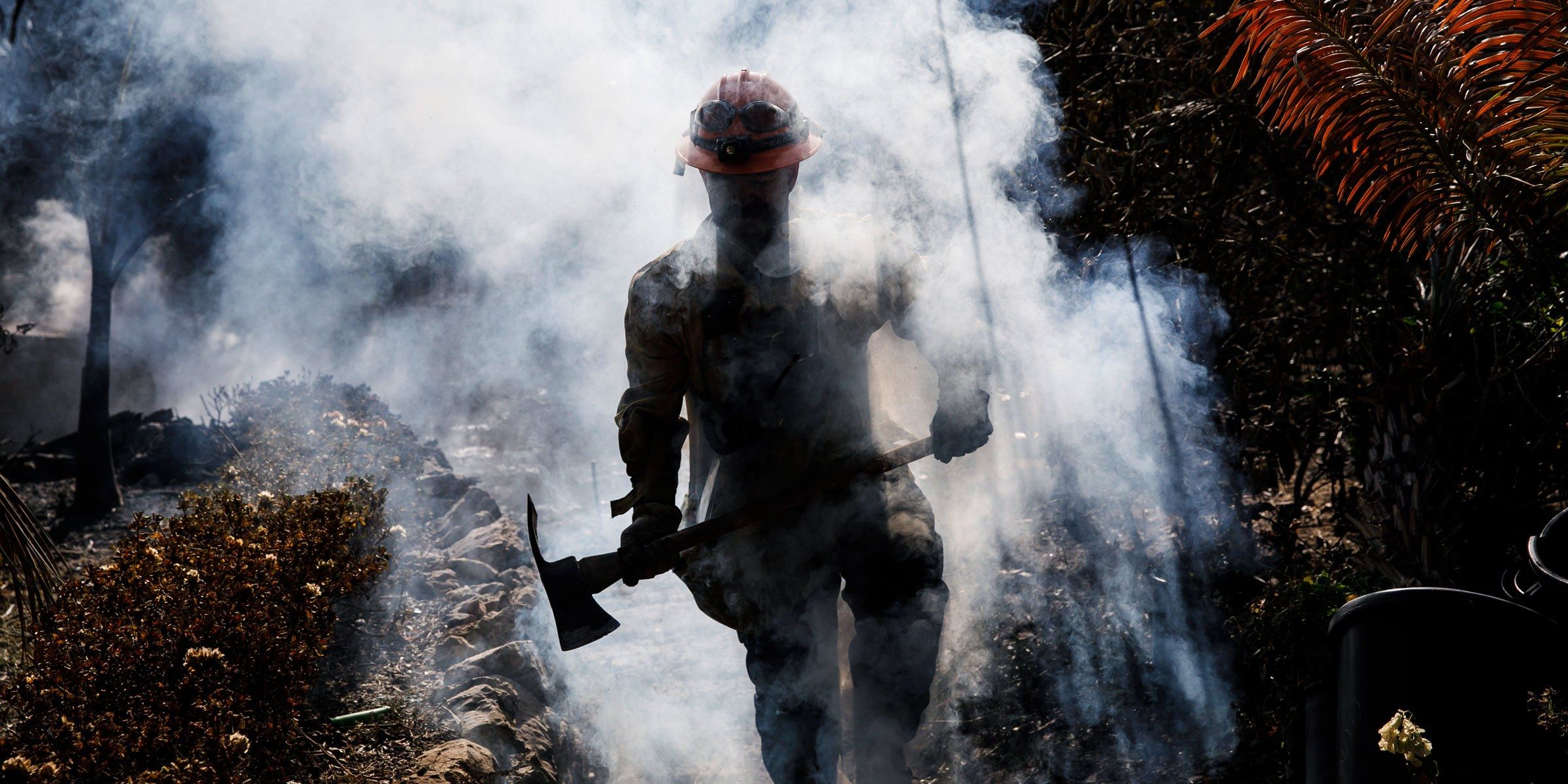
Soon enough, agriculture might need a lot more bots.
