Of course, a minimum level of fidelity is required, but what’s far more important is perceptual consistency. By this, I mean that all sensory signals (i.e. sight, sound, touch, and motion) feed a single mental model of the world within your brain. With augmented reality, this can be achieved with relatively low visual fidelity, as long as virtual elements are spatially and temporally registered to your surroundings in a convincing way. And because our sense of distance (i.e. depth perception) is relatively coarse, it’s not hard for this to be convincing.
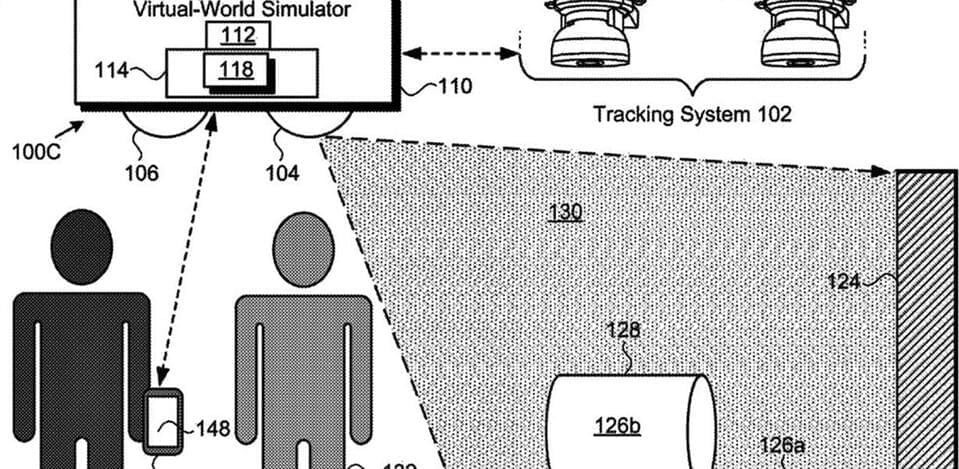
But for virtual reality, providing a unified sensory model of the world is much harder. This might sound surprising because it’s far easier for VR hardware to provide high-fidelity visuals without lag or distortion. But unless you’re using elaborate and impractical hardware, your body will be sitting or standing still while most virtual experiences involve motion. This inconsistency forces your brain to build and maintain two separate models of your world — one for your real surroundings and one for the virtual world that is presented in your headset.
When I tell people this, they often push back, forgetting that regardless of what’s happening in their headset, their brain still maintains a model of their body sitting on their chair, facing a particular direction in a particular room, with their feet touching the floor (etc.). Because of this perceptual inconsistency, your brain is forced to maintain two mental models. There are ways to reduce the effect, but it’s only when you merge real and virtual worlds into a single consistent experience (i.e. foster a unified mental model) that this truly gets solved.