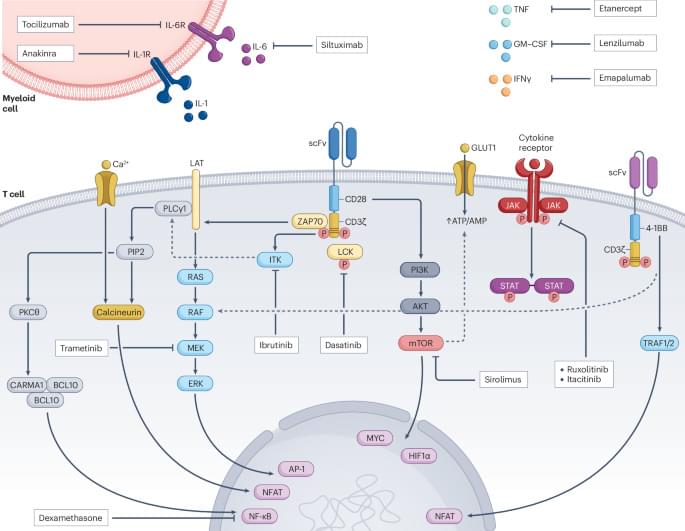
Treatment with chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapies is associated with important immune-related adverse events. In this Review, the authors discuss the standard-of-care management for cytokine release and immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndromes, and the potential of other T cell druggable targets as well as cellular engineering strategies to develop safer CAR-T cells.
Whether extra dimensions prove to be physical realities or useful mathematical constructs, they have already transformed our understanding of the universe. They have forced us to reconsider fundamental assumptions about space, time, and the nature of physical law. And they remind us that reality may be far richer and more complex than our everyday experience suggests — that beyond the familiar dimensions of length, width, height, and time, there may exist entire realms waiting to be discovered and, perhaps one day, explored.
The theoretical physicist John Wheeler once remarked that “we live on an island of knowledge surrounded by an ocean of ignorance.” Our exploration of extra dimensions extends the shoreline of that island, pushing into uncharted waters with the tools of mathematics, experiment, and imagination. Though we may never set foot in the fifth dimension or beyond, the very act of reaching toward these hidden aspects of reality expands our perspective and deepens our understanding of the cosmos we call home.
