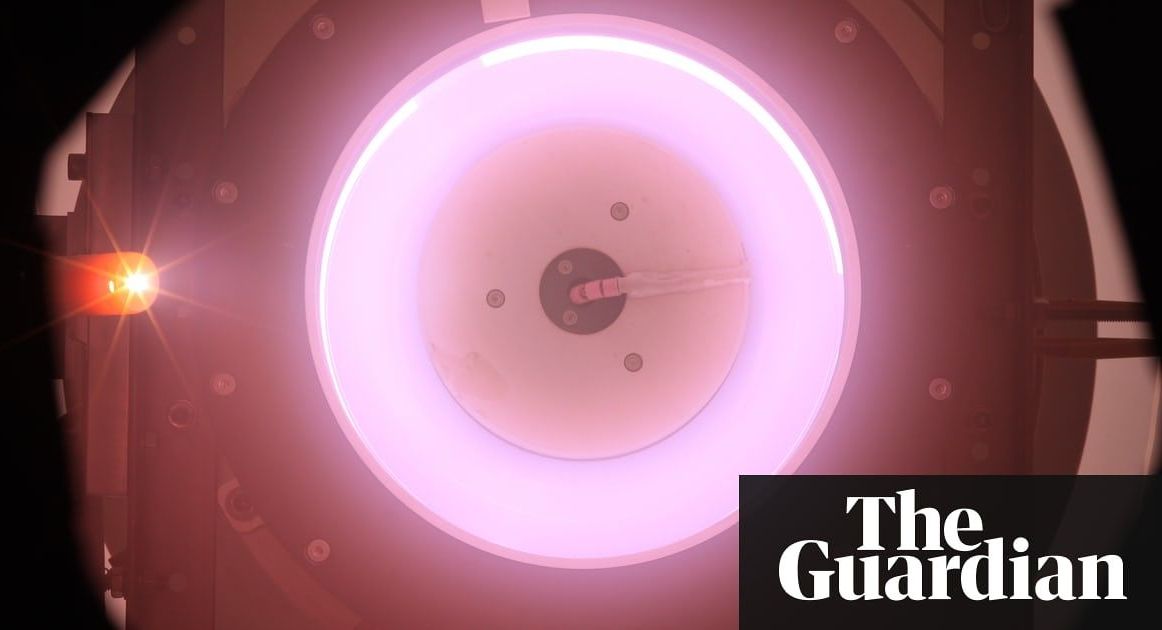
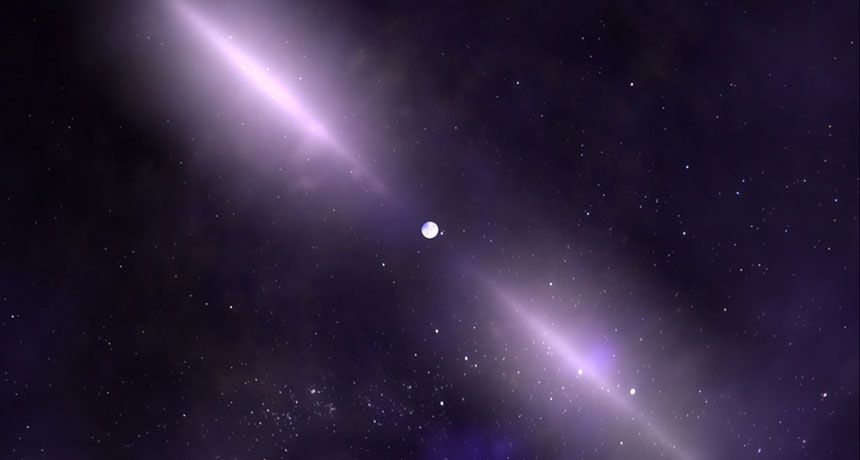
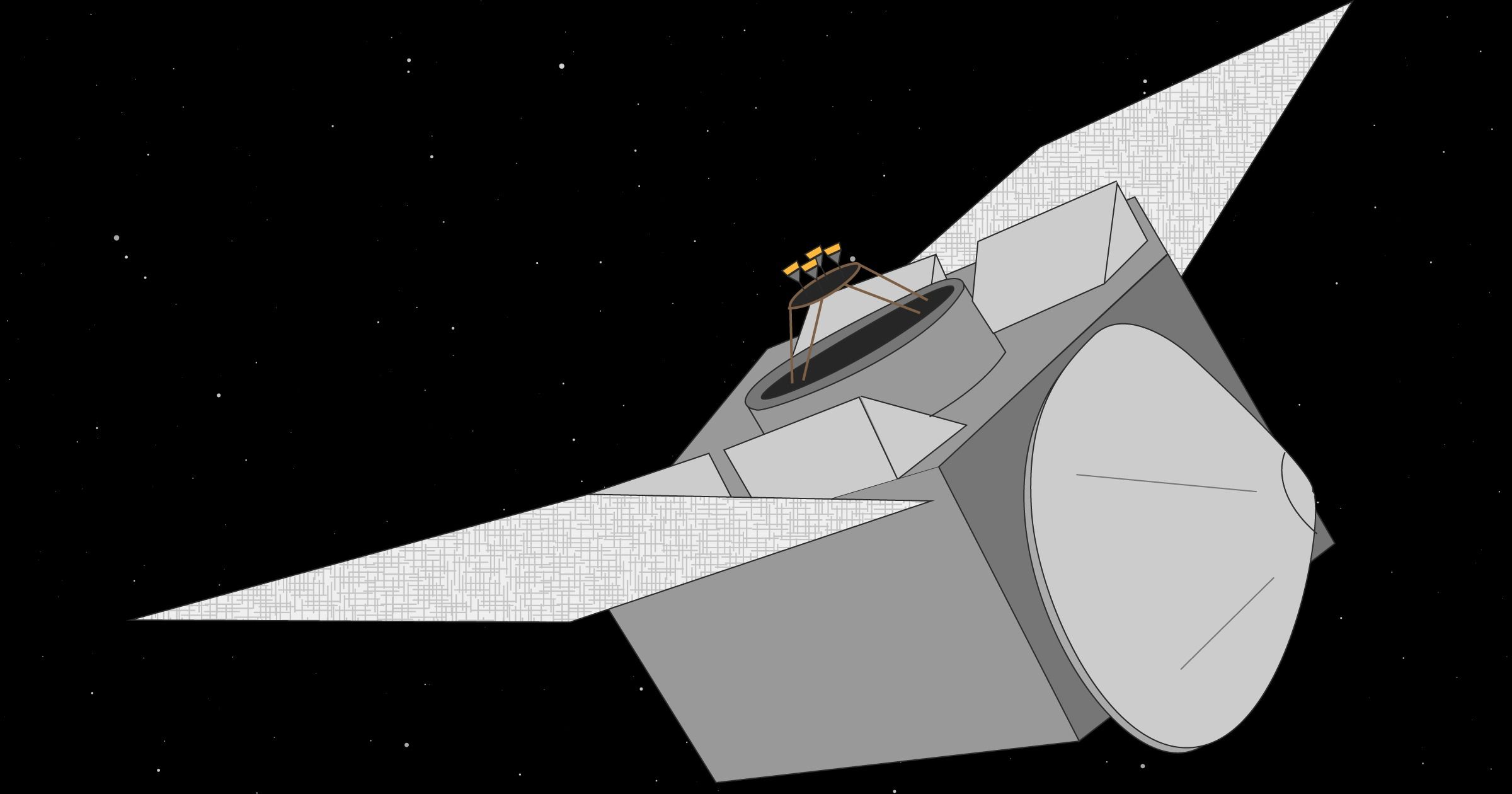
Electric thruster sucks in the scarce air molecules at the top of the Earth’s atmosphere, using them as propellant to fight drag.
VICE on HBO, Full Episode
Posted in employment, robotics/AI
Everyone is worried about robots stealing manufacturing jobs, but the real value (and threat) in robots may lie in whether they can become smart enough to actually think on their own.
One of the major milestones in creating human level intelligence is for machines to attain self-awareness. And Columbia University’s Creative Machines Lab may have already done it. “These robots learn overtime, to stimulate themselves in a future situation they haven’t actually experienced.” said Dr. Hod Lipson, the mechanical engineering professor leading the lab’s push to create self-aware robots.
“In other words, they don’t have to learn by doing,” Lipson told VICE News. “They can learn by thinking.”
The robotics department at UC Berkley has made similar advancements with their self-teaching robot BRETT. Using trial and error, BRETT can learn how to fold laundry, assemble LEGO blocks and fit pegs into a hole.
For weeks, digital clocks in Europe have been lagging behind. The unexpected source of the problem: Kosovo and Serbia, whose power grid operators can’t find common ground.
Clock radios and timers on microwaves and stoves have gotten out of sync in Europe in recent weeks. The reason: Coordination problems between the power grid operators of Kosovo and Serbia.
Since mid January power companies in Kosovo and Serbia have failed to mutually balance their electricity grids in the case of irregularities. According to the grid codes of the European Network of Transmission System Operators for Electricity (ENTSO-E), they are obliged to maintain a mean frequency of 50 hertz (oscillations per second) and help each other out if necessary.
Sending a spacecraft to the far reaches of our solar system to mine asteroids might seem like an improbable ambition best left to science fiction. But it’s inching closer to reality. A NASA mission is underway to test the feasibility on a nearby asteroid, and a niche group of companies is ramping up to claim a piece of the pie.
Industry barons see a future in finding and harnessing water on asteroids for rocket fuel, which will allow astronauts and spacecrafts to stay in orbit for longer periods. Investors, including Richard Branson, China’s Tencent Holdings and the nation of Luxembourg, see a longer-term solution to replenishing materials such as iron and nickel as Earth’s natural resources are depleted.
Millions of asteroids roam our solar system. Most are thought unsuitable for mining, either because they’re too small, too inaccessible to Earth or because the materials that make up the asteroid have little value. But we know of almost 1,000 asteroids that show potential. Timing is everything, though. The varied orbits of these asteroids mean that many are nearby only once every several years.