We all know that physics and maths can be pretty weird, but these three books tackle their mind-bending subjects in markedly contrasting ways. Clifford V. Johnson’s The Dialogues is a graphic novel, seeking to visualise cosmic ideas in comic-book style. Darling and Banerjee’s Weird Maths is a miscellany of fun oddities, ranging from chess-playing computers to prime-counting insects. Philip Ball’s Beyond Weird argues that we’ve got quantum mechanics all wrong: it’s not so weird actually, but quite sensible. All three books do a fine job for their respective audiences. Just make sure you know which target group you’re in.
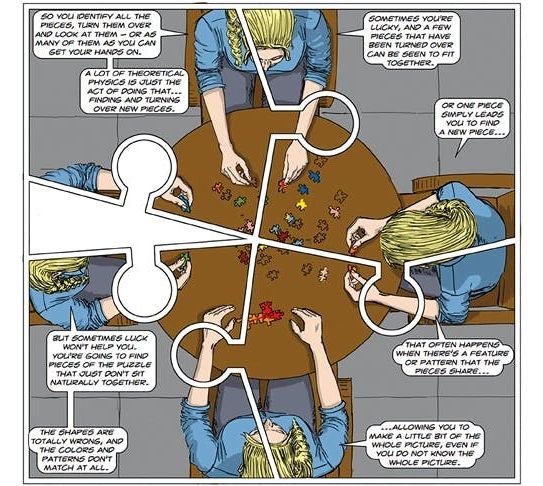
The Dialogues is a sequence of illustrated conversations, often between pairs of youthful and attractive characters, scrupulously diverse in race and gender, who happen to meet in a café, gallery or train carriage, and find themselves talking about physics. Perhaps ‘The Lectures’ would be a better title, since one interlocutor is the expert, while the other is an interested lay person whose role is to feed questions at appropriate intervals.
The author shows himself to be a highly talented graphic artist as well as being a distinguished theoretician, and while the ping-pong chats may be somewhat lacking in narrative drive, they do provide a platform for some admirably lucid explanations of topics such as Maxwell’s equations or Einstein’s cosmological constant. Not the kind of comic book you roll up in your pocket, but a weighty hardback that would grace any coffee table.