Scientists took conspiracy theories seriously and analyzed the coronavirus to reveal its natural origins.



By Bill D’Zio Originally published on www.westeastspace.com
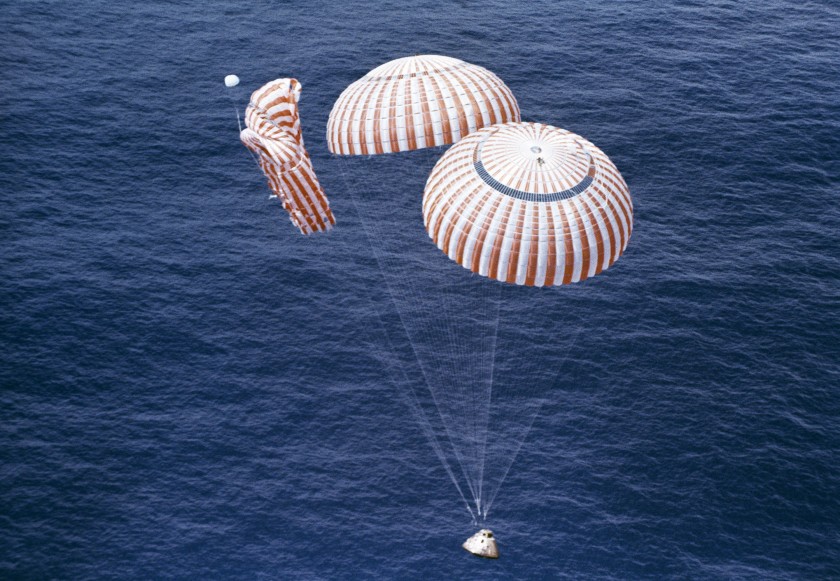
Parachutes are plaguing space programs. SpaceX doesn’t like Parachutes. They are difficult to design, hard to package, and easy to damage. The larger the mass of the spacecraft, the more effort to slow down. Larger, more efficient, complex parachute systems are needed. Several failures have hit the industry over the last few years, including SpaceX Crew Dragon, ESA ExoMars, Boeing CST-100, and the NASA Orion to name a few.
The idea of a parachute is simple. All falling objects fall the same when under the same conditions… that is so long as no outside force is exerted on it. So two objects dropped from the same altitude, one a feather and hammer will fall equally. Don’t believe me? NASA tested it on the Moon. During Apollo 15 moon walk, Commander David Scott performed a live demonstration for the television cameras. Commander Scott did the Apollo 15 Hammer and Feather test. He held out a geologic hammer and a Falcon feather and dropped them at the same time. Because there is not an atmosphere on the Moon, they were essentially in a vacuum. With no air resistance force, the feather fell at the same rate as the hammer. Ironically, Apollo 15 had a second demonstration of falling objects when one of the parachutes failed to function as planned.

Derek Haoyang Li, the founder of Squirrel AI Learning, is a serial entrepreneur who co-founded two publicly listed companies, and one of the companies has a market cap of $200 million. Squirrel AI Learning is the leading AI + education innovator and unicorn at the forefront of the K12 AI revolution. Within three years of its product release, Squirrel AI Learning has established more than 2,600+ learning centers in China and hosted the first series of human-vs-AI competitions in the Asia-Pacific region that proved the AI’s success. Squirrel AI Learning is recognized by Deloitte as one of the top 10 global AI enterprises with high growth. Squirrel AI Learning was also included in MIT Technology Review’s TR50 Smartest Companies in China list. Stanford Graduate School of Business has also published a case study on Squirrel AI Learning.
CHECK OUT SEASON 1 PLAYLIST: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ic9AV4mMbOQ&list=PL_GIV9cvJ8…itbMC34bPF
KEEP THE SHOW ON-AIR! : WWW.PATREON.COM/DEBTNATION
• PLEASE CHECK OUR SPONSOR: WWW.IAMTRANSHUMAN.ORG/
• LINK TO BOOK: https://www.amazon.com/Transhumanism-Handbook-Newton-Lee/dp/…atfound-20
.com%2Fsignin%3Faction_handle_signin%3Dtrue%26app%3Ddesktop%26feature%3Dpassive%26next%3D%252Fsignin_passive%26hl%3Den"]
IN THIS EPISODE:
•
…
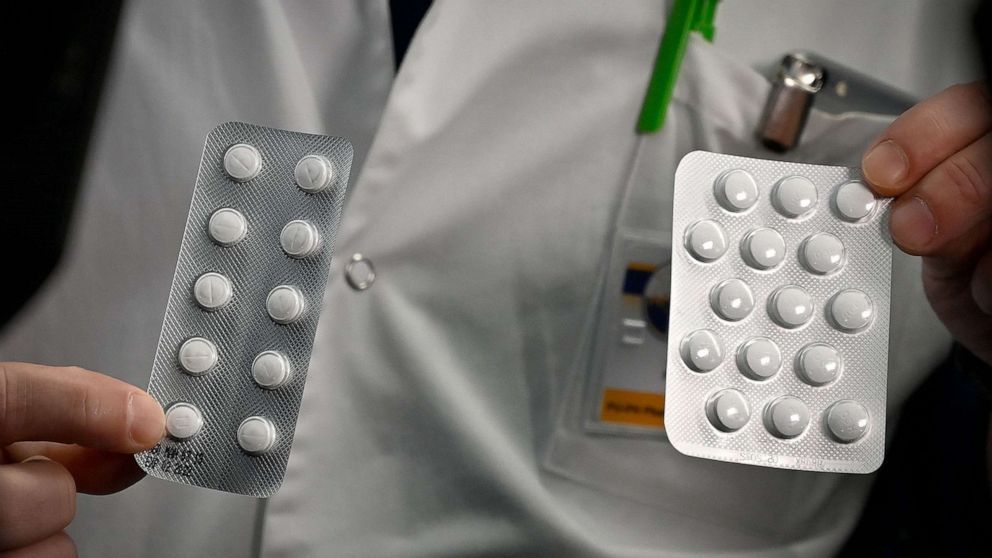
Officials are working out final details in plans to begin clinical trials next week for a malaria drug combination that appears to hold some promise for confronting the coronavirus pandemic.
New York state Health Department officials are making arrangements to determine what patients at which hospitals will be allowed to participate in trials with hydroxychloroquine, Zithromax and chloroquine, a senior official at the department with knowledge of the plan told ABC News. The bulk of the patients are expected to be in the New York City metro area because the region has the biggest cluster of cases.
New York Gov. Andrew Cuomo announced earlier this week that he was eager to get the trials started. By Tuesday, the drugs were in New York and officials were working to identify who could participate.
The medications, originally developed to fight malaria, have raised hope among many that they could aid in treating coronavirus. The core of the medical therapy is chloroquine, closely related to hydroxychloroquine, which has been used to treat malaria since 1944. It can be given before exposure to malaria to prevent infection, and it can also be given as treatment afterward. It’s also currently used to treat autoimmune diseases like lupus. Doctors are adding the antibiotic Zithromax to the cocktail.

