Having lived with an ALS diagnosis since 2018, Kate Nycz can tell you firsthand what it’s like to slowly lose motor function for basic tasks. “My arm can get to maybe 90 degrees, but then it fatigues and falls,” the 39-year-old said. “To eat or do a repetitive motion with my right hand, which was my dominant hand, is difficult. I’ve mainly become left-handed.”
People like Nycz who live with a neurodegenerative disease like ALS or who have had a stroke often suffer from impaired movement of the shoulder, arm or hands, preventing them from daily tasks like tooth-brushing, hair-combing or eating.
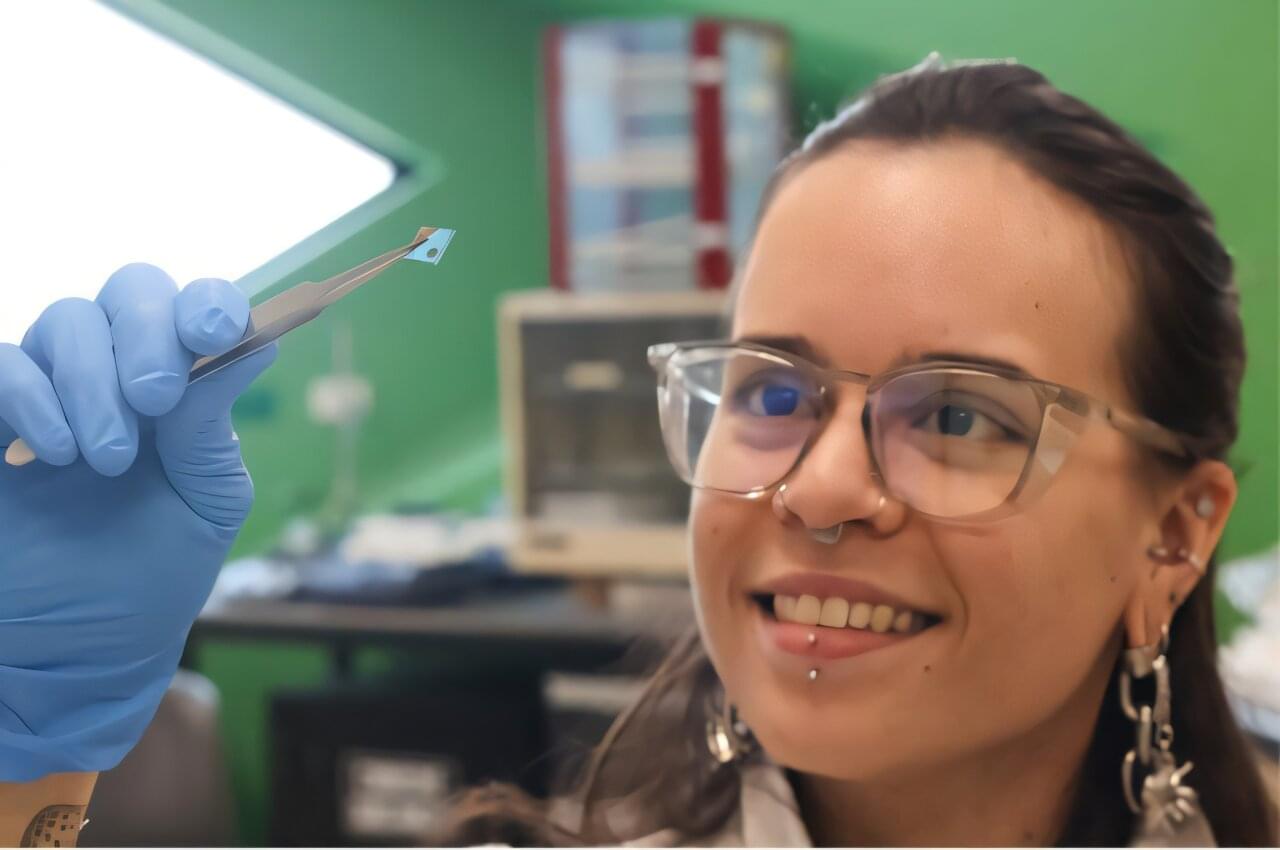
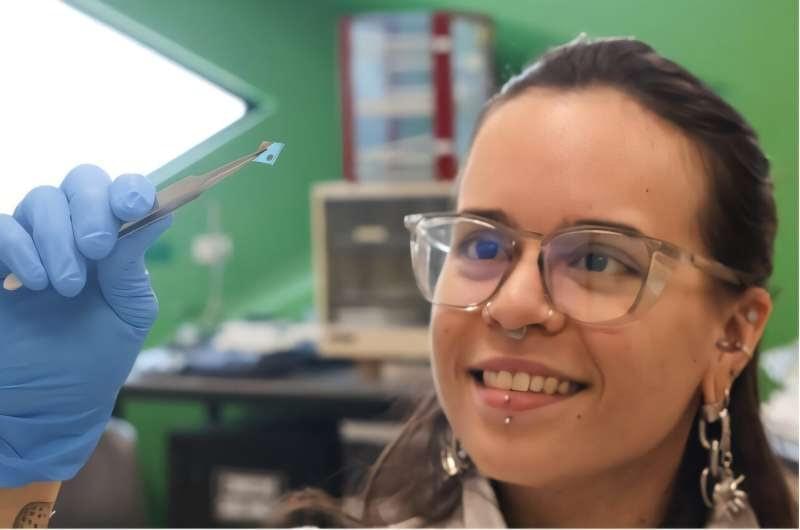
For the last several years, Harvard bioengineers have been developing a soft, wearable robot that not only provides movement assistance for such individuals but could even augment therapies to help them regain mobility.
But no two people move exactly the same way. Physical motions are highly individualized, especially for the mobility-impaired, making it difficult to design a device that works for many different people.
It turns out advances in machine learning can create a more personal touch. Researchers in the John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS), together with physician-scientists at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, have upgraded their wearable robot to be responsive to an individual user’s exact movements, endowing the device with more personalized assistance that could give users better, more controlled support for daily tasks.