By matt simon and melanie ruiz


Amidst the ongoing threat of the California wildfires, a Tesla Model 3 owner has posted a brief demonstration of the electric sedan’s capability to maintain the air quality inside its cabin, despite the vehicle not being equipped with the Model S and X’s hospital-grade HEPA filter or a dedicated “Bioweapon Defense Mode.”
Elon Musk took to Twitter last week to offer the Model S and Model X as vehicles that can be used to transport people away from the ongoing CA wildfires. The Model S and X are capable of scrubbing the air inside the car, thanks to their large HEPA filters that are fitted with separate acid and alkaline gas neutralization layers. Later social media updates and anecdotes from Model S and X owners driving through the CA area indicate that Bioweapon Defense Mode helped maintain the air quality inside their vehicles.
In a follow-up tweet, Elon Musk noted that the Model 3’s air filtration system is not on the same “hospital-grade” level as that of the Model S and X, since the smaller vehicle does not have enough space to accommodate the HEPA filtration system in Tesla’s two flagship vehicles. This could be seen in the parts catalog for the vehicles, where the Model X HEPA filter was listed as “FILTER, HEPA, MDL X,” while the Model 3’s system was simply listed as “HVAC, CABIN FILTER, M3.”

At this rate of progress, the book could be published by year end. Feedback welcome! https://transpolitica.org/projects/abundance-manifesto/

Eco-consciousness is a hot trend. It’s become common occurrence to see shoppers with reusable grocery totes at the supermarket. Bamboo straws are flying off shelves as people opt for eco-friendly products. Urban gardening and composting, too, has taken root as consumers try to minimize their carbon footprints.
These small actions are encouraging first steps, but they’re not enough when it comes to tackling agricultural contributions to climate change. Strong-worded warnings from the UN’s Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) detail the potential for climate disasters to worsen if modern consumption patterns don’t change — and soon.
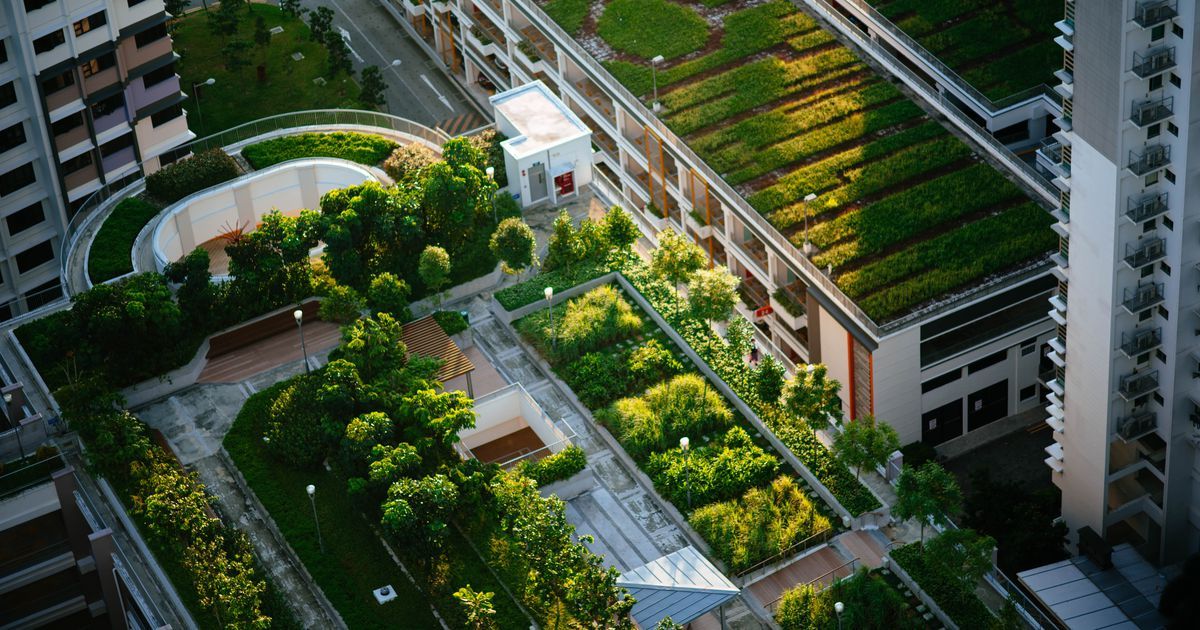
There’s evidence that reimagining urban environments’ food systems might help reduce carbon emissions. With more than 60% of the global population expected to live in cities by 2030, urban agriculture might be one piece of the puzzle for reducing strain on city resources. The practice typically involves growing food in smaller, city environments such as on rooftops, apartment balconies, or even walls.
