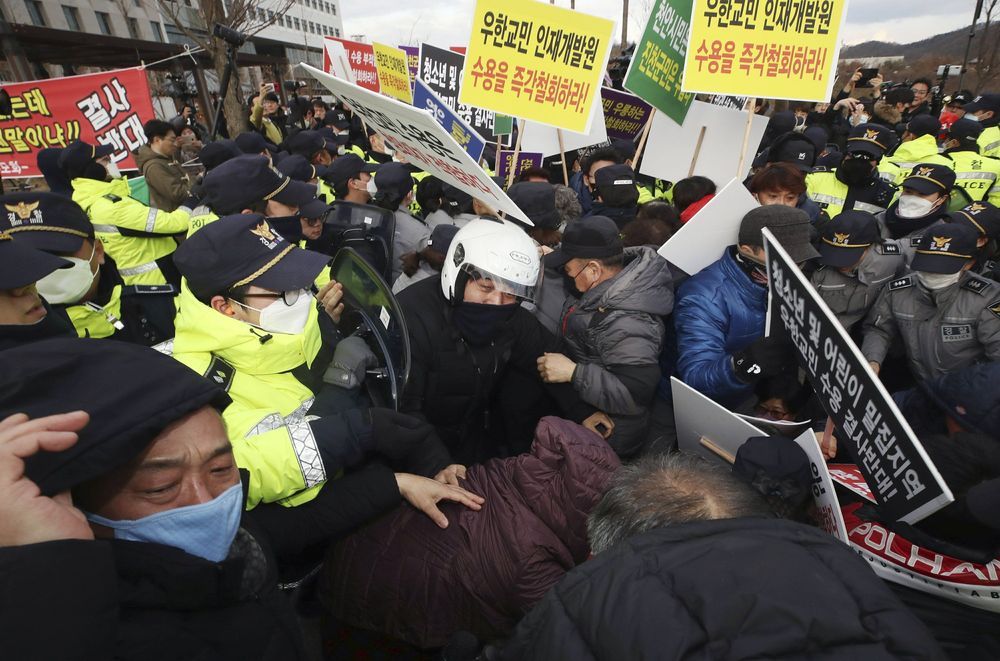


China counts 170 virus deaths, new countries find infections
BEIJING (AP) — China counted 170 deaths from a new virus Thursday and more countries reported infections, including some spread locally, as foreign evacuees from China’s worst-hit region returned home to medical observation and even isolation.
India and the Philippines reported their first cases, in a traveler and a student who had both been in Wuhan, the central Chinese city where the new type of coronavirus first surfaced in December. South Korea confirmed a case that was locally spread, in a man who had contact with a patient diagnosed earlier.
Locally spread cases outside China have been a worrying concern among global health officials, as potential signs of the virus spreading more easily and the difficulty of containing it. The World Health Organization is reconvening experts on Thursday to assess whether the outbreak should be declared a global emergency.
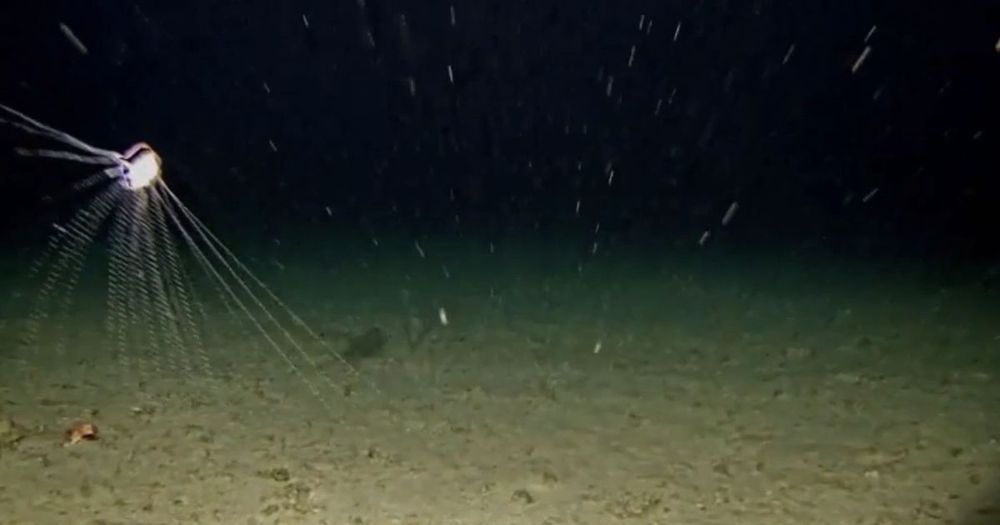