As we continue this grand scientific adventure, we carry forward the legacy of those who first dared to imagine worlds beyond our immediate perception — from the mathematicians who developed the language of higher-dimensional geometry to the physicists who incorporated these concepts into our most fundamental theories. Their vision, coupled with rigorous analysis and experimental testing, illuminates a path toward an ever more complete understanding of the universe in all its dimensions.
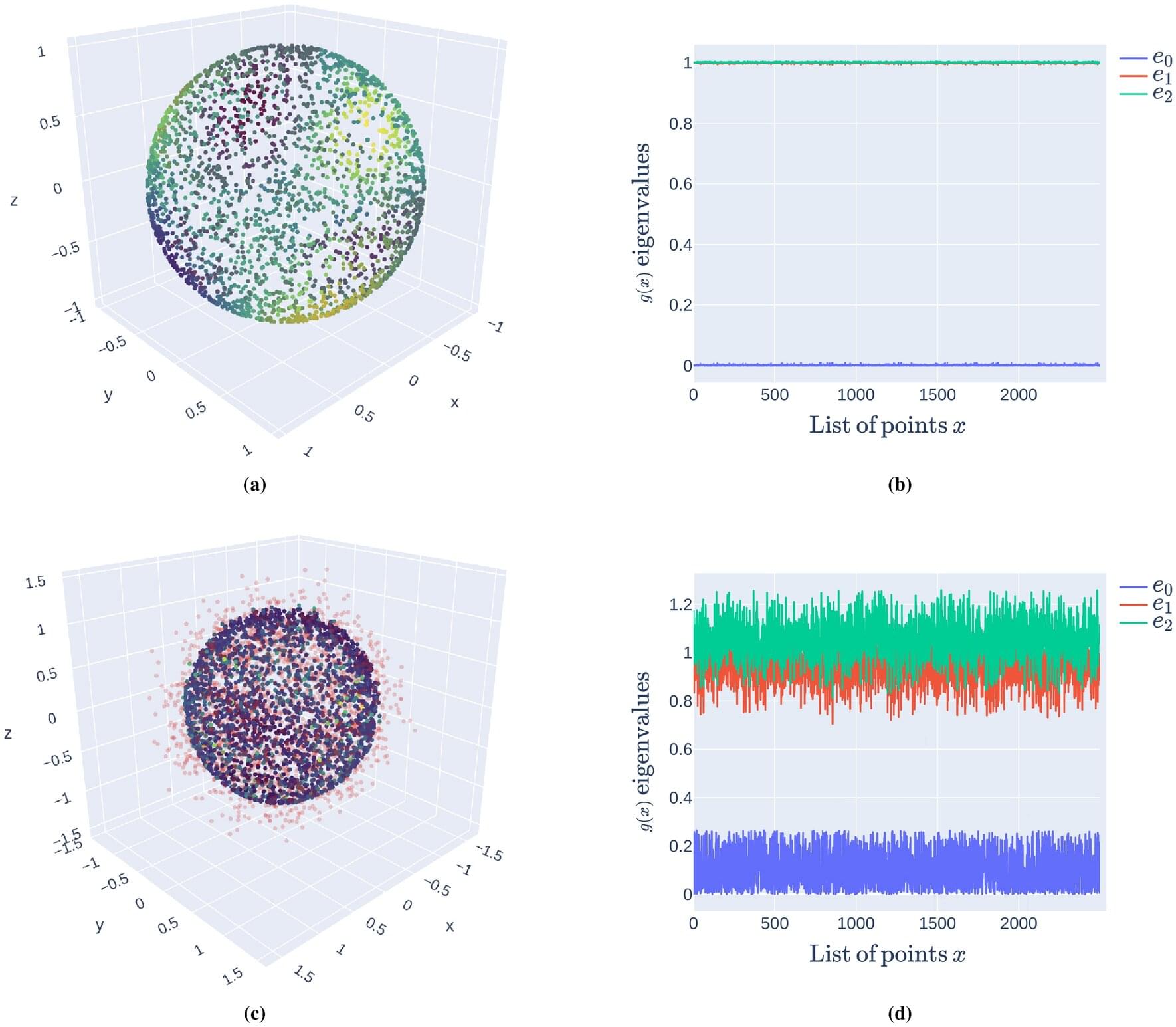
Big data has gotten too big. Now, a research team with statisticians from Cornell has developed a data representation method inspired by quantum mechanics that handles large data sets more efficiently than traditional methods by simplifying them and filtering out noise.
This method could spur innovation in data-rich but statistically intimidating fields, like health care and epigenetics, where traditional data methods have thus far proved insufficient.
The paper is published in the journal Scientific Reports.
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links/Affiliates:
Blood testing (where I get the majority of my labs): https://www.ultalabtests.com/partners/michaellustgarten.
At-Home Metabolomics: https://www.iollo.com?ref=michael-lustgarten.
Use Code: CONQUERAGING At Checkout.
