The immersive qualities of virtual-reality gaming are making effective biofeedback treatment of anxiety and other conditions more affordable and accessible.



Color is a foundational aspect of visual experience that aids in segmenting objects, identifying food sources, and signaling emotions. Intuitively, it feels that we are immersed in a colorful world that extends to the farthest limits of our periphery. How accurate is our intuition? Here, we used gaze-contingent rendering in immersive VR to reveal the limits of color awareness during naturalistic viewing. Observers explored 360° real-world environments, which we altered so that only the regions where observers looked were in color, while their periphery was black-and-white. Overall, we found that observers routinely failed to notice when color vanished from the majority of their visual world. These results show that our intuitive sense of a rich, colorful world is largely incorrect.
Color ignites visual experience, imbuing the world with meaning, emotion, and richness. As soon as an observer opens their eyes, they have the immediate impression of a rich, colorful experience that encompasses their entire visual world. Here, we show that this impression is surprisingly inaccurate. We used head-mounted virtual reality (VR) to place observers in immersive, dynamic real-world environments, which they naturally explored via saccades and head turns. Meanwhile, we monitored their gaze with in-headset eye tracking and then systematically altered the visual environments such that only the parts of the scene they were looking at were presented in color and the rest of the scene (i.e., the visual periphery) was entirely desaturated. We found that observers were often completely unaware of these drastic alterations to their visual world. In the most extreme case, almost a third of observers failed to notice when less than 5% of the visual display was presented in color.
UC Santa Barbara researchers continue to push the boundaries of LED design a little further with a new method that could pave the way toward more efficient and versatile LED display and lighting technology.
In a paper published in Nature Photonics, UCSB electrical and computer engineering professor Jonathan Schuller and collaborators describe this new approach, which could allow a wide variety of LED devices—from virtual reality headsets to automotive lighting—to become more sophisticated and sleeker at the same time.
“What we showed is a new kind of photonic architecture that not only allows you to extract more photons, but also to direct them where you want,” said Schuller. This improved performance, he explained, is achieved without the external packaging components that are often used to manipulate the light emitted by LEDs.
Waves, whether they are light waves, sound waves, or any other kind, travel in the same manner in forward and reverse directions—this is known as the principle of reciprocity. If we could route waves in one direction only—breaking reciprocity—we could transform a number of applications important in our daily lives. Breaking reciprocity would allow us to build novel “one-way” components such as circulators and isolators that enable two-way communication, which could double the data capacity of today’s wireless networks. These components are essential to quantum computers, where one wants to read a qubit without disturbing it. They are also critical to radar systems, whether in self-driving cars or those used by the military.
A team led by Harish Krishnaswamy, professor of electrical engineering, is the first to build a high-performance non-reciprocal device on a compact chip with a performance 25 times better than previous work. Power handling is one of the most important metrics for these circulators and Krishnaswamy’s new chip can handle several watts of power, enough for cellphone transmitters that put out a watt or so of power. The new chip was the leading performer in a DARPA SPAR (Signal Processing at RF) program to miniaturize these devices and improve performance metrics. Krishnaswamy’s group was the only one to integrate these non-reciprocal devices on a compact chip and also demonstrate performance metrics that were orders of magnitude superior to prior work. The study was presented in a paper at the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference in February 2020, and published May 4, 2020, in Nature Electronics.
“For these circulators to be used in practical applications, they need to be able to handle watts of power without breaking a sweat,” says Krishnaswamy, whose research focuses on developing integrated electronic technologies for new high-frequency wireless applications. “Our earlier work performed at a rate 25 times lower than this new one—our 2017 device was an exciting scientific curiosity but it was not ready for prime time. Now we’ve figured out how to build these one-way devices in a compact chip, thus enabling them to become small, low cost, and widespread. This will transform all kinds of electronic applications, from VR headsets to 5G cellular networks to quantum computers.”


“It’s not just about the smell,” said Adrian Cheok, one of the scientists behind the experiments. “It is part of a whole, integrated virtual reality or augmented reality. So, for example, you could have a virtual dinner with your friend through the internet. You can see them in 3D and also share a glass of wine together.”
In real life, odors are transmitted when airborne molecules waft into the nose, prompting specialized nerve cells in the upper airway to fire off impulses to the brain. In the recent experiments, performed on 31 test subjects at the Imagineering Institute in the Malaysian city of Nusajaya, researchers used electrodes in the nostrils to deliver weak electrical currents above and behind the nostrils, where these neurons are found.
The researchers were able to evoke 10 different virtual odors, including fruity, woody and minty.

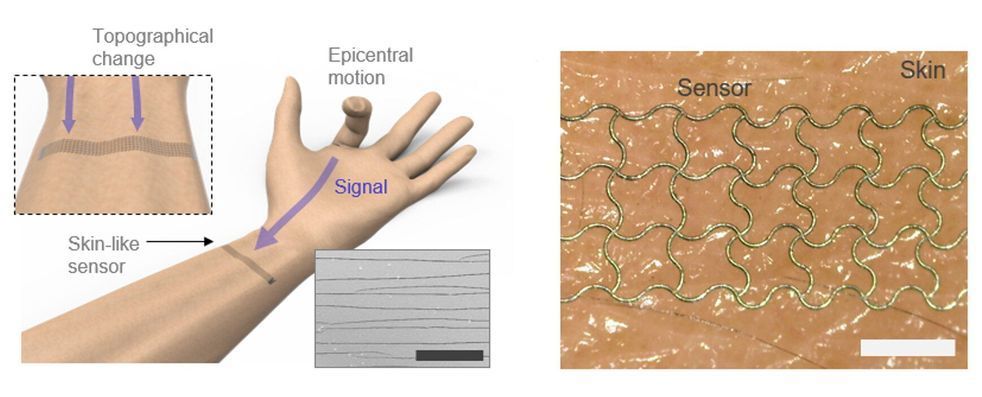
Researchers at Seoul National University and Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) have recently developed a sensor that can act as an electronic skin and integrated it with a deep neural network. This deep learning-enhanced e-skin system, presented in a paper published in Nature Communications, can capture human dynamic motions, such as rapid finger movements, from a distance.
The new system stems from an interdisciplinary collaboration that involves experts in the fields of mechanical engineering and computer science. The two researchers who led the recent study are Seung Hwan Ko, a professor of mechanical engineering at Soul National University and Sungho Jo, a computing professor at KAIST.
For several years, Prof. Ko had been trying to develop highly sensitive strain sensors by generating cracks in metal nanoparticle films using laser technology. The resulting sensor arrays were then applied to a virtual reality (VR) glove designed to detect the movements of people’s fingers.


In 2033, people can be “uploaded” into virtual reality hotels run by 6 tech firms. Cash-strapped Nora lives in Brooklyn and works customer service for the luxurious “Lakeview” digital afterlife. When L.A. party-boy/coder Nathan’s self-driving car crashes, his high-maintenance girlfriend uploads him permanently into Nora’s VR world. Upload is created by Greg Daniels (The Office).