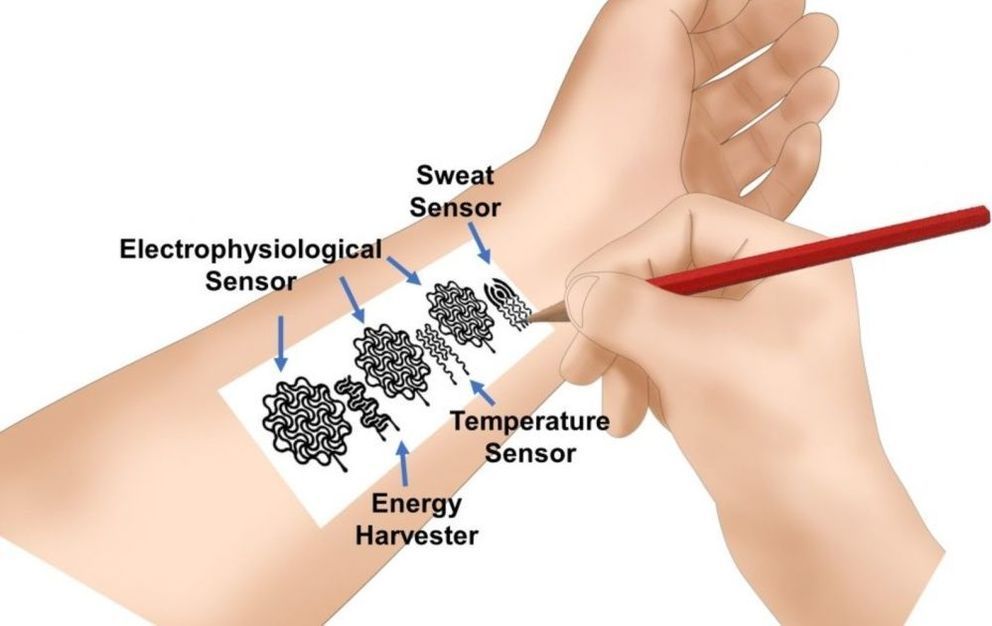
Cheap paper and pencil-based medical wearables could one day replace expensive health monitors.

Hello Robot’s Stretch wants to reinvent how mobile manipulators perform tasks in home environments.
Singapore has just begun to get its second wave of coronavirus under control. Now, it’s on track to face its worst-ever outbreak of another viral infection: dengue.
More than 14,000 dengue cases have been reported in the city-state since the start of the year, according to the National Environment Agency (NEA). The total number for the whole year is expected to exceed the 22,170 cases reported in 2013 — the largest dengue outbreak in Singapore’s history, the agency said.
Dengue is a viral infection transmitted by the Aedes mosquito, the same insect responsible for spreading Zika, chikungunya and yellow fever. It is commonly found in hot, wet regions of the tropics and subtropics during the rainy months.
Unlimited Clean Energy with The Wavestar machine. Harness the Power of Wave Energy with the World’s Strongest Wave Power Concept. Oceans cover more than 70% of Earth’s surface and ocean waves carry enormous power. By utilizing the largest source of untapped clean energy, it could supply a substantial part of the world’s electricity. Wave energy is more predictable compared to wind power, the waves come and go slowly and can be forecasted 24 hours ahead. Also the production continues 6–8 hours after the wind settles. This makes wave energy an ideal complement for wind turbines and could satisfy the continuously increasing demand for renewable energy in the grid.
The concept was invented by sailing enthusiasts Niels and Keld Hansen in 2000. The challenge was to create a regular output of energy from ocean swells and waves that are 5–10 seconds apart. This was achieved with a row of half-submerged buoys, which rise and fall in turn as the wave passes, forming the iconic part of Wavestar’s design. This allows energy to be continually produced despite waves being periodic.
The machine’s unique storm protection system, one of the many patented aspects of the design, guarantees the machine’s sea survivability and represents a real milestone in the development of wave energy machines. Wave energy will play a crucial role in securing our energy future, but only machines that can withstand the strongest storms will survive.
Environmental issues demand swift diversification to multiple renewable sources in order for us to fulfill our future energy needs. Wavestar will work in harmony with other clean energy methods to support the alternative energy movement and ensure a continuous supply of clean energy. Imagine what we can do together.
Music: Svadhisthana (Dance Mix) by Dhruva Aliman
https://dhruvaaliman.bandcamp.com/album/hello-moon
http://www.dhruvaaliman.com/
Had some spare time today so this is what I built. A #Tesla #turbine #levitating on #neodymium #magnets
Check out these other videos of the awesome stuff I’ve been working on.
I built a car wheel out of epoxy
I built a guitar out of epoxy and candy



A new study offers a better understanding of the hidden network of underground electrical signals being transmitted from plant to plant – a network that has previously been shown to use the Mycorrhizal fungi in soil as a sort of electrical circuit.
Through a combination of physical experiments and mathematical models based on differential equations, researchers explored how this electrical signalling works, though it’s not clear yet exactly what messages plants might want to transmit to each other.
The work builds on previous experiments by the same team looking at how this subterranean messaging service functions, using electrical stimulation as a way of testing how signals are carried even when plants aren’t in the same soil.

🤔
It’s not yet clear why some people infected with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, get really sick, while others have only mild symptoms. There’s some evidence that chronic health conditions—such as hypertension and diabetes can play a role, and scientists know that people’s genes can influence how their bodies react to other viruses. In a preprint posted to medRxiv on June 2, researchers describe a genome-wide association study (GWAS) of from 1,610 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 and 2,205 healthy controls. The authors identified variants in two regions—the locus that encodes blood type and a multi-gene cluster on chromosome 3—that were linked to respiratory failure during SARS-CoV-2 infection.
In a genome-wide association study, variants in both the ABO blood group locus and a cluster of genes on human chromosome 3 are more common among COVID-19 patients with respiratory failure than in the general population.

The first reliable way of isolating sperm stem cells from the testes and growing them outside the body could help infertile men have genetic children of their own.
A few teams have claimed to have isolated sperm stem cells before, but haven’t been able to repeat the results. “The general feeling is that there is no reliable method,” says Miles Wilkinson at the University of California, San Diego.