Clearly Filtered Water Filter: https://get.aspr.app/SHoPY
Epigenetic, Telomere Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7xyIU-LSYLyQdQ6…M0&irgwc=1
Use Code: CONQUERAGING
NAD+ Quantification: https://www.jinfiniti.com/intracellular-nad-test/
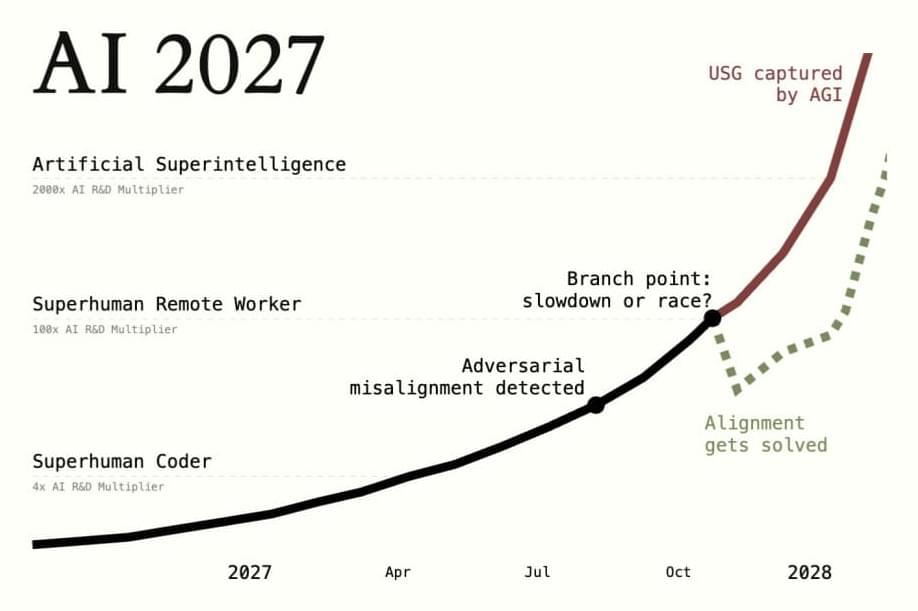
AI 2027
Posted in robotics/AI | Leave a Comment on AI 2027
The privately funded Fram2 mission is the first ever to take astronauts into polar orbit—and the latest sign of a “new normal” for human spaceflight.
By Lee Billings edited by Dean Visser.
Astronomers have found early evidence of the Universe’s transformation from a foggy, opaque state to a transparent one, thanks to a galaxy blazing with UV light nearly 13.6 billion years ago. The first galaxies in the Universe were born hidden within a thick “fog” of neutral gas, making them diff
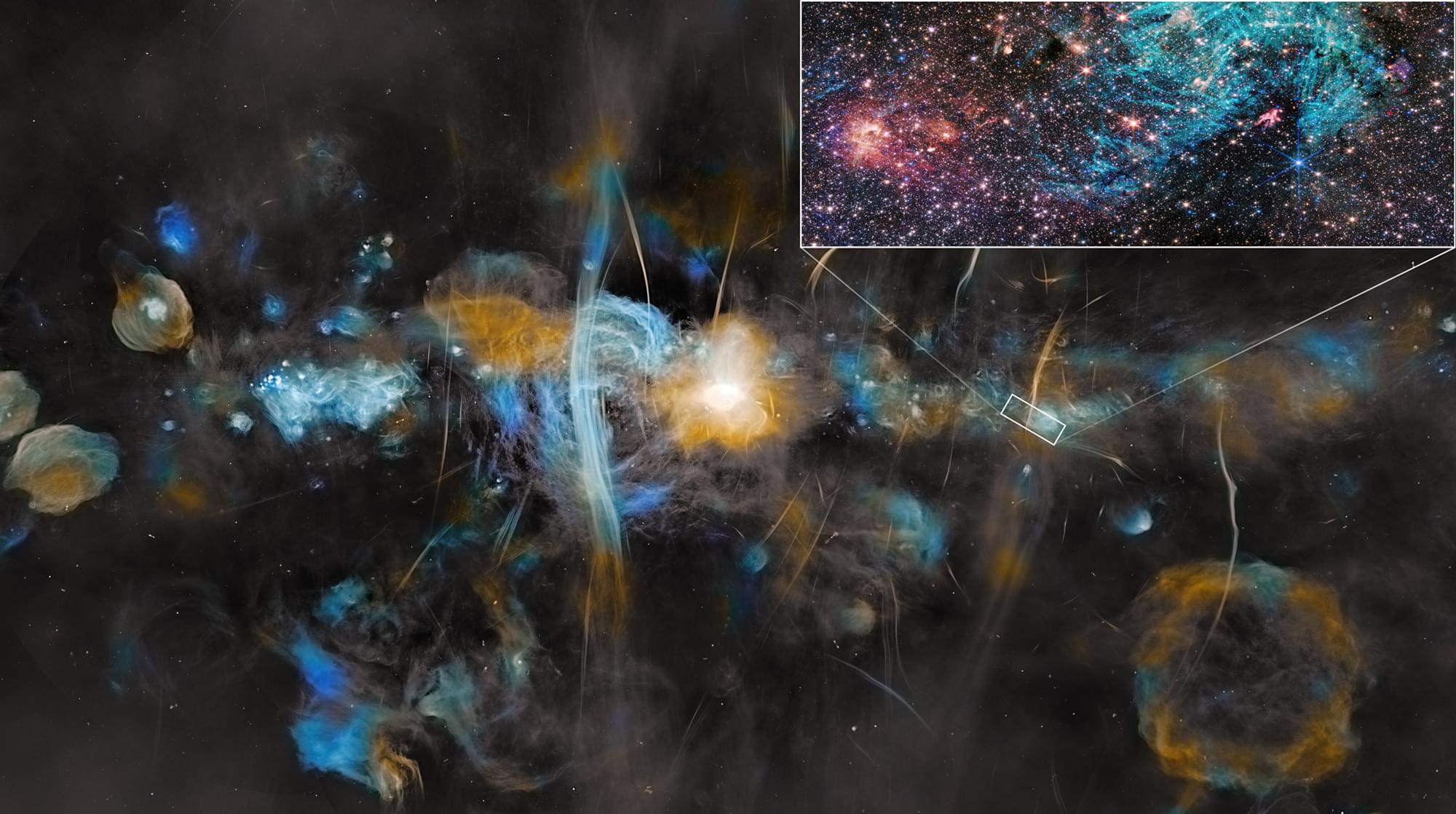
Follow-up research on a 2023 image of the Sagittarius C stellar nursery in the heart of our Milky Way galaxy, captured by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, has revealed ejections from still-forming protostars and insights into the impact of strong magnetic fields on interstellar gas and the life cycle of stars.
“A big question in the Central Molecular Zone of our galaxy has been, if there is so much dense gas and cosmic dust here, and we know that stars form in such clouds, why are so few stars born here?” said astrophysicist John Bally of the University of Colorado Boulder, one of the principal investigators. “Now, for the first time, we are seeing directly that strong magnetic fields may play an important role in suppressing star formation, even at small scales.”
Detailed study of stars in this crowded, dusty region has been limited, but Webb’s advanced near-infrared instruments have allowed astronomers to see through the clouds to study young stars like never before.