As for coronavirus patients in serious condition, the ministry proposed – in addition to treating respiratory failure and supportive treatment – using Gilead’s drug Remdesivir, which was used in the case of Patient 16. The 38-year-old bus driver from East Jerusalem was in serious condition and the drug improved his situation dramatically, so much so that he was in good condition after the treatment.
They said that research into treating the virus is only in the research stage since the virus was only discovered some months ago.
The 43-year-old scientist is a member of the Technion’s Wolfson Faculty of Chemical Engineering, and his lab first developed a food additive to boost the immune system of animals to protect them from contracting viral diseases. This invention formed the basis of his own commercialized start-up company, ViAqua Therapeutics, which focused the development of the drug on shrimp, as over 30% of the global shrimp population is wiped out yearly by a viral disease known as white spot syndrome.
Israeli scientist and entrepreneur Prof. Avi Schroeder is working on a preventative drug for the coronavirus by adapting a food additive designed for shrimp.
The project is one of the several emergency projects that are the focus of around-the-clock work by 20 different labs at the Technion Institute of Technology to work on coronavirus vaccines, therapeutic treatments, diagnostic methods and patient treatment methods.
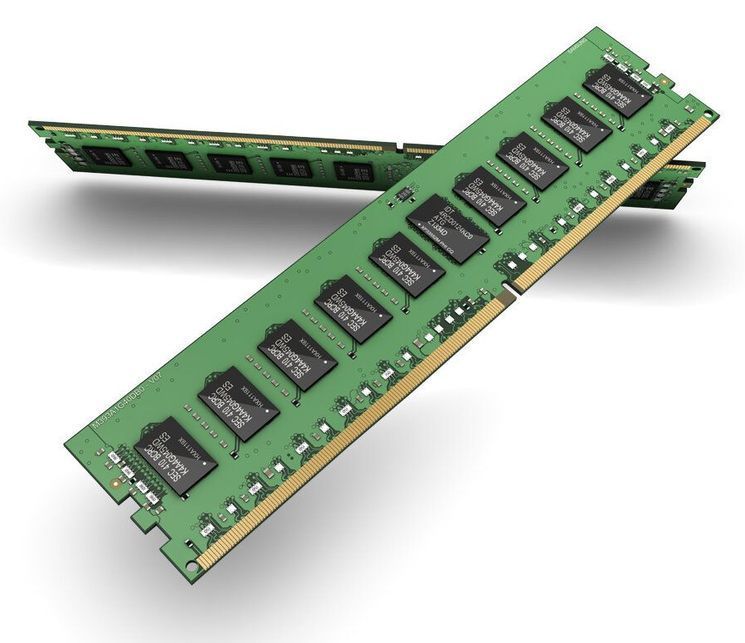
Samsung Electronics today announced it will be introducing the first DRAM memory modules in the industry designed with cutting-edge Extreme Ultraviolet Technology (EUV).
One of the world’s leading memory manufacturers, Samsung says that response to a million evaluation units of its first line of 10nm-class DDR4 DRAM modules has been positive and that it will soon begin processing orders for worldwide distribution.
EUV technology allows memory modules to be manufactured more accurately and more quickly. It speeds up the lithography process by reducing the number of repetitive steps and facilitates the production of complex chip patterns. It means greater performance accuracy and a shortened development time.

The last point is that Taiwan has a very good healthcare system, especially compared with the U.S. Taiwan’s health insurance system is affordable for the general public, which means everyone can get a medical examination or hospital treatment when necessary. It is also a scientific one: The health insurance system collects personal data and medical records, so hospitals and doctors can make good judgments about every patient’s condition. The quality of the national health system is quite important in the healing of patients and the containment of coronavirus.
Taiwan’s coronavirus response so far has been exemplary. Other nations, especially the U.S., should take note, says former Taiwan Premier Jiang Yi-huah.