Caption: The Solar Express is a conceptual space train that would ferry humans, supplies, and minerals between celestial bodies and space stations. Boris Schwarzer.


One of the biggest things driverless vehicles is going to do to the average person is to take away the semi driver jobs.
It’s an unfortunate fact and one that will continue to spread to other facets of the workforce, but for now we won’t have to worry, that’s a while off. Either way there’s still the first in what will hopefully be a long line of elegant driverless semi’s, and the two you’re about to see come straight from the geniuses at Audi. The first of these beautiful trucks is the street truck, designed for active use on the road. The second is their show truck, and looks to be much less practical but much cooler to be in!

Joshua Brown, 40, believed in the power of engineering. He was a former Navy SEAL, a technology consultant, and a Tesla fan. He had posted YouTube videos of himself driving a Tesla Model S on autopilot, taking his hands off the wheel to show how the car could avoid a collision on its own. He had nicknamed his car “Tessy.”
The driver of a Tesla car died in Florida in May after colliding with a lorry.
Under scrutiny is Tesla’s Autopilot feature, which automatically changes lanes and reacts to traffic.
In a statement, Tesla said it appeared the Model S car was unable to recognise “the white side of the tractor trailer against a brightly lit sky” that had driven across the car’s path.
Tesla is being investigated following a crash in which a man died after colliding with a lorry in Florida.

This couldn’t of happened at a worse time. Everyone was starting to ramp up for self driving cars. It looked like everyone was going to start taking them to market in 2020. This one incident might move things back 5 years.
Elon Musk’s confidence in Tesla’s technology has seemed boundless, but trying to stay ahead of the competition has posed risks.

Exponential Finance celebrates the incredible opportunity at the intersection of technology and finance. Apply here to join Singularity University, CNBC, and hundreds of the world’s most forward-thinking financial leaders at Exponential Finance in June 2017.
One day in the future, we’ll look back in wonder at how our physical objects used to be singular, disconnected pieces of matter.
We’ll be in awe of the fact that a car used to be just a piece of metal full of gears and belts that we would drive from one place to another, that a refrigerator was a box that kept our food cold — and a phone was a piece of plastic we used to communicate to one other person at a time.


Imagine a future full of electric cars where everyone’s a passenger. Where traffic is not only managed but controlled by a digital network. Where on-demand ride-sharing services have become the norm, and the only human drivers are emergency crews behind the wheel of super-fast vintage “antiques” tasked with taking down AI cars that have gone haywire.
Some of that sounds like the vision of today’s automakers, city planners, tech visionaries and the like, who all salivate at the thought of removing the human element from our roadways as much as possible. Recent developments in driverless technology are surprisingly close to the vision of autonomy portrayed in Kōsuke Fujishima’s 2000 Japanese anime series éX-Driver, which has even more to say about what could become our future in transportation.
éX-Driver follows the adventures of Lisa, Lorna, and their new teammate Sōichi as they wrangle autonomous vehicles that have run amok. These out-of-control “AI cars” endanger not only the helpless passengers inside, but other road users as well. Not looking forward to “autonomobiles”? This could be the perfect gig for you.
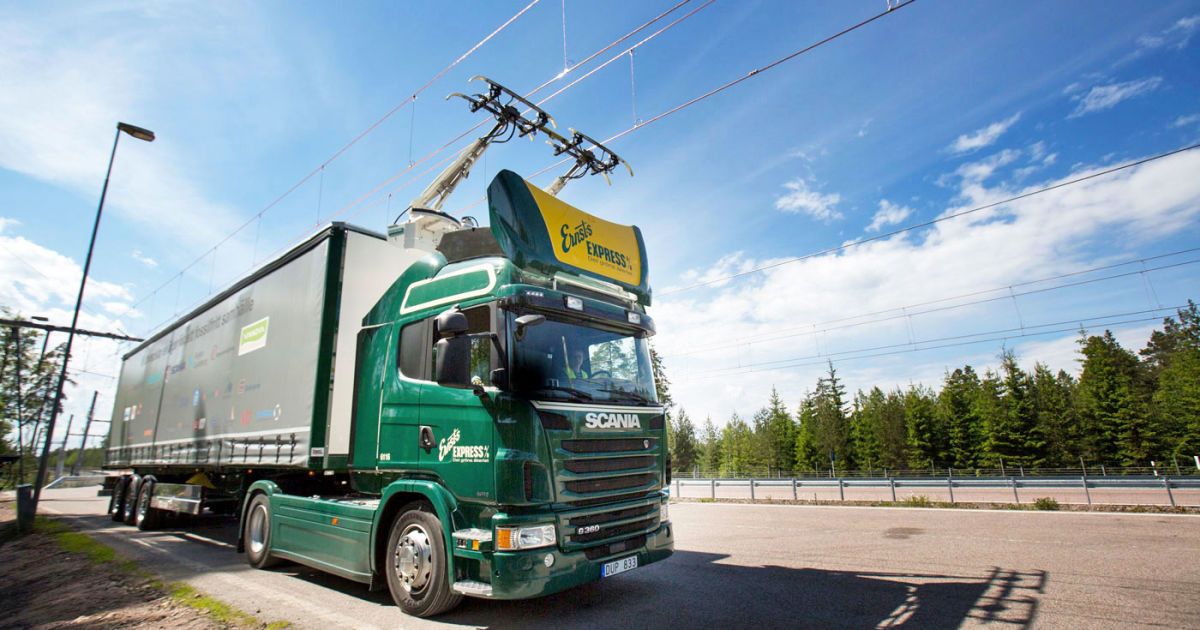

Underground wireless charging will be a better idea!
Fossil fuels are bad for the planet, and freight haulage is one of the more carbon-intensive activities that operate today. That’s why Siemens and Scania have teamed up to trial what’s being called the world’s first “electric highway.” Much like an electrified railroad, the 1.2 mile stretch has a series of wires hanging overhead that a pantograph-equipped truck can connect to. Then, the vehicle can deactivate its fuel-burning engine and coast along on that delicious, dirt-cheap electricity, switching back when the wires stop.
Scania official Claes Erixon has said that the project is “one important milestone on the journey towards fossil-free transport.” Cleantech Canada quotes an unnamed Siemens representative, who says the move could cut energy consumption in half. As it stands, this is the culmination of a two-year project to develop this test track, with more work to be done to determine if it could be rolled out across the country. That is, unless, an alternative freight-transport network that’s even more energy-efficient and speedy, can make its case to governments across the world.
“You might own a car like some people own a horse. They might take a ride on the weekends or something.” Travis Kalanick, CEO Uber.