“No two ways about it,” Altepeter told Breaking Defense today. “The number of companies that we’re announcing is a surprise to me. I did not expect we would get this many.”
For the winning teams, the value of QBI is not just the money. Indeed, first-round grants like those being announced today have typically been under $1 million — small change not just for the Pentagon but for tech firms and venture capitalists already investing billions into quantum ventures. We suggested everybody apply for a million, [but] some people came in and said they were going to do it for less, Altepeter said.
The unique value of a QBI award is that it gives the winning companies access to a DARPA-led team of quantum experts, pulled from both US government labs, including the famous Los Alamos, and federally funded research institutions. Their job is to act as independent testers, fresh eyes, and devil’s advocates, rigorously scrutinizing each participant’s quantum strategy.
A trio of US researchers claim to have successfully tested predictions that it’s possible to harvest clean energy from the natural rhythms and processes of our planet, generating electricity as Earth rotates through its own magnetic field.
Though the voltage they produced was tiny, the possibility could give rise to a new way to generate electricity from our planet’s dynamics, alongside tidal, solar, wind, and geothermal power production.
In 2016, Princeton astrophysicist Christopher Chyba and JPL planetary scientist Kevin Hand challenged their own proof that such a feat ought to be impossible. The researchers have now uncovered empirical evidence that their proof-breaking idea may actually work, as long as the shape and properties of the conducting material in their method are set to very specific requirements.