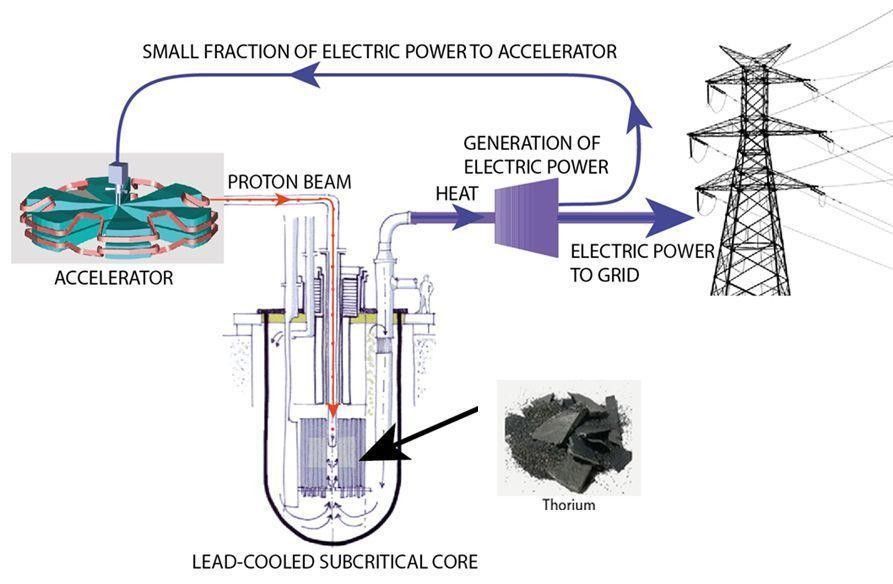
If not for long-term radioactive waste, then nuclear power would be the ultimate “green” energy. The alternative to uranium is thorium, a radioactive ore whose natural decay is responsible for half of our geothermal energy, which we think of as “green energy.” More than 20 years of research at the European Centre for Nuclear Research (CERN), the birthplace of the internet and where Higgs boson was discovered, demonstrate that thorium could become a radically disruptive source of clean energy providing bountiful electricity any place and at any time.
Coal and gas remain by far the largest sources of electricity worldwide, threatening our climate equilibrium. Non-fossil alternatives, such as solar power, use up a forbidding amount of land, even in sunny California, plus the decommissioning will pose a serious recycling challenge within 20 years. Solar is best used on an individual household basis, rather than centralized plants. Wind requires an even larger surface area than solar.
As Michael Shellenberger, a Time magazine “Hero of the Environment”, recently wrote: “Had California and Germany invested $680 billion into nuclear power plants instead of renewables like solar and wind farms, the two would already be generating 100% or more of their electricity from clean energy sources.” Correct, but the disturbing issue of long-term nuclear waste produced by conventional, uranium based, nuclear plants still remains.