Rare ‘floating city’ deep-sea creature caught on camera by stunned scientists
A creature so rare that it has only a few recorded sightings across the world has been caught on camera by stunned scientists.
The benthic siphonophore, which looks like a single animal, is actually a “floating city” of many smaller organisms working together.
The creatures are so rarely seen that their ecology is almost unknown, though they are thought to make their home at depths of up to 3000m.
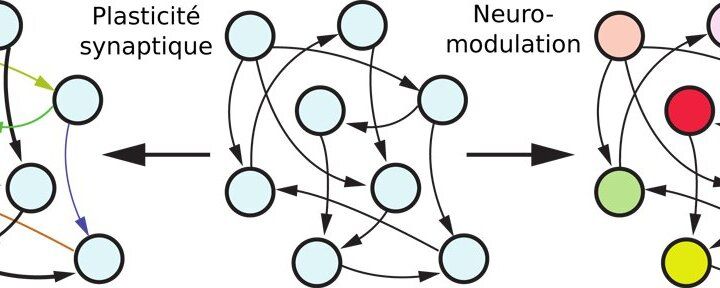
New artificial intelligence inspired by the functioning of the human brain
Inspired by the functioning of the human brain and based on a biological mechanism called neuromodulation, it allows intelligent agents to adapt to unknown situations.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has enabled the development of high-performance automatic learning techniques in recent years. However, these techniques are often applied task by task, which implies that an intelligent agent trained for one task will perform poorly on other tasks, even very similar ones. To overcome this problem, researchers at the University of Liège (ULiège) have developed a new algorithm based on a biological mechanism called neuromodulation. This algorithm makes it possible to create intelligent agents capable of performing tasks not encountered during training. This novel and exceptional result is presented this week in the magazine PLOS ONE.
Despite the immense progress in the field of AI in recent years, we are still very far from human intelligence. Indeed, if current AI techniques allow to train computer agents to perform certain tasks better than humans when they are trained specifically for them, the performance of these same agents is often very disappointing when they are put in conditions (even slightly) different from those experienced during training.
Coronavirus Outbreak: Thai Woman Dies In Kolkata; Germany & Sri Lanka Confirm First Cases
While China reels under Coronavirus outbreak, India has reported death of a Thai woman, Coronavirus suspect in Kolkata hospital.

Scientists develop a concept of a hybrid thorium reactor
Russian scientists have proposed a concept of a thorium hybrid reactor in that obtains additional neutrons using high-temperature plasma held in a long magnetic trap. This project was applied in close collaboration between Tomsk Polytechnic University, All-Russian Scientific Research Institute Of Technical Physics (VNIITF), and Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics of SB RAS. The proposed thorium hybrid reactor is distinguished from today’s nuclear reactors by moderate power, relatively compact size, high operational safety, and a low level of radioactive waste.
“At the initial stage, we get relatively cold plasma using special plasma guns. We retain the amount by deuterium gas injection. The injected neutral beams with particle energy of 100 keV into this plasma generate the high-energy deuterium and tritium ions and maintain the required temperature. Colliding with each other, deuterium and tritium ions are combined into a helium nucleus so high-energy neutrons are released. These neutrons can freely pass through the walls of the vacuum chamber, where the plasma is held by a magnetic field, and entering the area with nuclear fuel. After slowing down, they support the fission of heavy nuclei, which serves as the main source of energy released in the hybrid reactor,” says professor Andrei Arzhannikov, a chief researcher of Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics of SB RAS.
The main advantage of a hybrid nuclear fusion reactor is the simultaneous use of the fission reaction of heavy nuclei and synthesis of light ones. It minimizes the disadvantages of applying these nuclear reactions separately.