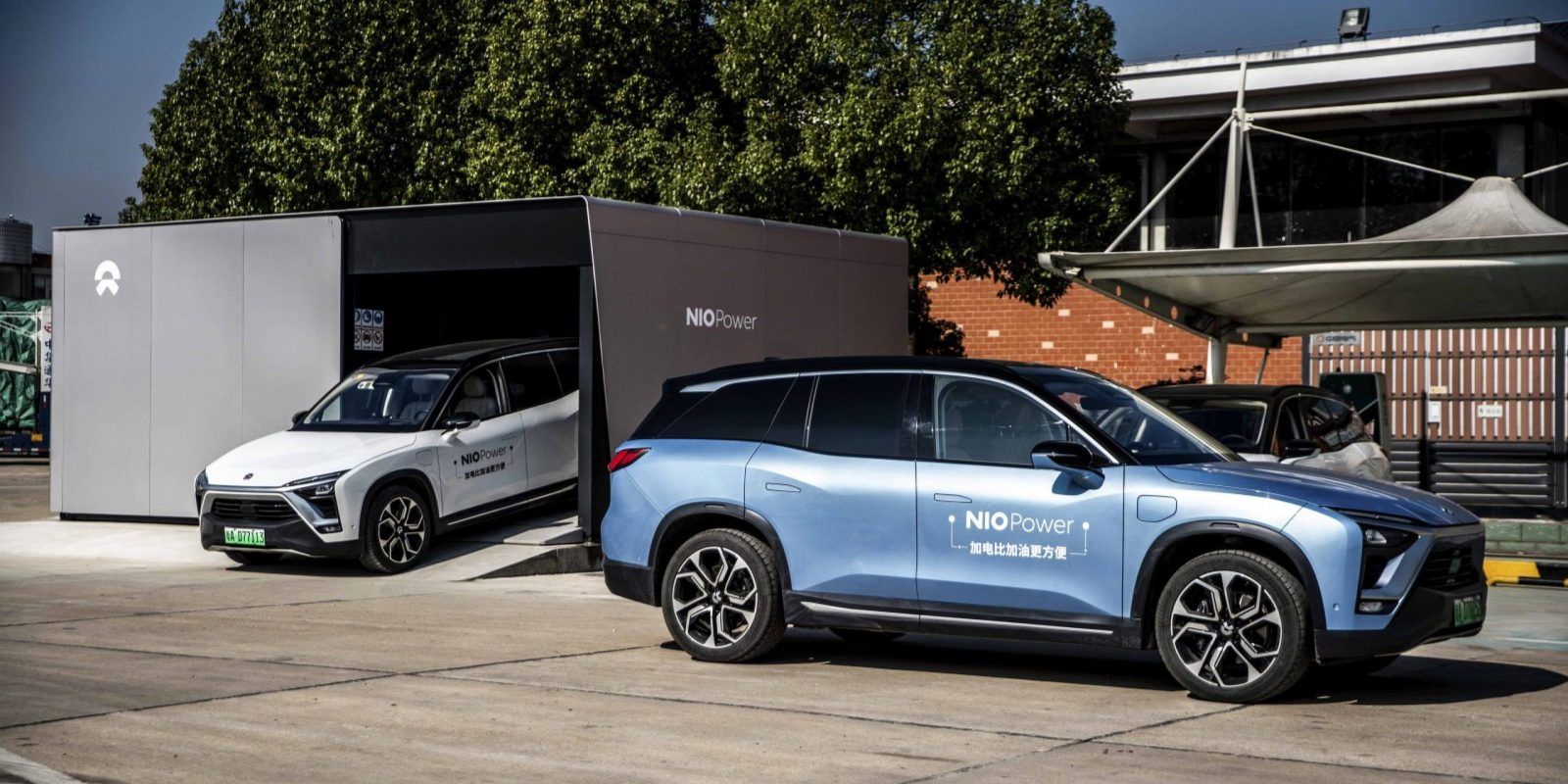


No one in the electric vehicle space has managed to make battery swapping work yet, but Nio is trying big time with 18 new battery swap stations covering a 2,000+ km expressway in China.
Several companies tried and failed at battery swapping. Tesla had a battery swap system that they seemingly abandoned and Better Place went bankrupt.
But you could say Tesla didn’t try that hard and has instead bet on fast-charging and Better Place was a little too ahead of its time.
